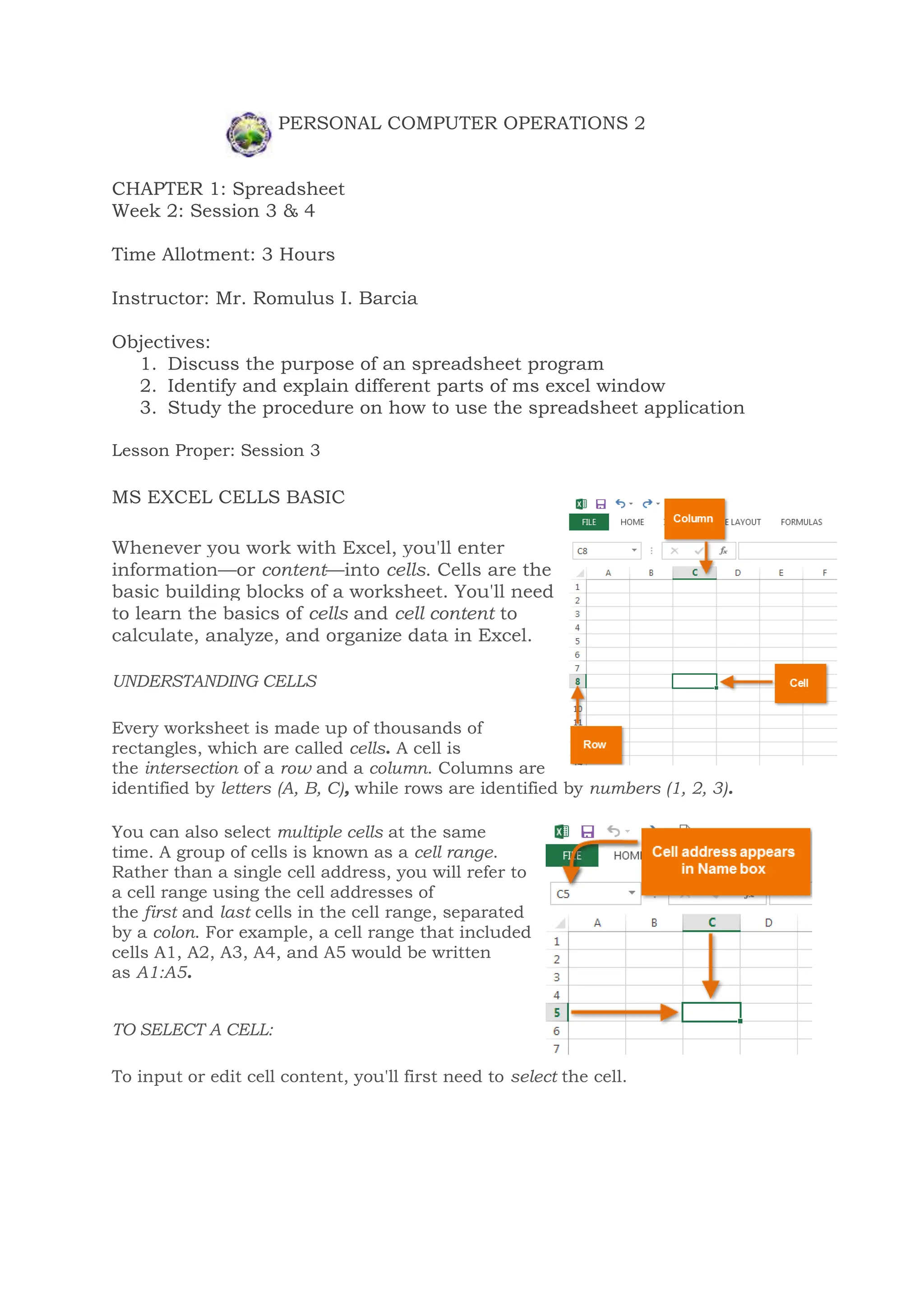
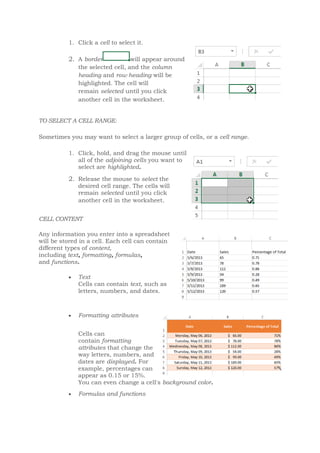
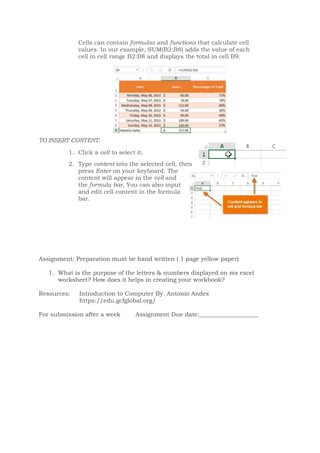
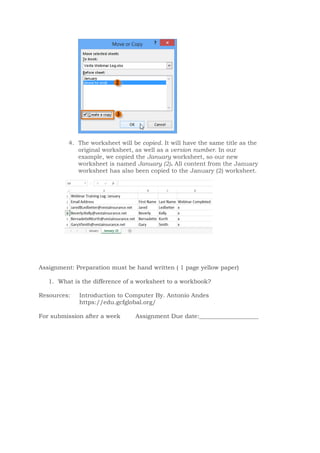
This document discusses the basics of using Microsoft Excel, including cells, cell ranges, and cell content. It covers how to select cells and cell ranges, insert different types of content like text and formulas, and the basics of worksheets including renaming, inserting, deleting, and copying worksheets. The objectives are to discuss the purpose of spreadsheets, identify parts of the Excel window, and learn procedures for using the spreadsheet application. Students are assigned to write about the purpose of letters and numbers on an Excel worksheet and the difference between a worksheet and workbook.