Embed presentation




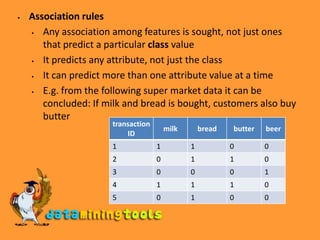














This document discusses concepts related to data mining input, including concepts, instances, and attributes. It also covers different types of learning in data mining like classification, numeric prediction, clustering, and association rules. Key steps to prepare data for mining are discussed, such as data assembly, integration, cleaning, and preparation. Formats for data like ARFF files and handling sparse data are also covered.

















