Welding Safety Training is essential for protecting welders and those around them from hazards such as burns, electric shock, fumes, and fire. Here's a comprehensive overview of what should be included in effective welding safety training.
🔧 Welding Safety Training Outline
1. Introduction to Welding Hazards
Types of Welding: MIG, TIG, Stick, Arc, etc.
Common Hazards:
Burns from sparks and molten metal
Electric shock
Fire and explosion
Toxic fumes and gases
Eye damage (UV radiation, arc flash)
Noise exposure
Flying particles
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Eye and Face Protection:
Welding helmets with appropriate shade filters
Safety goggles and face shields for grinding
Gloves and Protective Clothing:
Flame-resistant gloves
Long-sleeved shirts and pants (leather or FR-rated)
Respiratory Protection:
Fume extraction systems
Respirators when welding in confined or poorly ventilated areas
Hearing Protection:
Earplugs or earmuffs in high-noise environments
Foot Protection:
Steel-toed boots with metatarsal guards
3. Work Area Safety
Ventilation:
Use of local exhaust ventilation or general ventilation
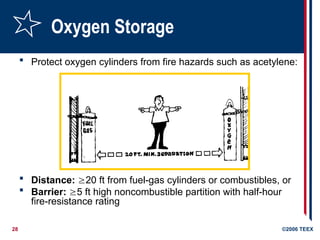
Fire Prevention:
Keep flammable materials away
Have fire extinguishers readily accessible
Use fire-resistant blankets or curtains
Housekeeping:
Keep work areas clean and free of clutter
Welding Screens:
Use to protect nearby workers from arc flash
4. Equipment Safety
Inspection and Maintenance:
Daily checks of cables, electrodes, and connections
Remove damaged equipment from service
Proper Setup and Grounding:
Ensure all equipment is properly grounded
Electrical Safety:
Never touch live electrical parts
Use dry gloves and clothing
Stand on insulating mats when necessary
5. Safe Work Practices
Arc Flash Prevention:
Never look directly at the arc without proper eye protection
Keep helmet down before striking an arc
Hot Work Permits:
Required for welding in areas with potential fire risks
Confined Spaces:
Use gas detection equipment
Ensure proper ventilation and standby personnel
6. Fume and Gas Control
Identify materials that release toxic fumes (e.g., galvanized metals, lead-based coatings)
Use exhaust hoods and ventilation systems
Understand symptoms of overexposure: dizziness, headaches, nausea
7. Emergency Procedures
Burns:
Cool with water and seek medical attention
Electric Shock:
Call emergency services; do not touch the victim if the power is still on
Eye Injuries:
Seek medical attention for arc flash or foreign objects
Fire Response:
Know fire extinguisher locations and evacuation routes
8. Regulations and Standards
OSHA 1910 Subpart Q – Welding, Cutting, and Brazing
ANSI Z49.1 – Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes
NFPA 51B – Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding
📋 Training Delivery Methods
Classroom-based instruction
On-the-job training
Videos and simulations
Hands-on practice with PPE and equipment
Quizzes and final assessments Training Completi