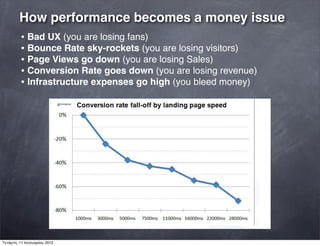
The document discusses web performance and identifies several factors that can cause delays, including issues with client hardware/software, server hardware/software, and network connectivity. It notes that performance issues cost companies money by hurting the user experience, conversion rates, and other metrics. The document then outlines several laws of web performance and provides tips for optimizing performance on both the server-side and client-side of web applications and websites.

















![Load Testing
ab - Apache HTTP server benchmarking tool
$ ab -n 1000 -c 5 http://www.inf.uth.gr
[...]
Requests per second: 0.59 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 1688.597 [ms] (mean)
[...]
... or Apache JMeter
... or httperf (HP labs)
... or OpenSTA (heavyweight tool)
... or even cloud services like Blitz.io (paid)
Τετάρτη, 11 Ιανουαρίου 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch-141204163553-conversion-gate02/85/Ch-x-web-performance-21-320.jpg)