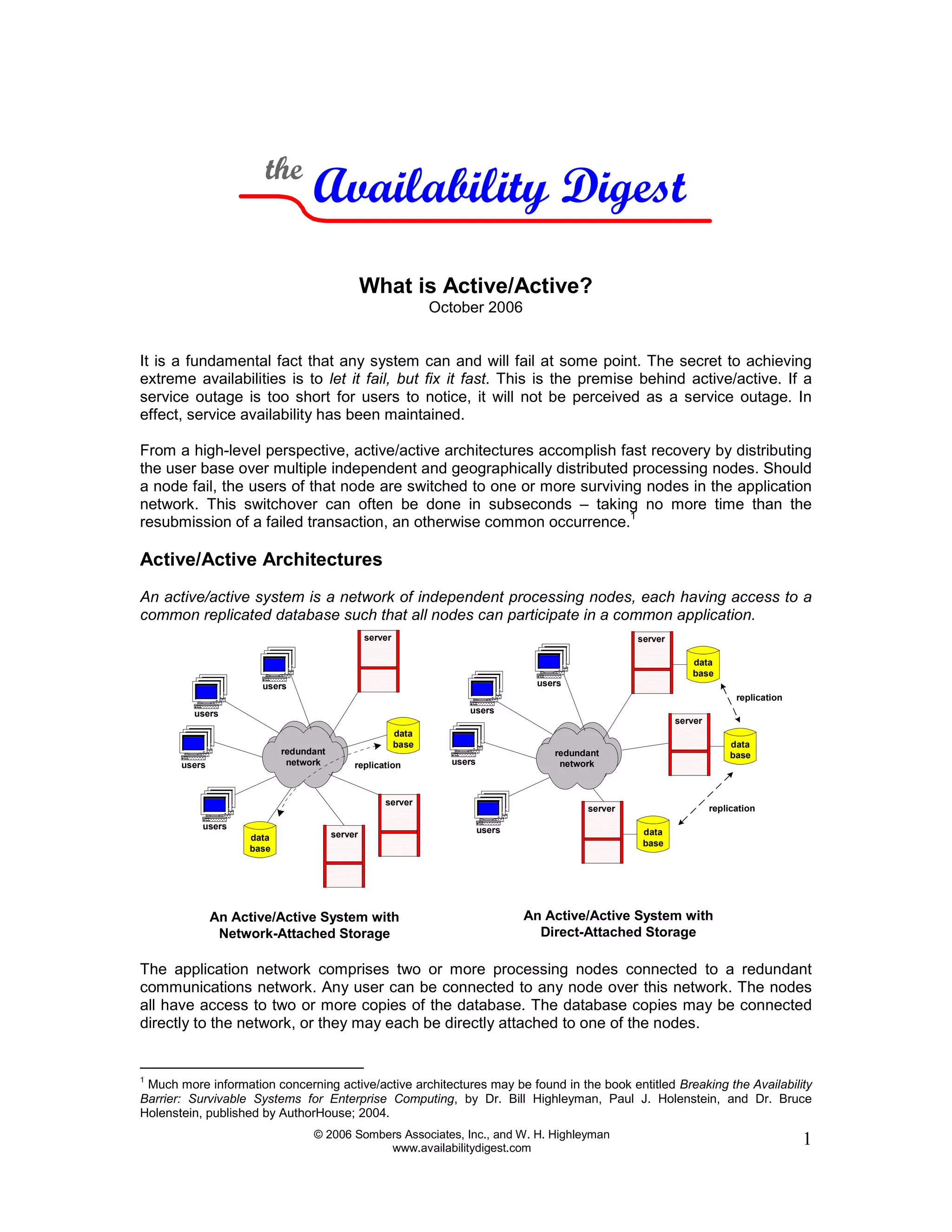
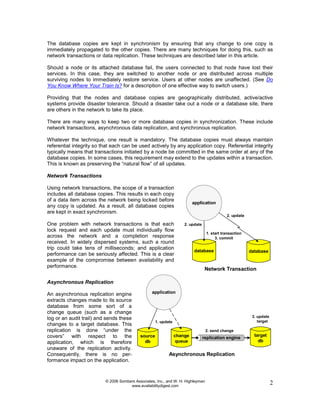
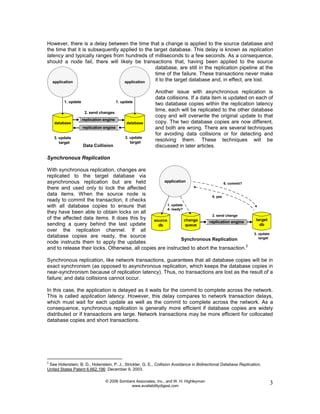
Active/active architectures improve availability by distributing processing across multiple independent nodes with access to a common replicated database. If one node fails, its users are quickly switched to surviving nodes, often in under a second, preventing perceived downtime. This is achieved through techniques like network transactions or asynchronous/synchronous data replication to keep database copies in synchronization. While active/active eliminates single points of failure and planned downtime, it requires addressing issues like automatic user switching, data collision handling, and performance impacts of maintaining highly available systems.