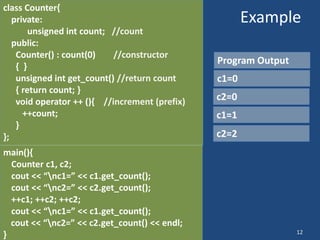
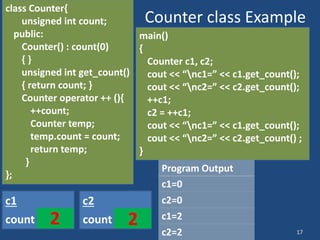
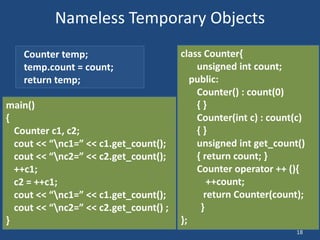
Operator overloading allows operators like + and << to be used with user-defined types by defining corresponding member functions. For example, the + operator can be overloaded to add two Distance objects by defining the member function operator+. This makes code more readable compared to explicit function calls. Overloading unary operators like ++ requires defining operator++(), while overloading binary operators like + requires defining both operator+() and operator+=(). The return type and arguments of overloaded operators must match the conventional operator.