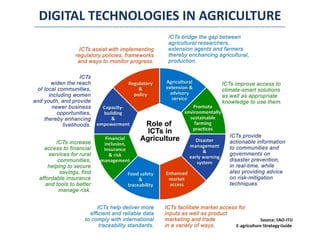
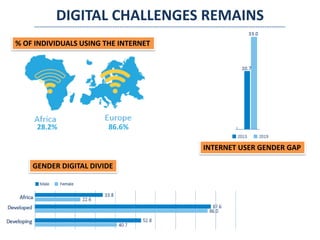
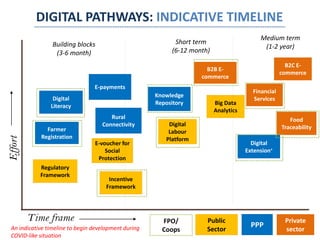
The document discusses how digitalization can transform agriculture in Africa beyond COVID-19. It outlines several impacts of COVID-19 on agriculture, including trade and logistics disruptions and labor shortages. It then discusses opportunities for digital technologies in agriculture across areas like e-commerce, extension services, financial services, and infrastructure. An indicative timeline is provided for beginning development of digital solutions. Key enablers of digital ecosystem development in Africa are identified as regulatory frameworks, legal frameworks, data governance, infrastructure, and capacity development.