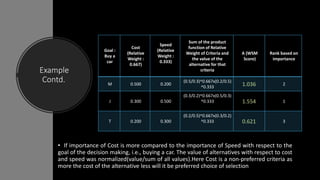
The weighted product method (WPM) is a multi-criteria decision-making approach that determines the ranking of alternatives based on the multiplication of their normalized performance values and the relative weights of criteria. For instance, in choosing a car, factors like cost and speed are considered, with cost being a non-preferred criterion. The method allows for a systematic comparison and ranking of alternatives, illustrated through a car selection example where Mercedes-Benz, Jaguar, and Toyota were evaluated.