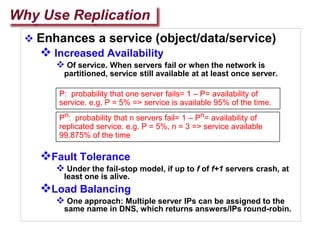
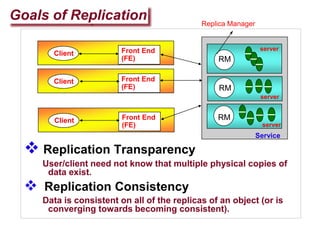
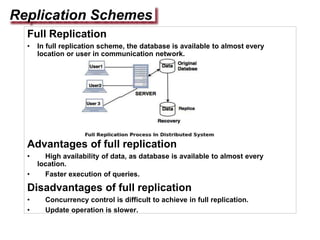
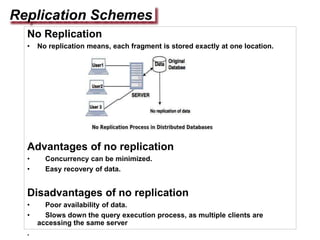
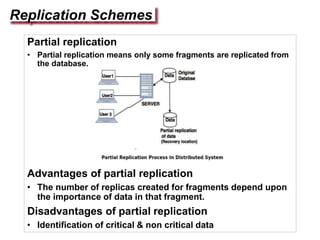
Replication involves creating multiple copies of data across distributed systems to improve reliability, performance, and scalability. There are key issues in replicating data like where to place replicas and how to keep them consistent. Replication can be server-initiated to enhance performance or client-initiated to improve access times. Different replication schemes like full, partial, and no replication involve tradeoffs between consistency, availability, and performance.