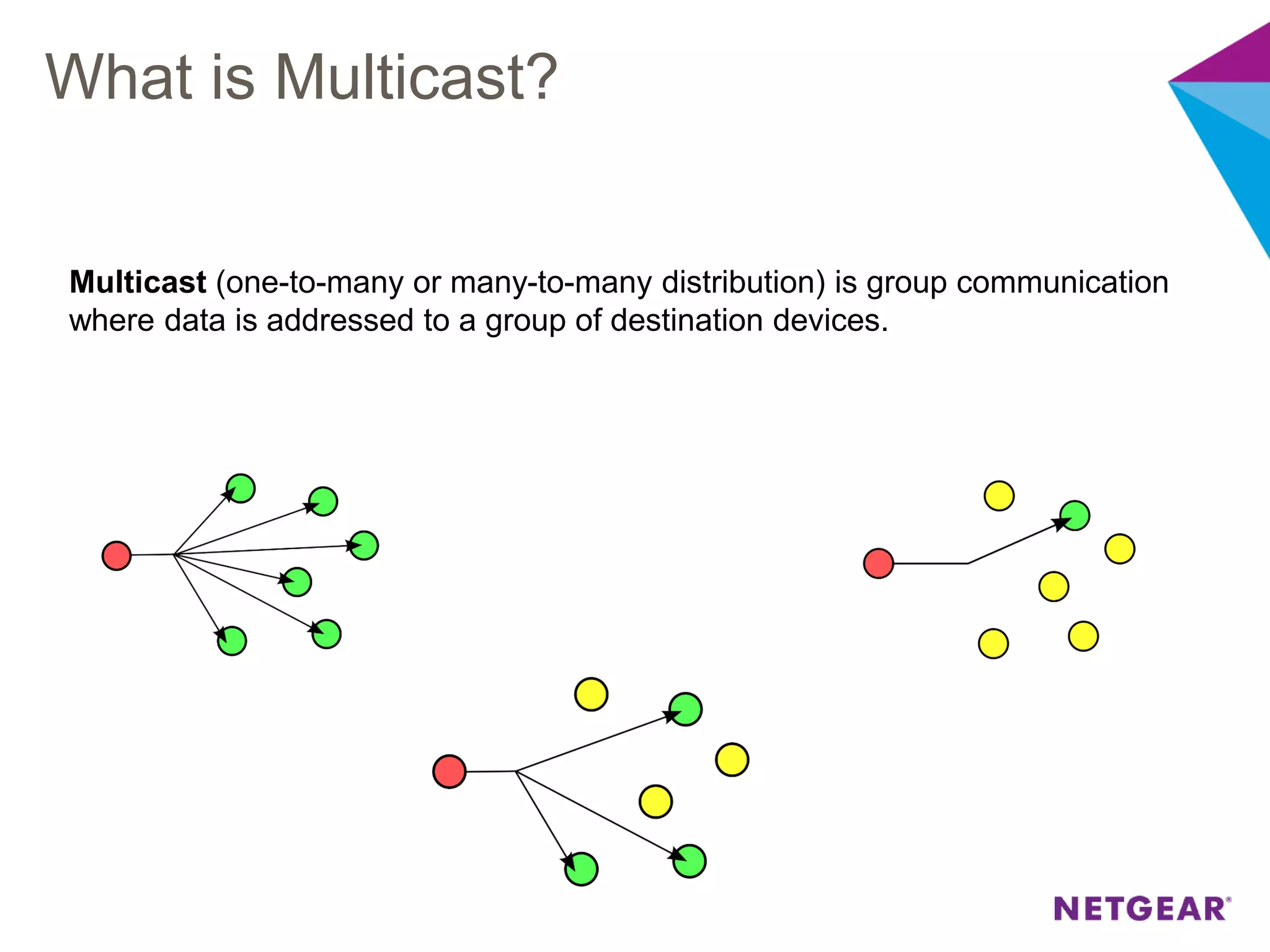
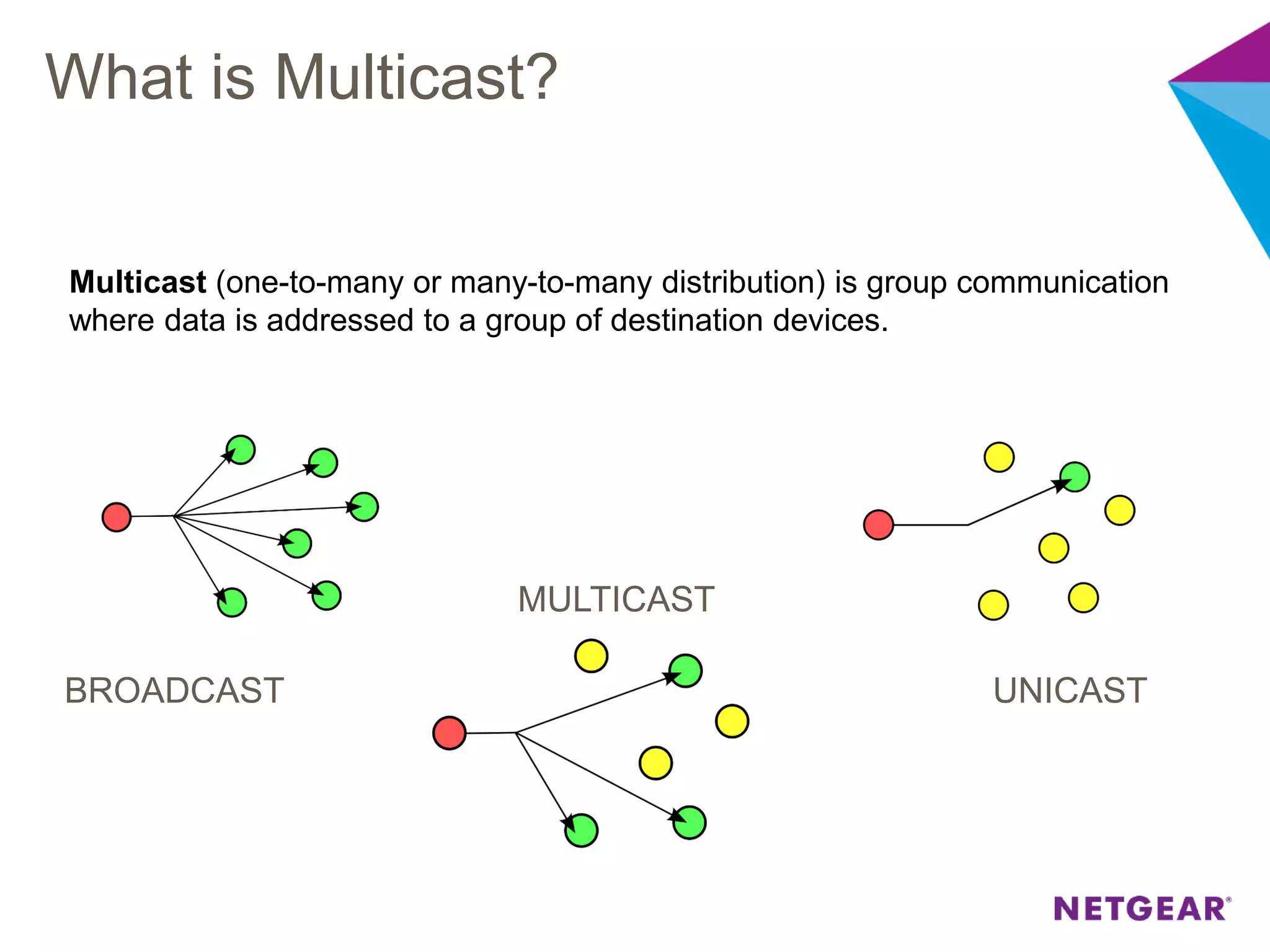
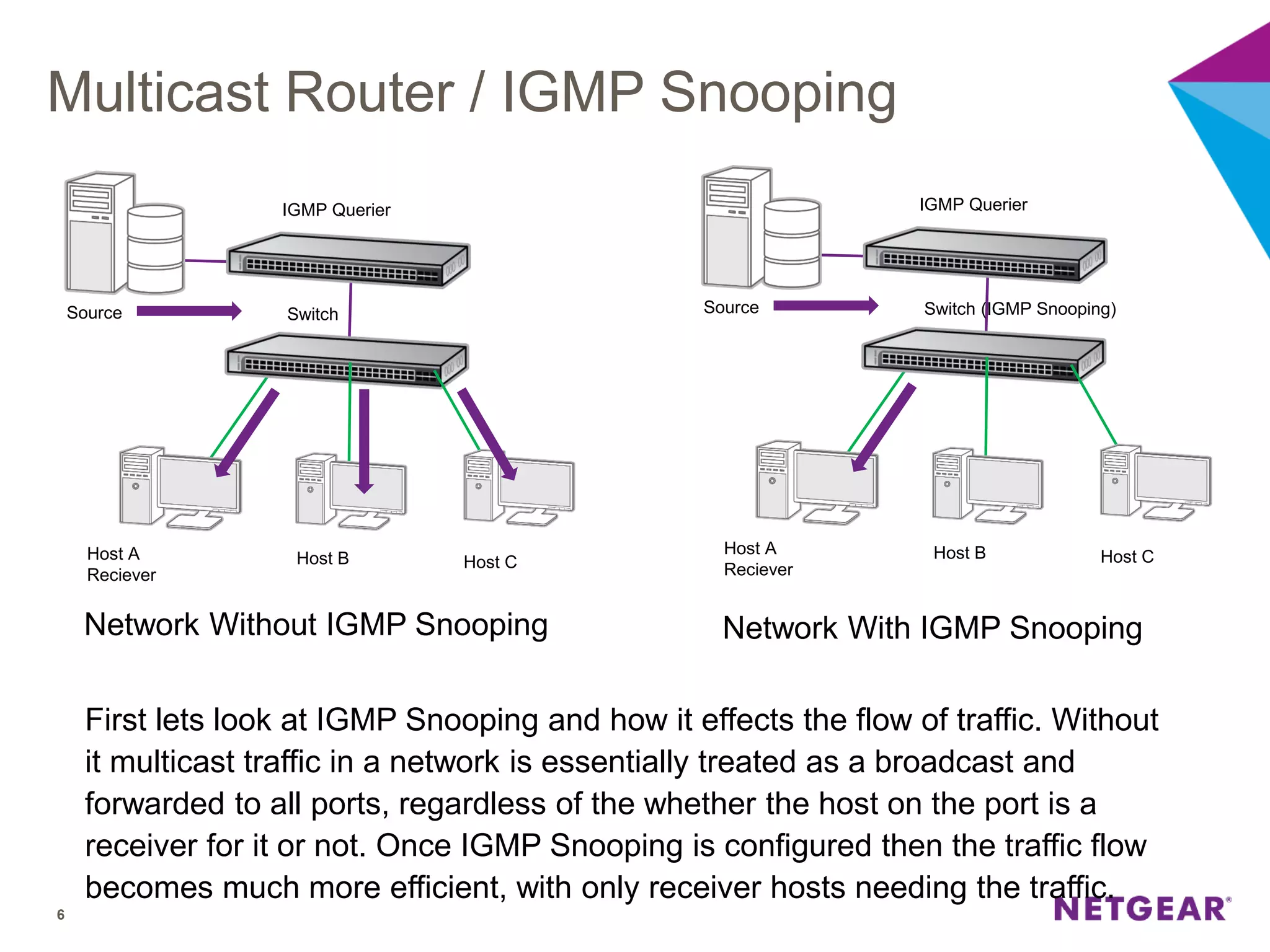
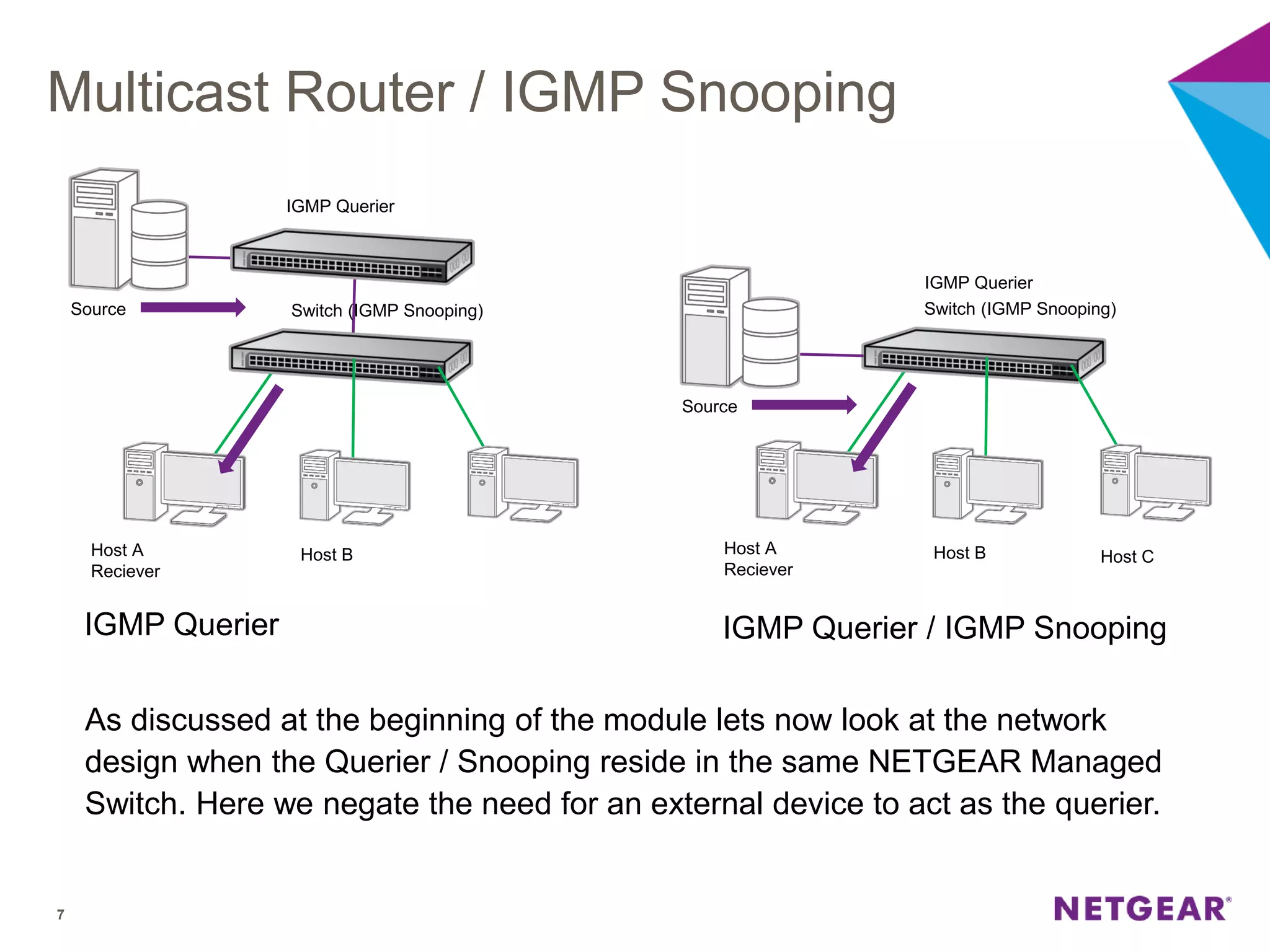
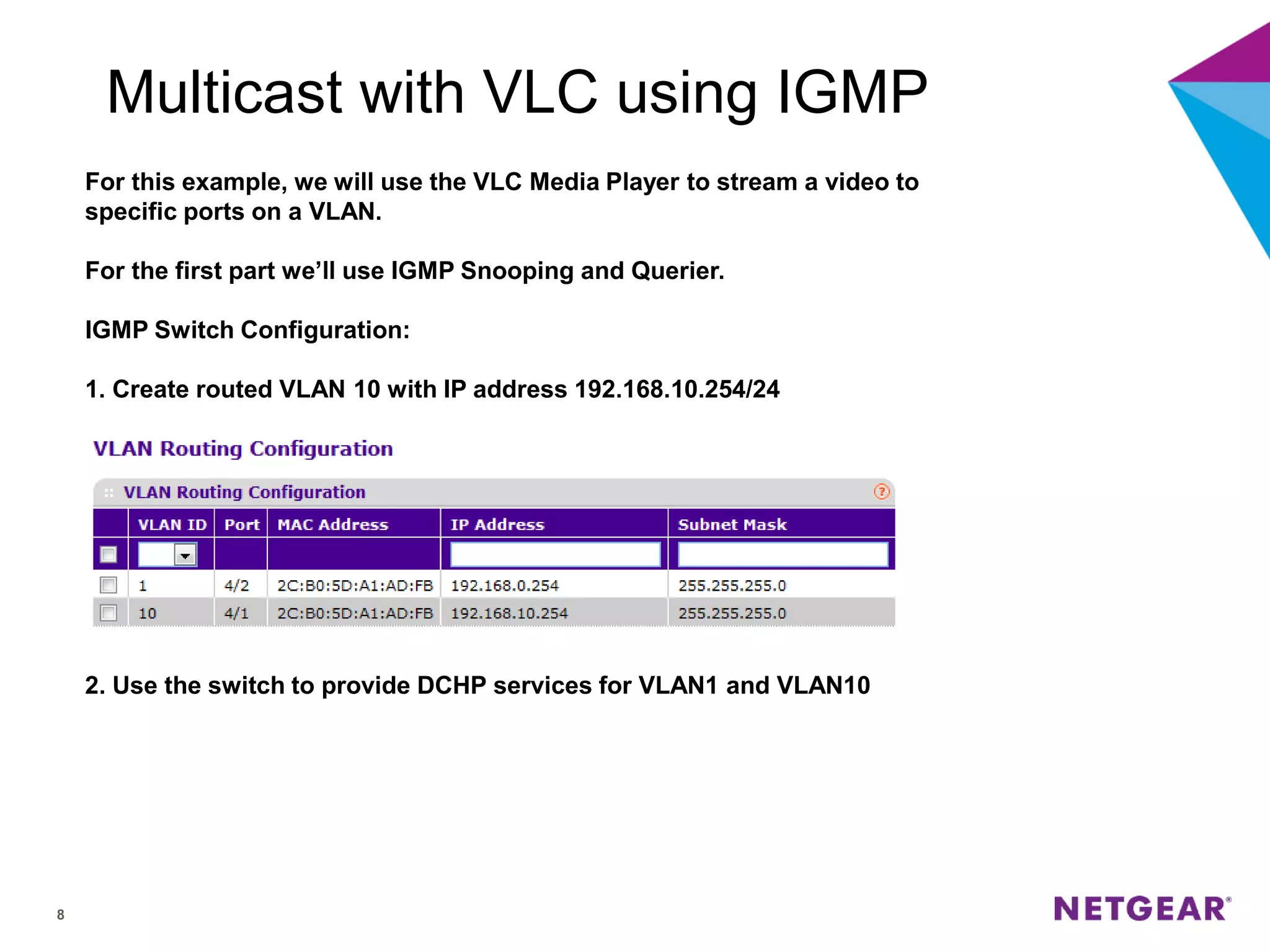
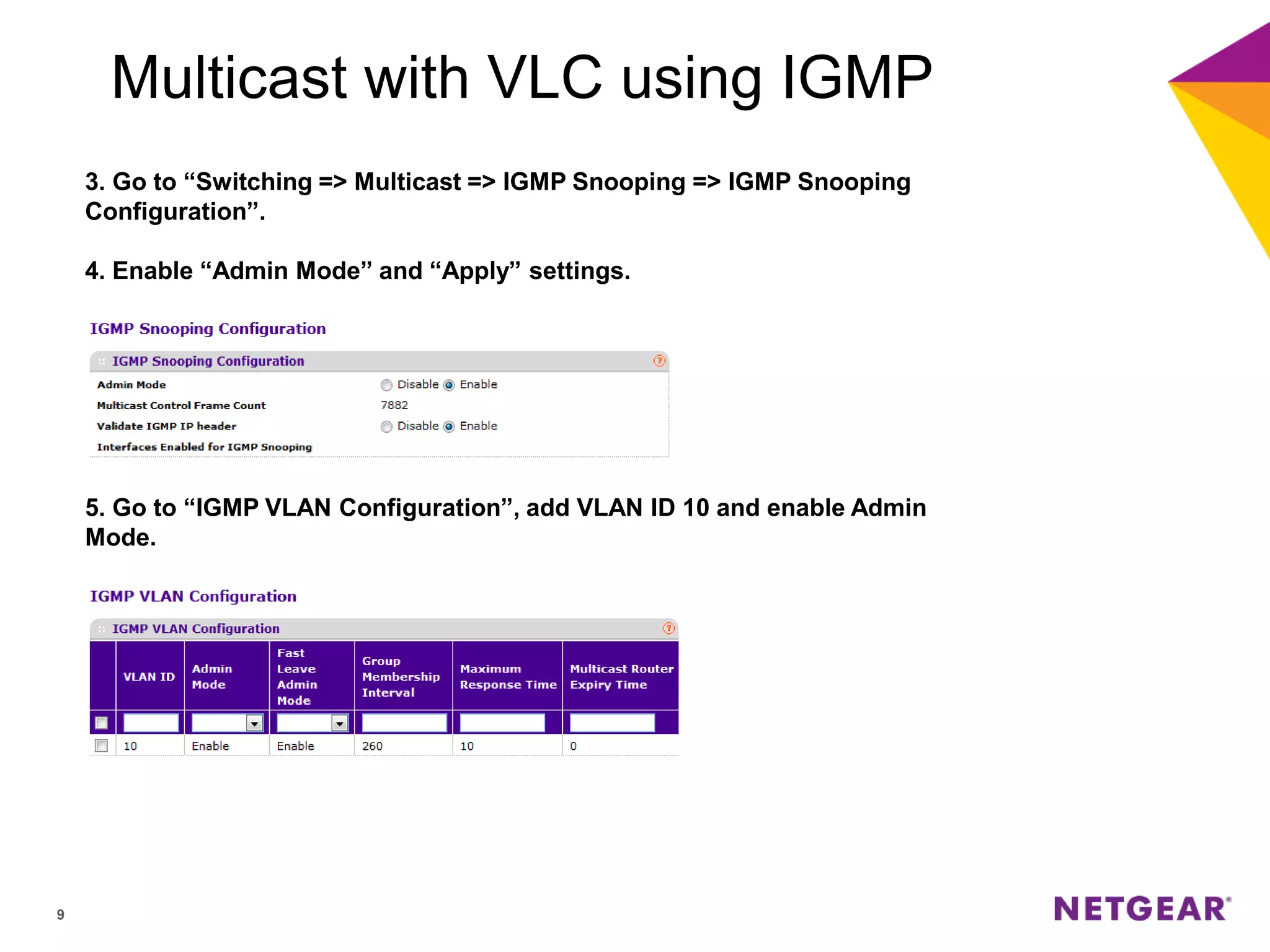
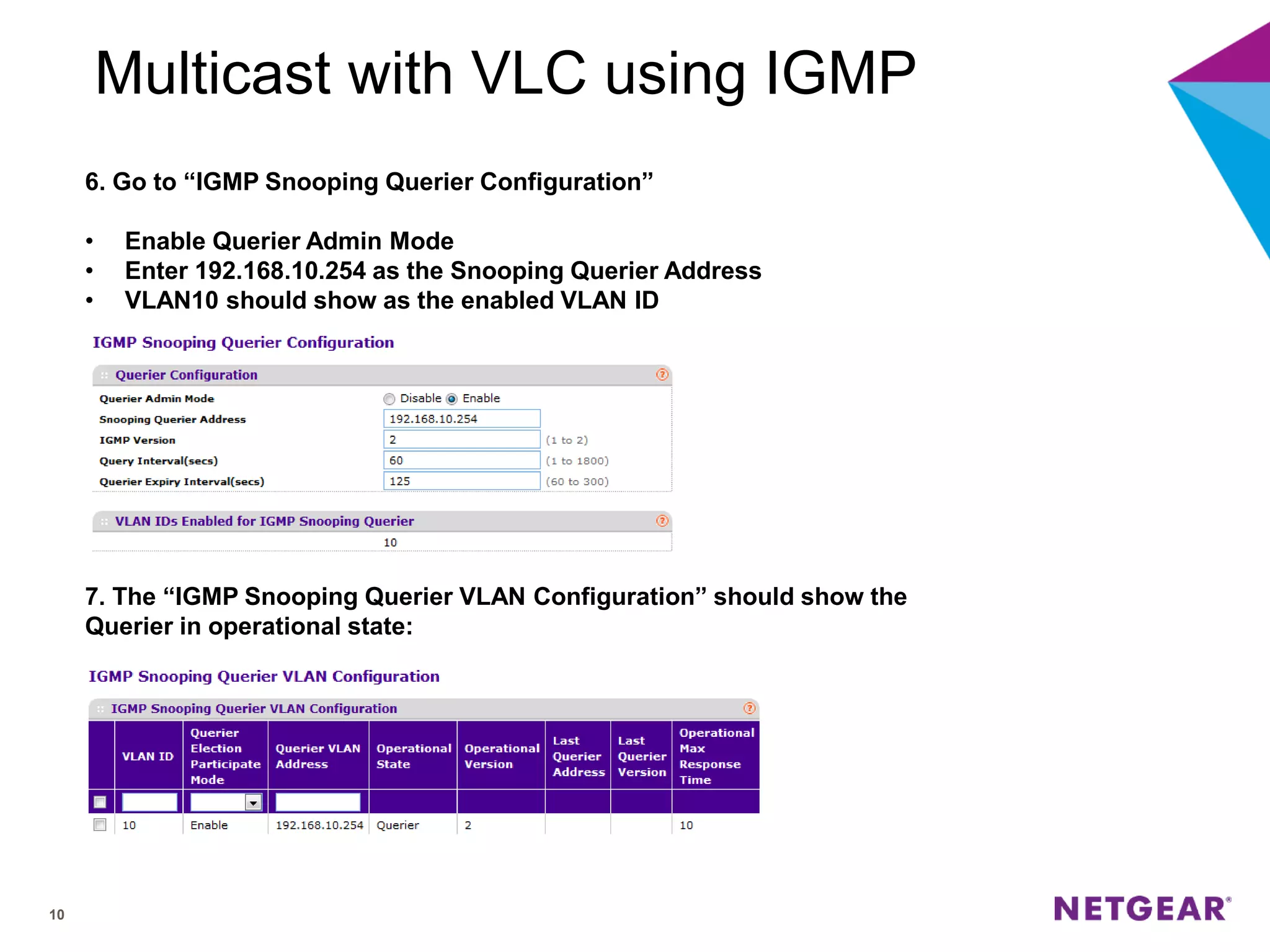
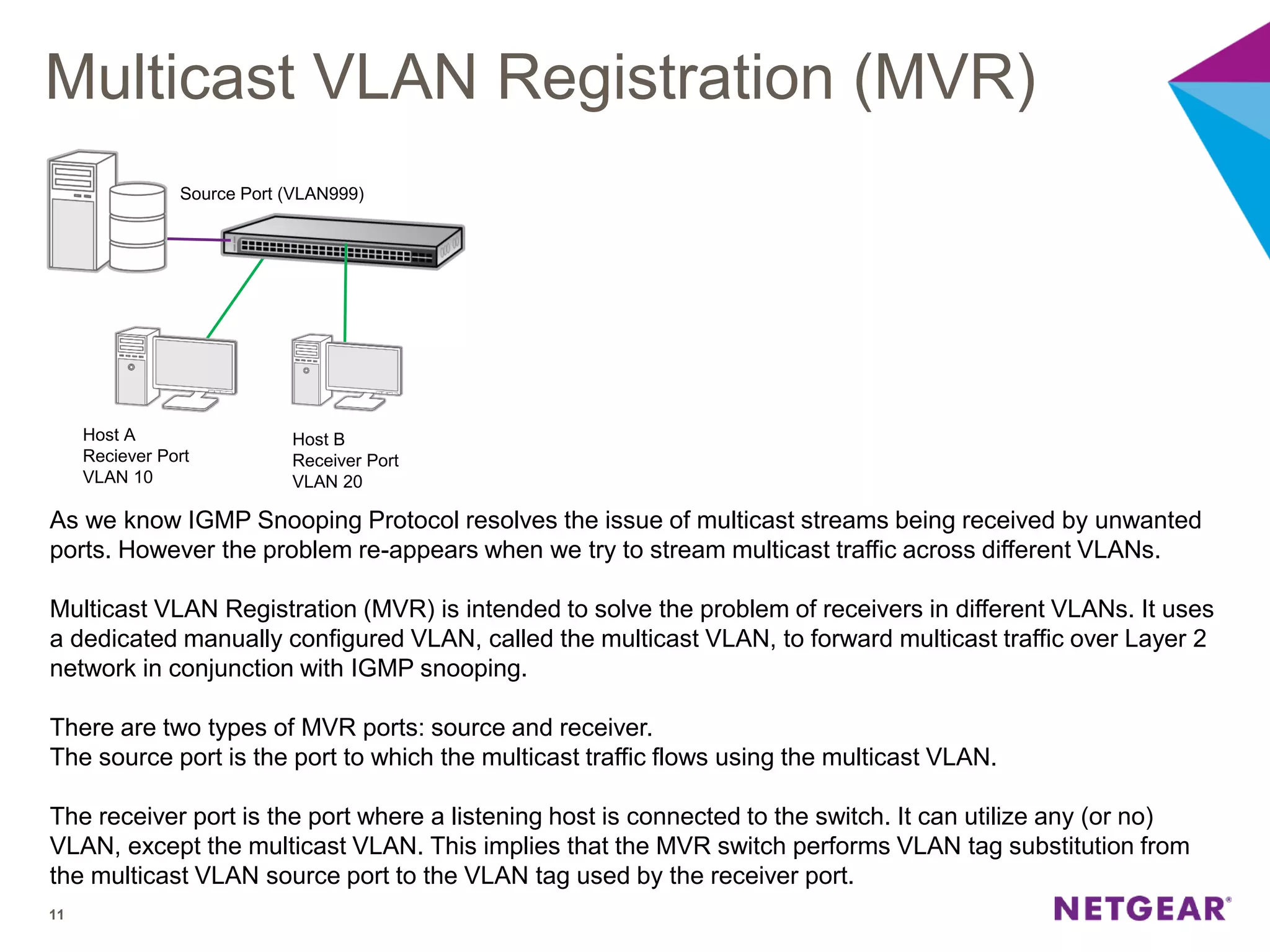
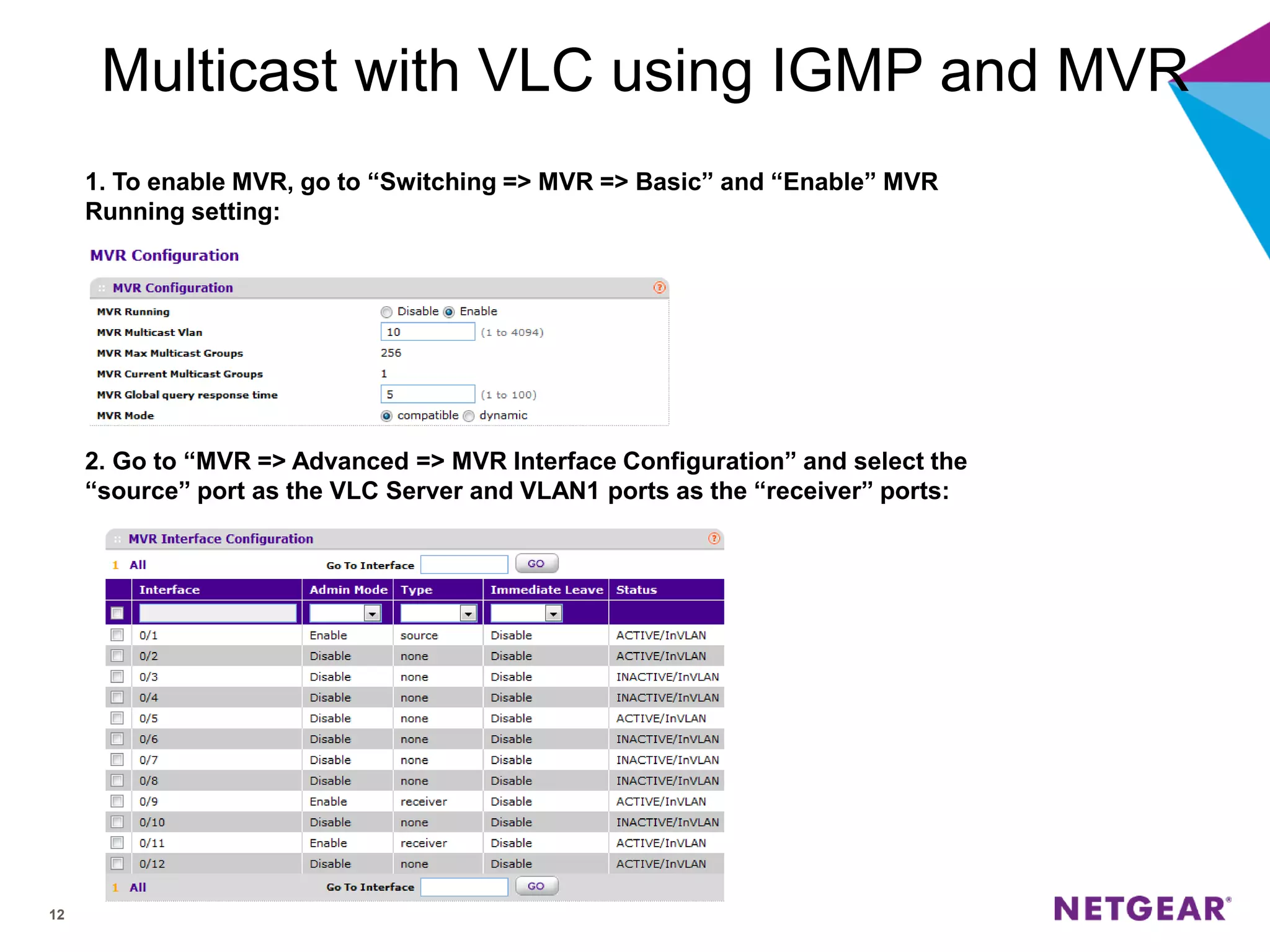
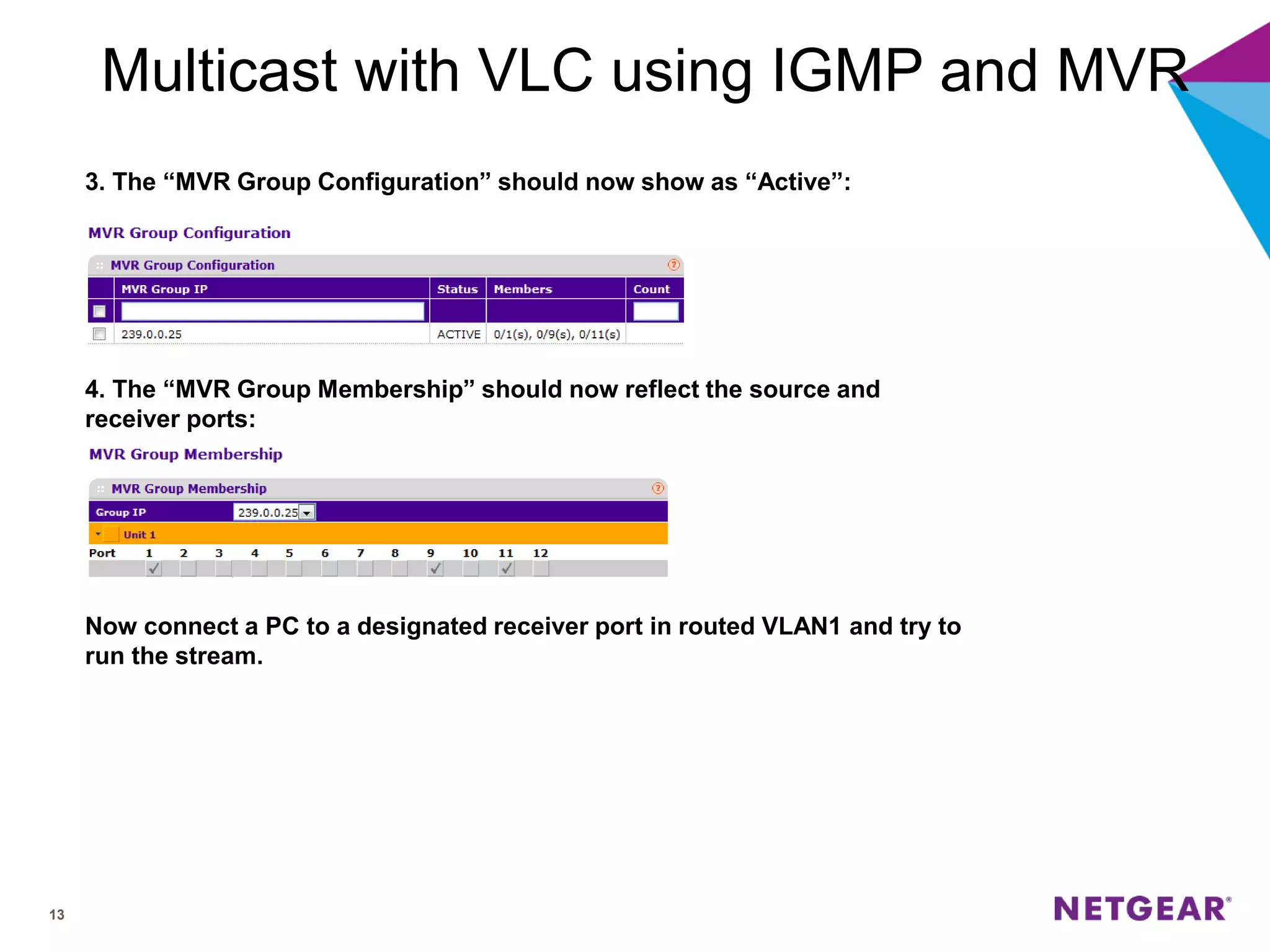
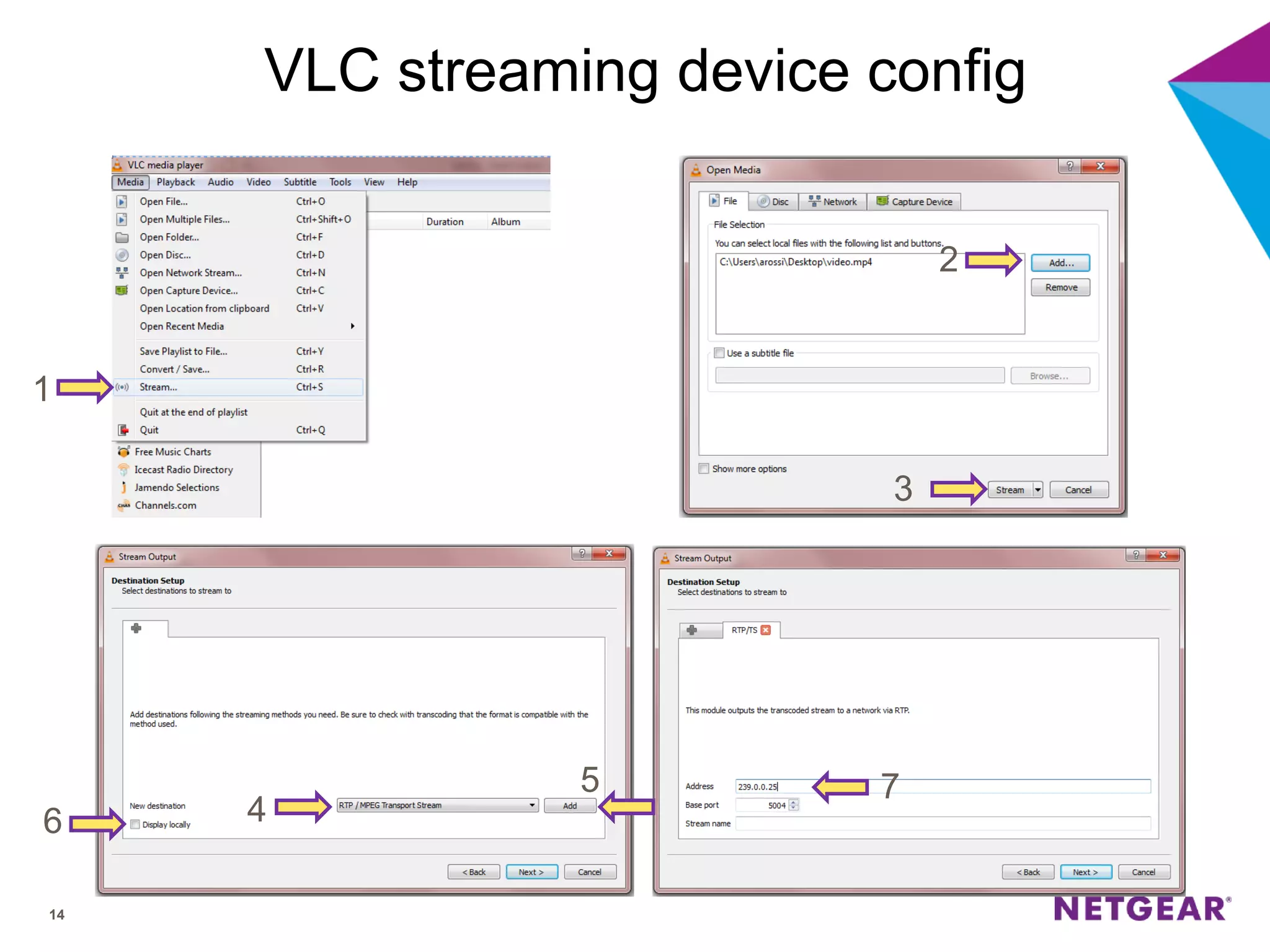
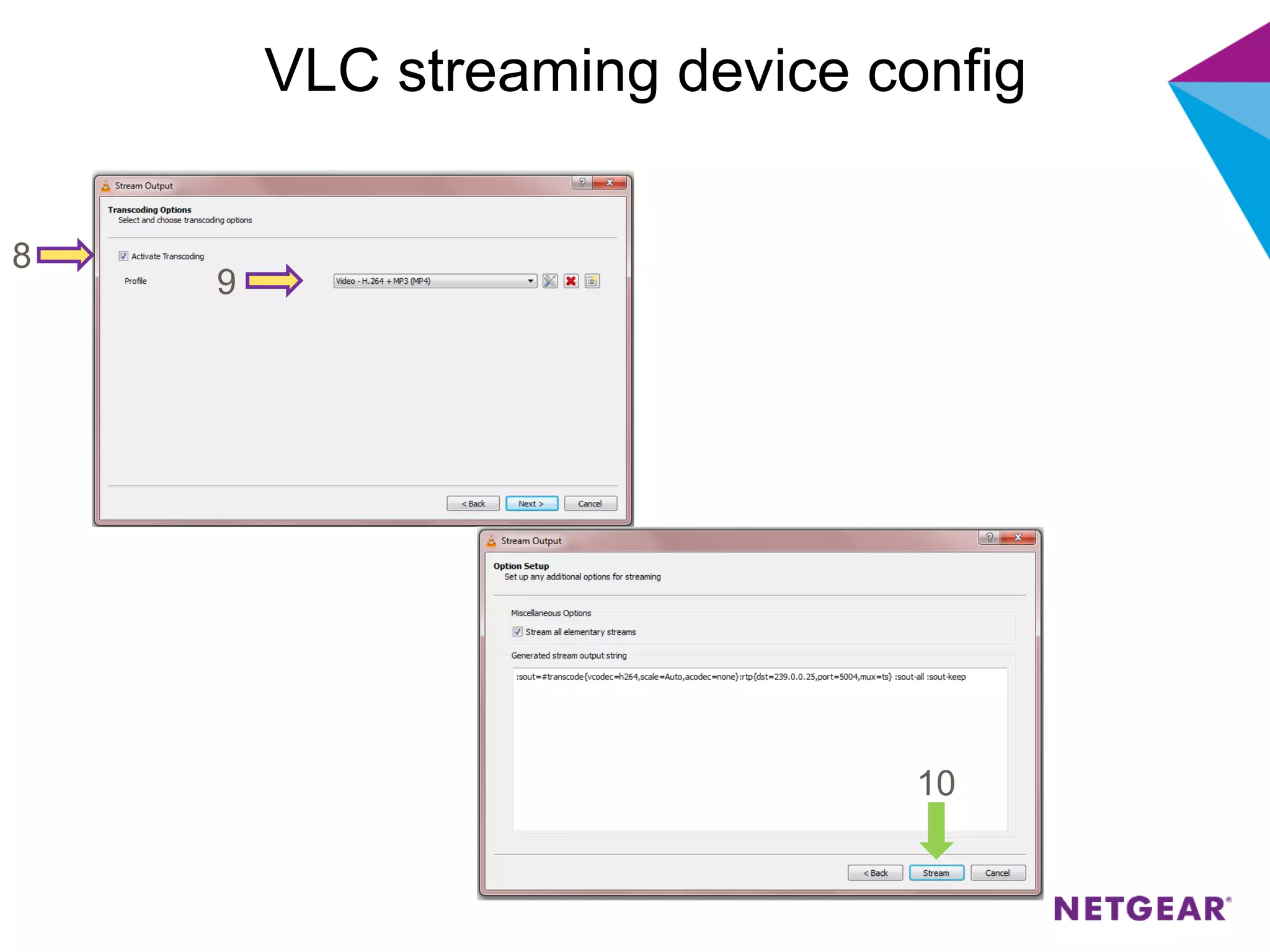
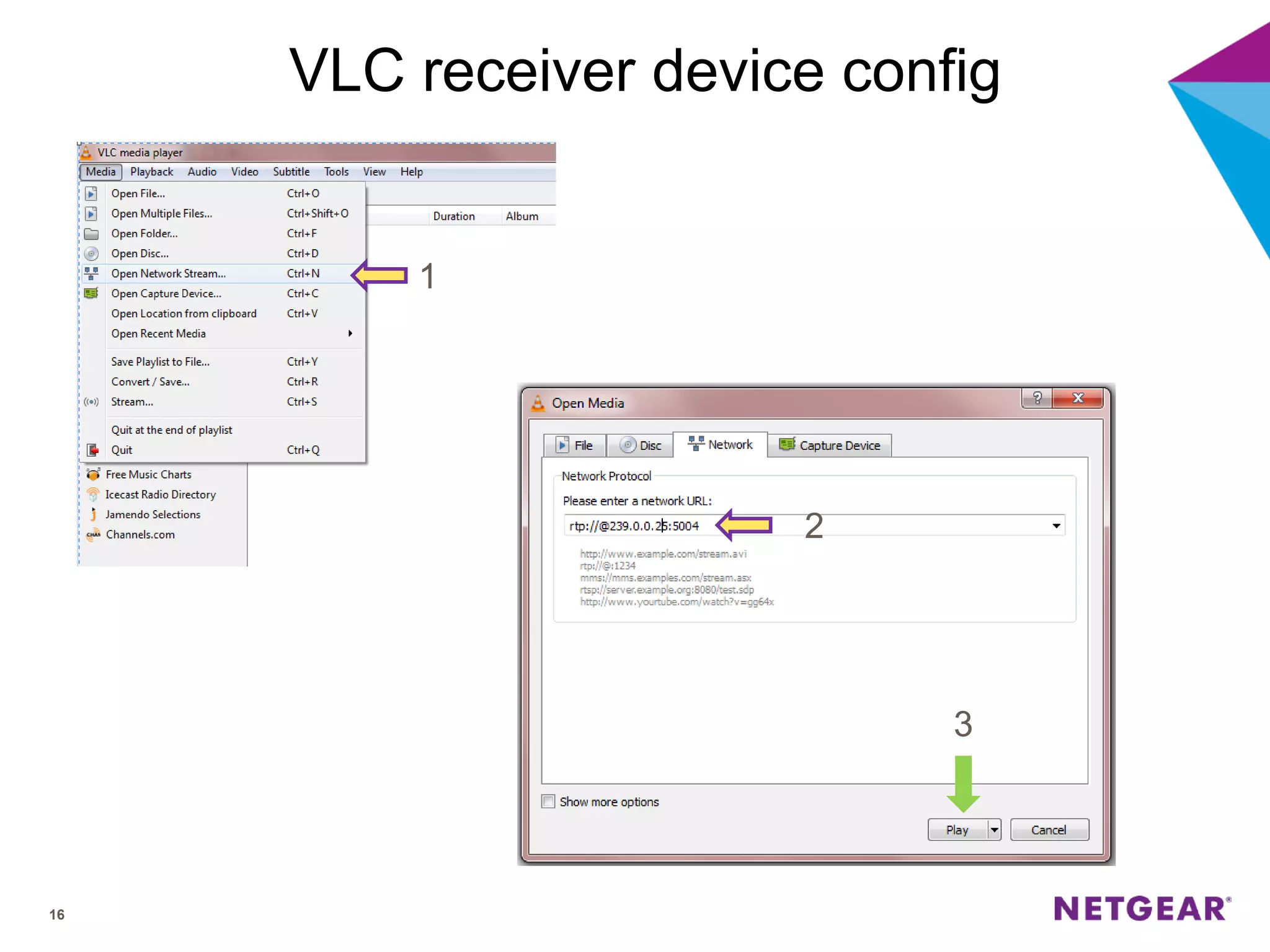
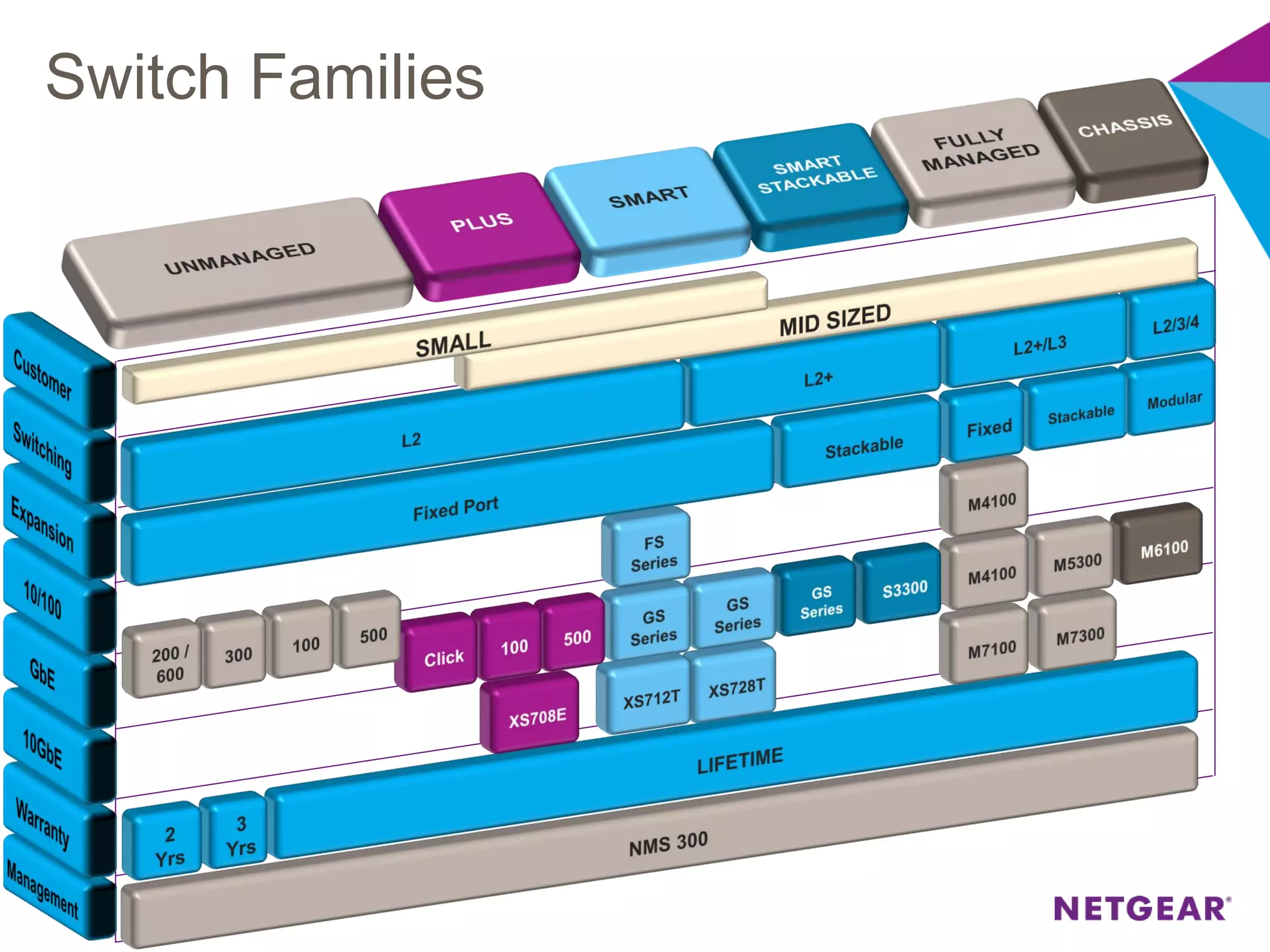
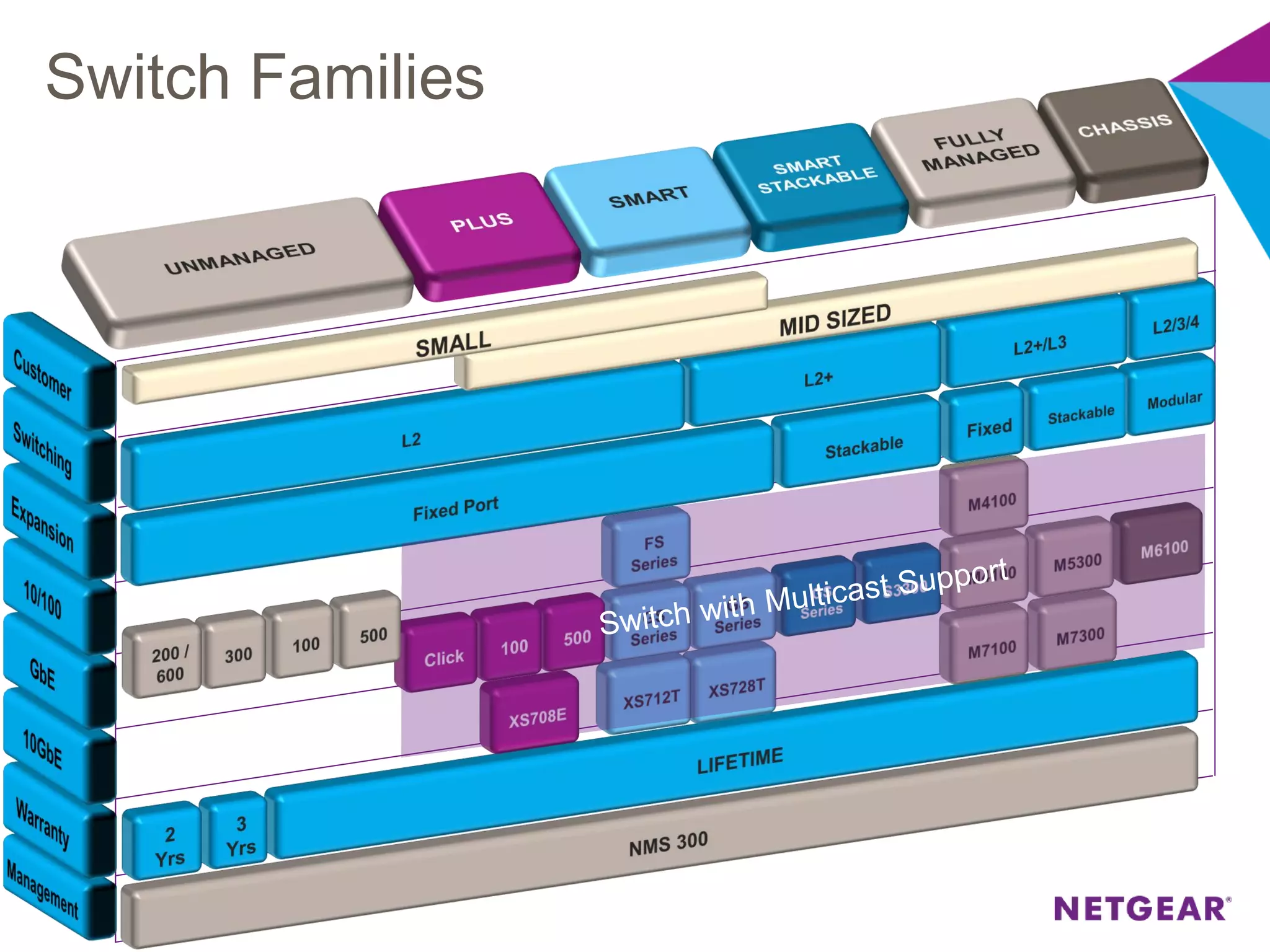
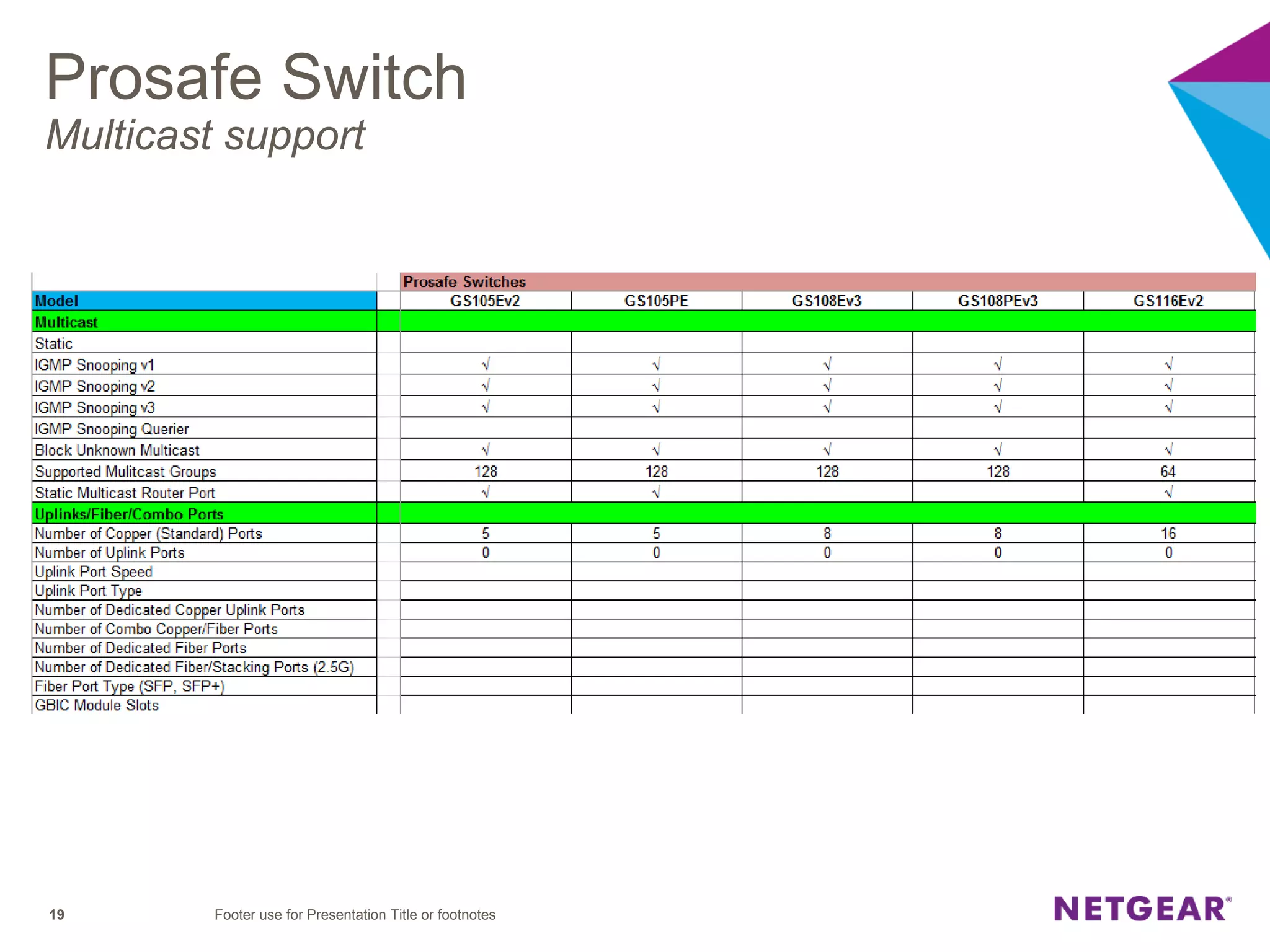
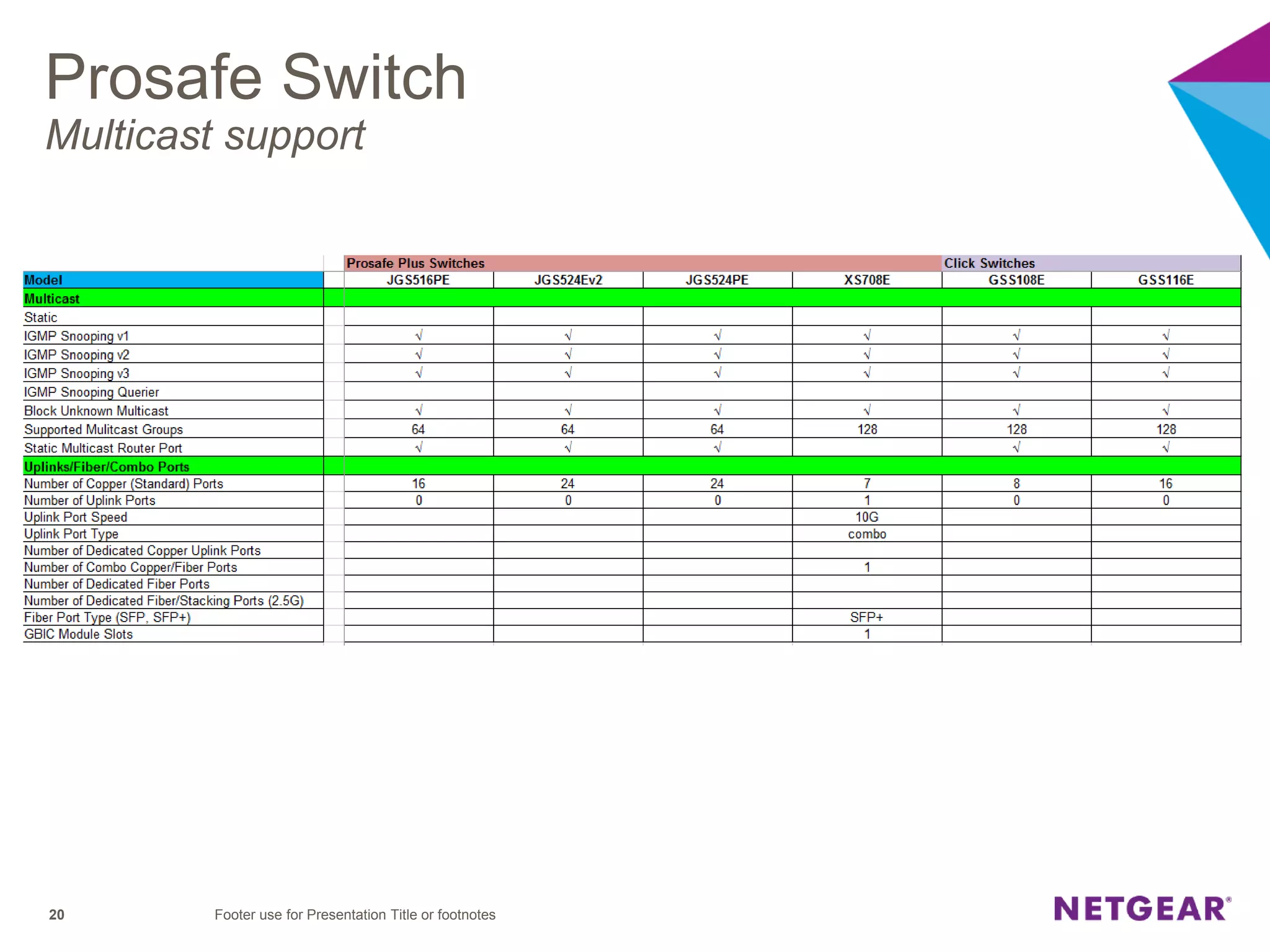
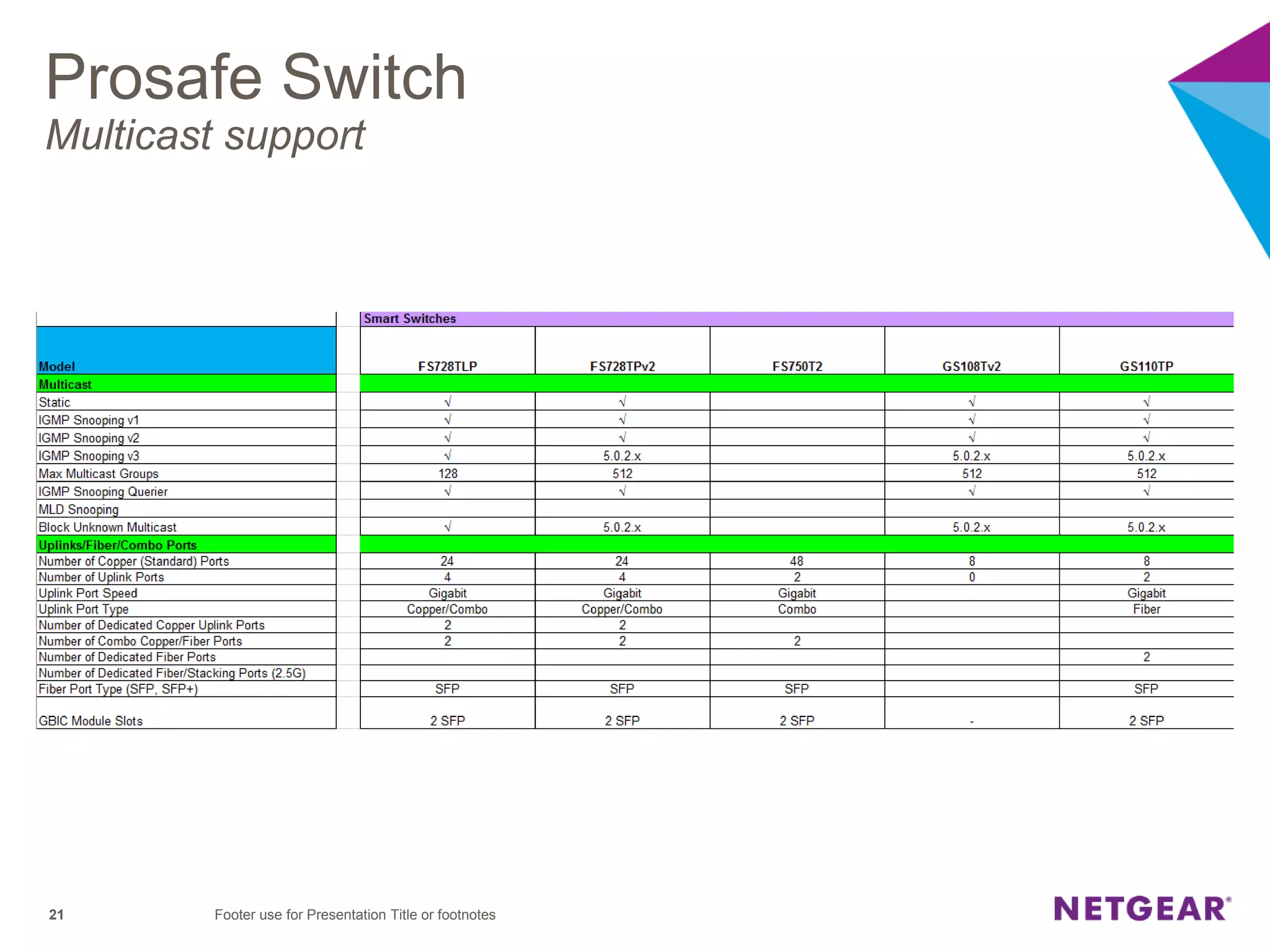
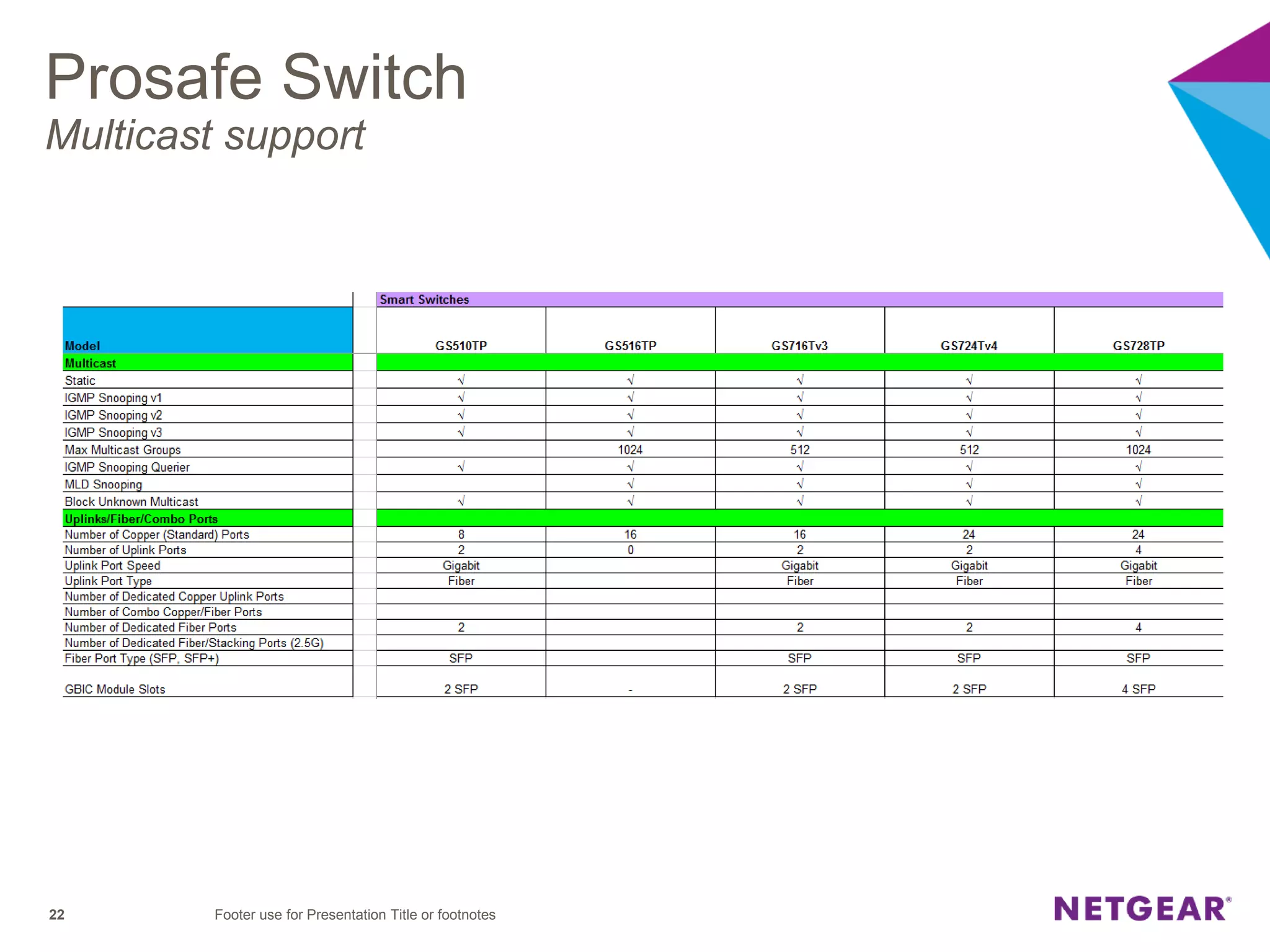
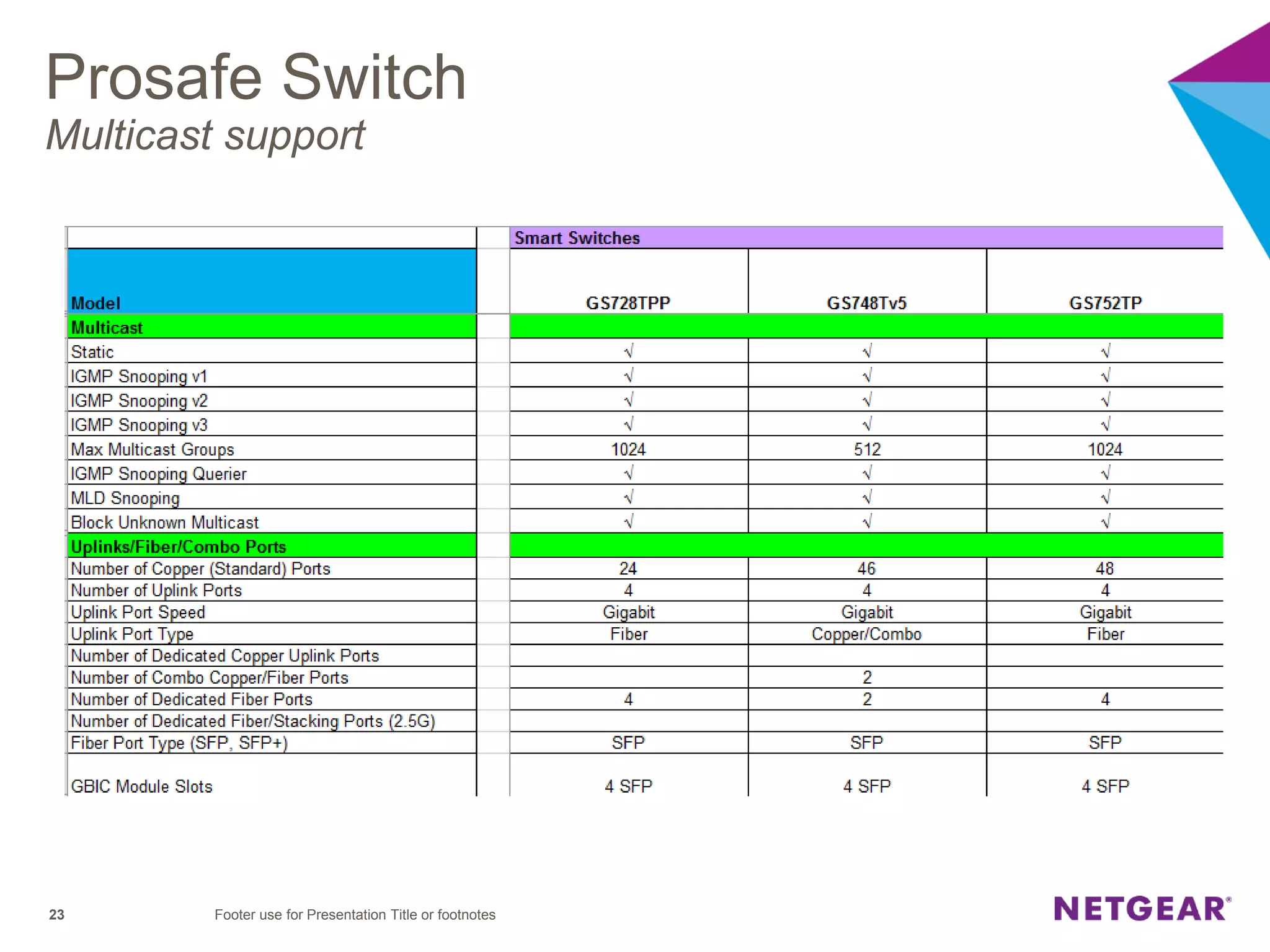
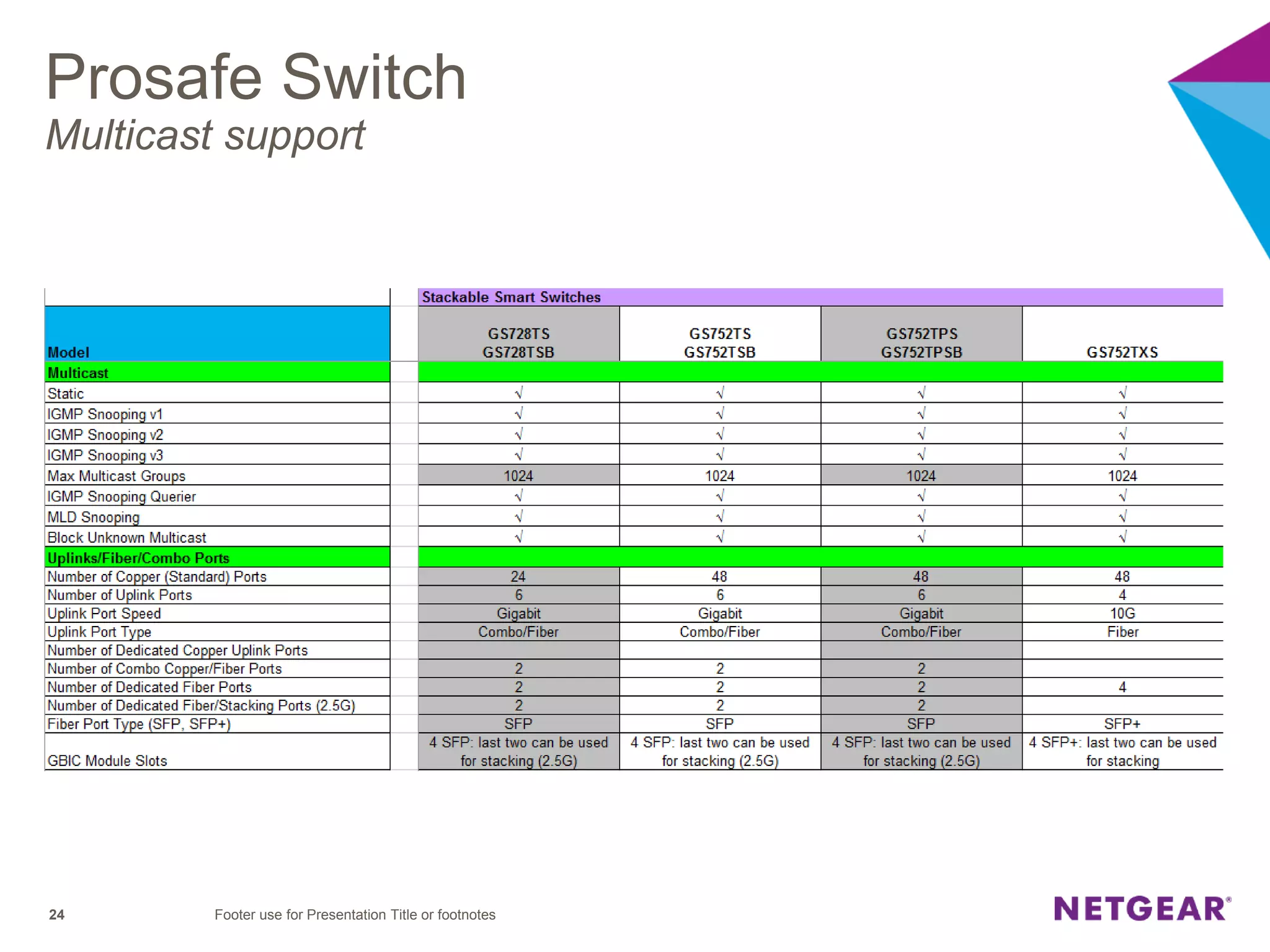
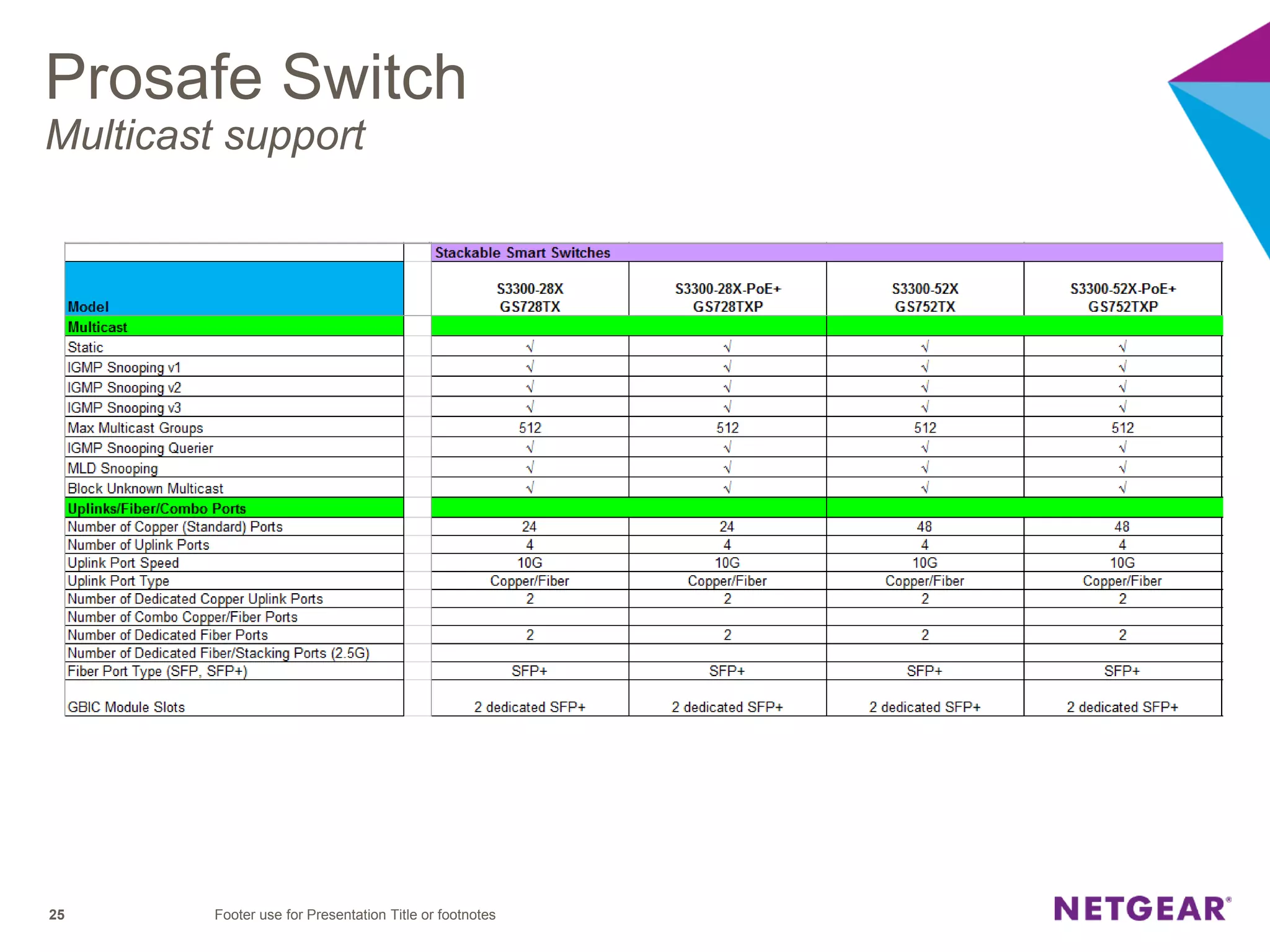
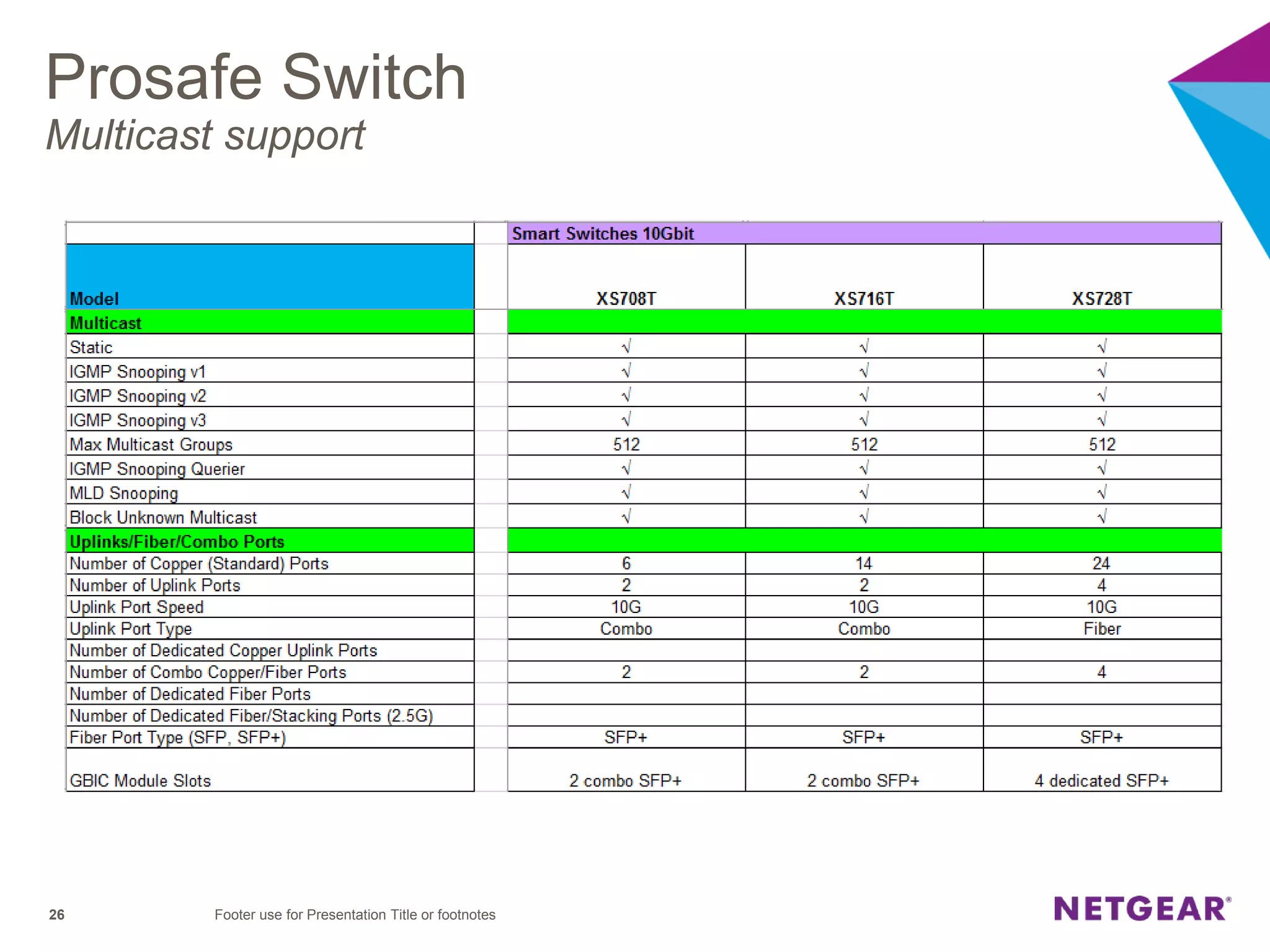
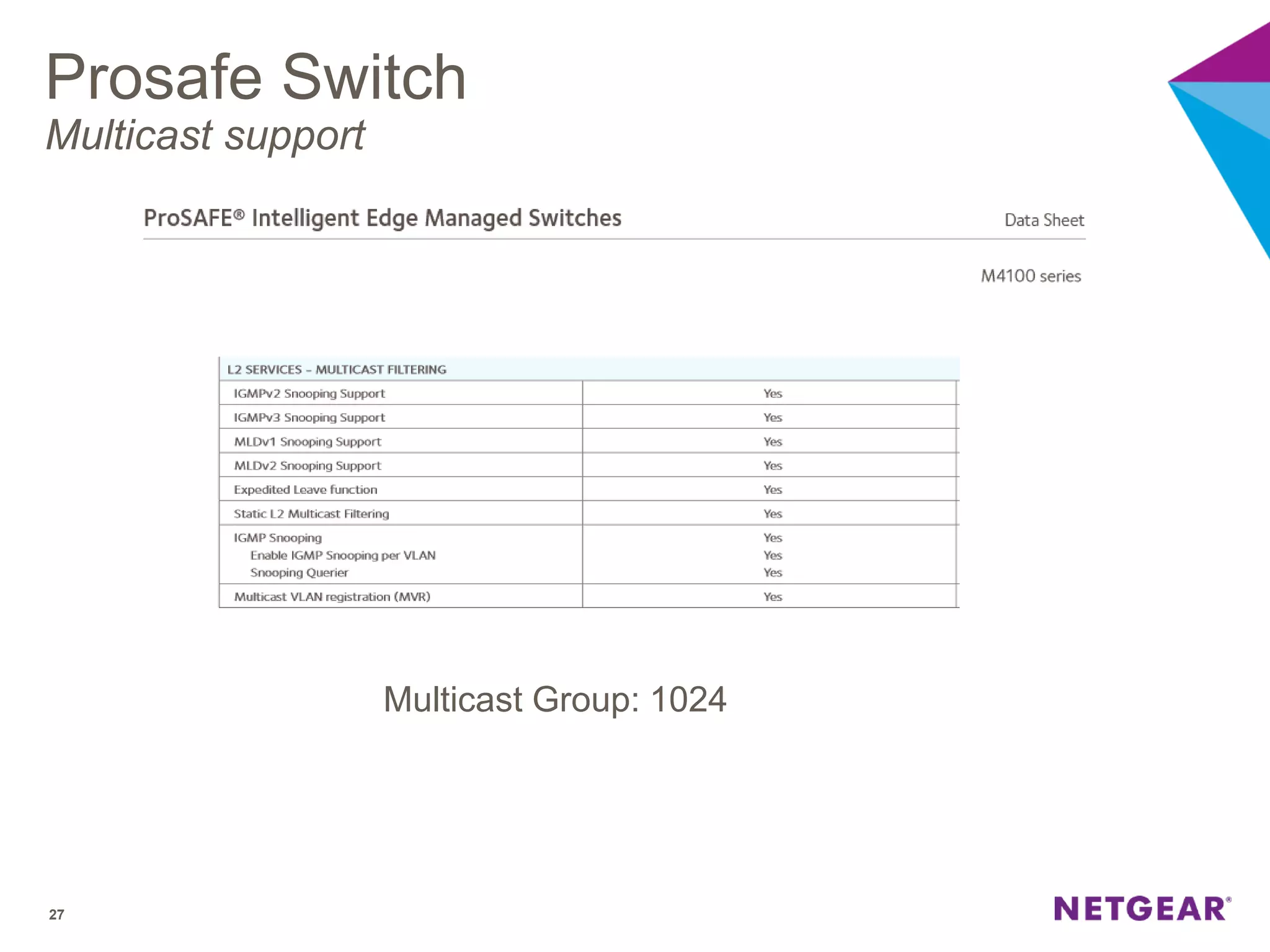
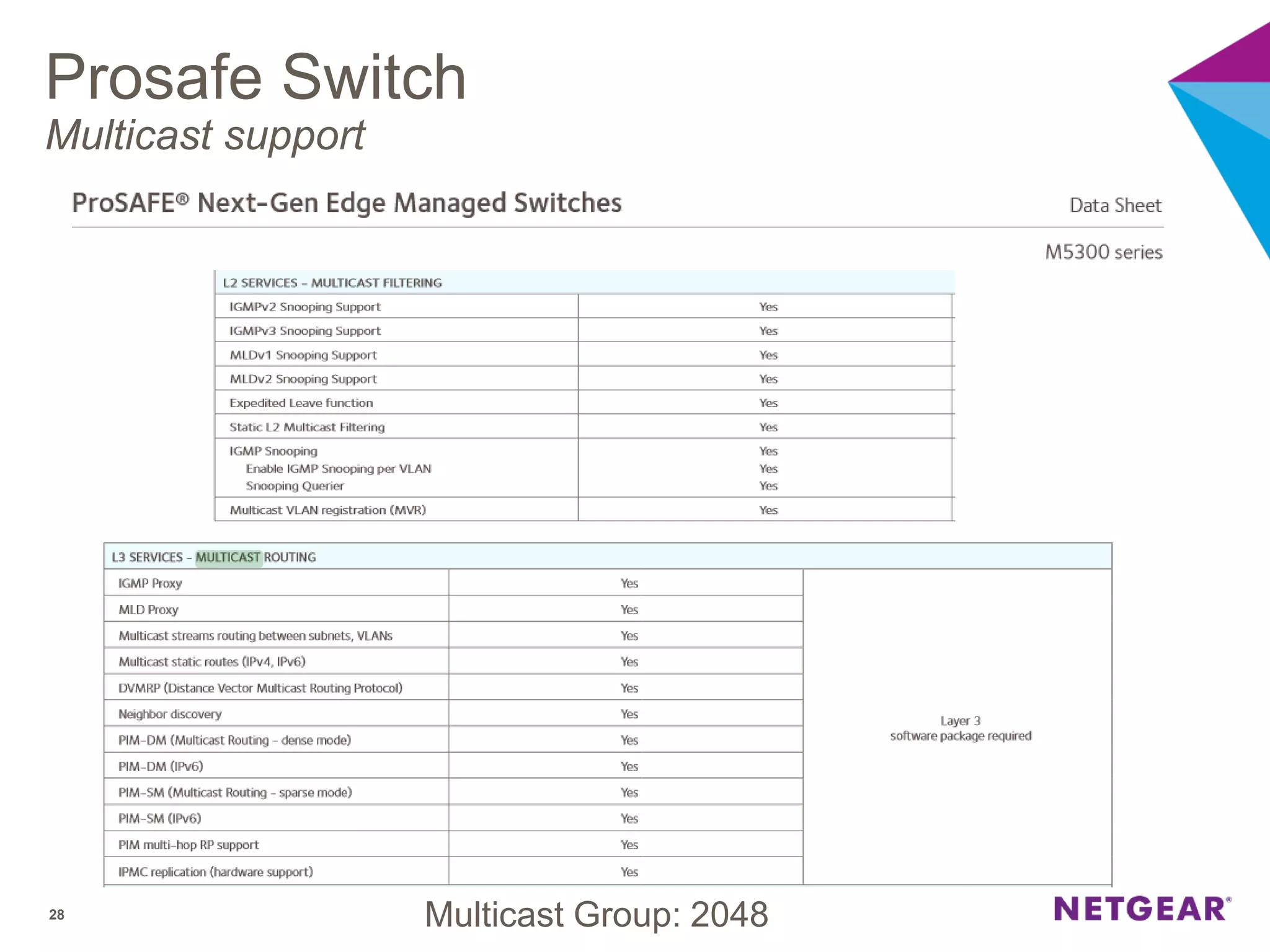
The document explains multicast communication, which enables the distribution of data to a group of devices rather than individual ones. It discusses the importance of IGMP snooping for efficient traffic management in networks that utilize video services like IPTV, facilitating the creation of multicast groups without needing an external device when built into a switch. Additionally, it covers multicast VLAN registration (MVR) to enable multicast traffic between different VLANs and outlines configuration steps using the VLC media player.