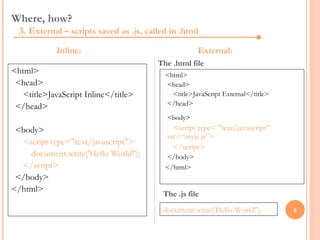
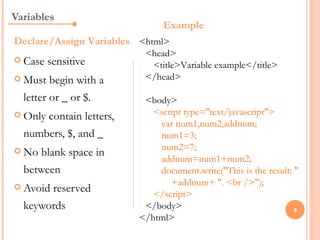
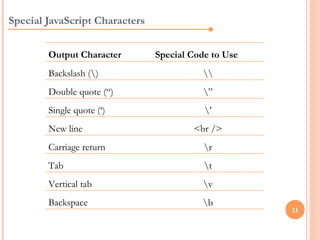
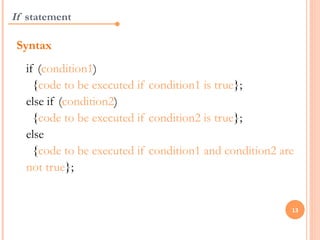
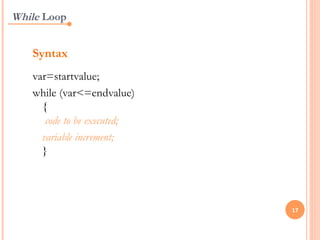
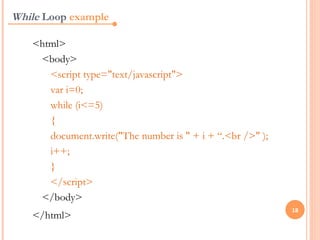
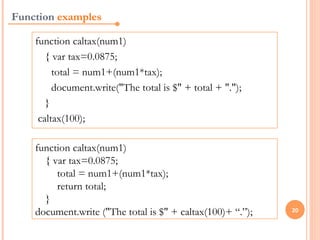
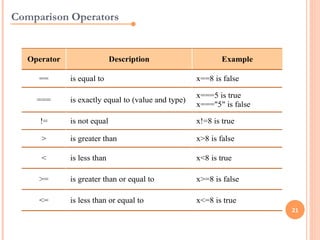
JavaScript is a client-side scripting language that adds interactivity to web pages. It runs in the browser rather than on the server. JavaScript code can be added inline, internally, or externally. Common statements include document.write to output content, variables to store values, if/else conditions to check statements, and for/while loops to iterate. Functions allow code reuse. Operators like ==, >, && are used to compare values and check logic.