The document discusses the basics of JavaScript including:
1. JavaScript allows adding programming to webpages and is not a standalone language like Java.
2. Common uses of JavaScript include browser detection, storing cookies, controlling browser windows, and validating forms.
3. Scripts can be placed internally between HTML tags or externally via link tags.
4. JavaScript includes objects, properties, methods, variables, operators, statements, and event handlers.
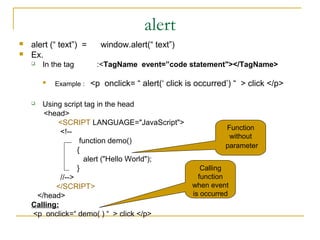
5. Common output methods are alert, write, and print while input methods include confirm and prompt.
6. Other basics covered are variables, conditional statements like if/else, switch, and iterations like for and while loops.