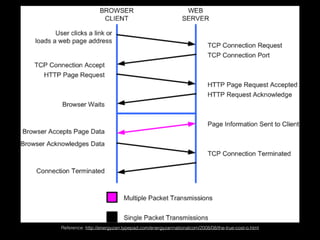
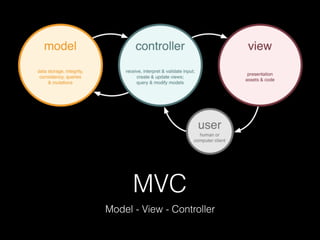
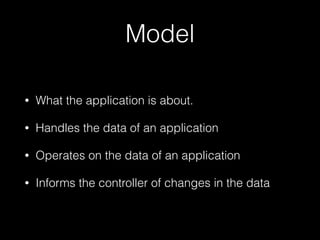
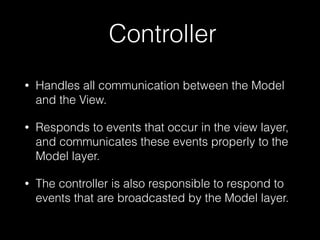
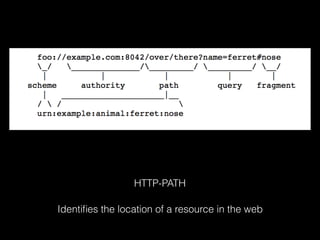
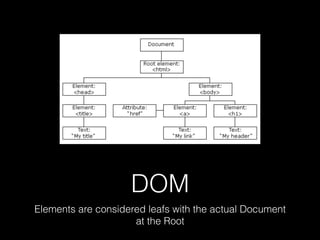
This document provides an overview of key concepts in web development including tools, version control, web servers, and application architecture. It discusses JavaScript and Node.js for programming, Git for version control, and the model-view-controller (MVC) pattern for application structure with models for data, views for display, and controllers for communication. HTTP is covered for browser-server interaction using requests and responses along standard methods and formats.