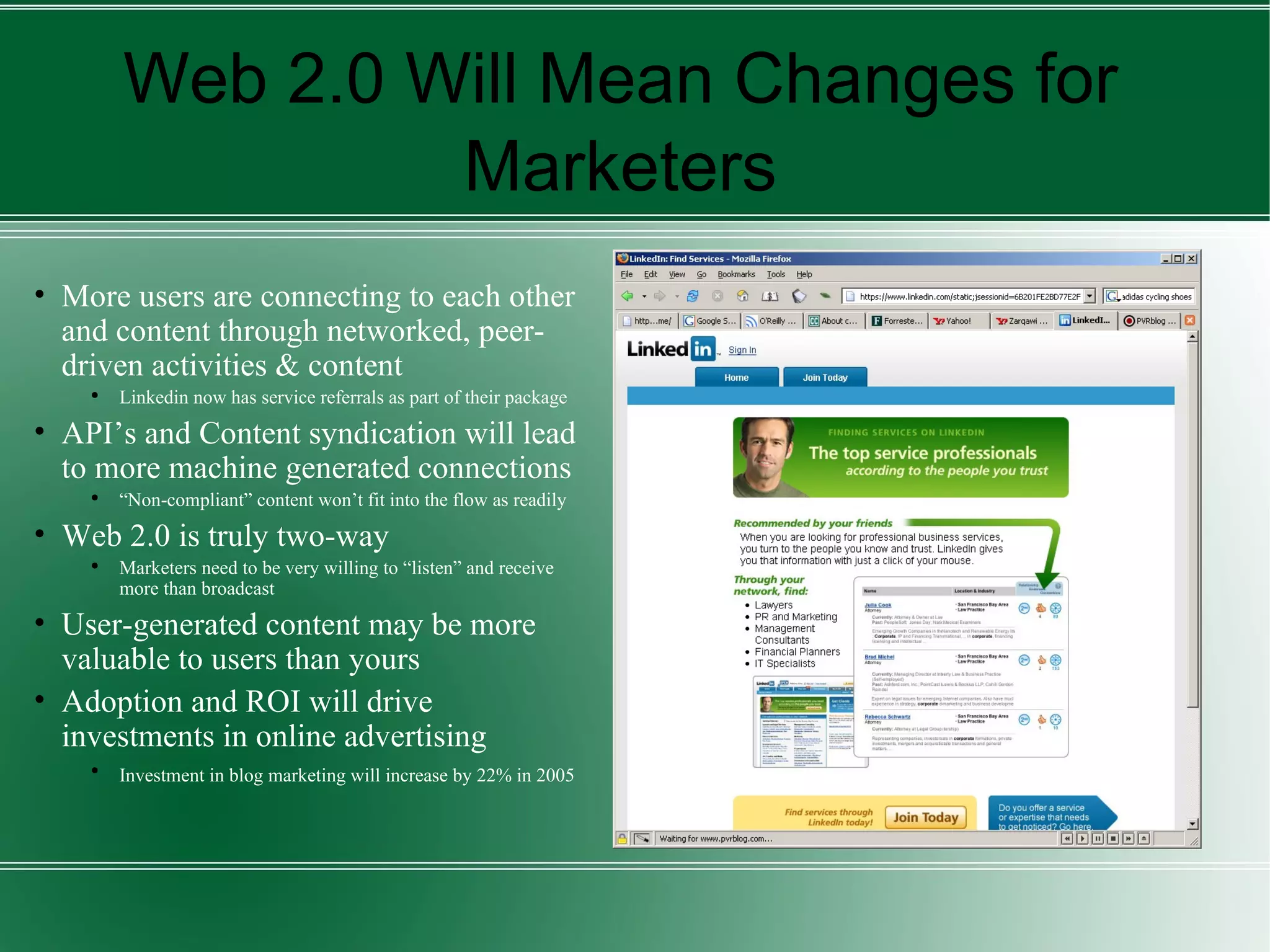
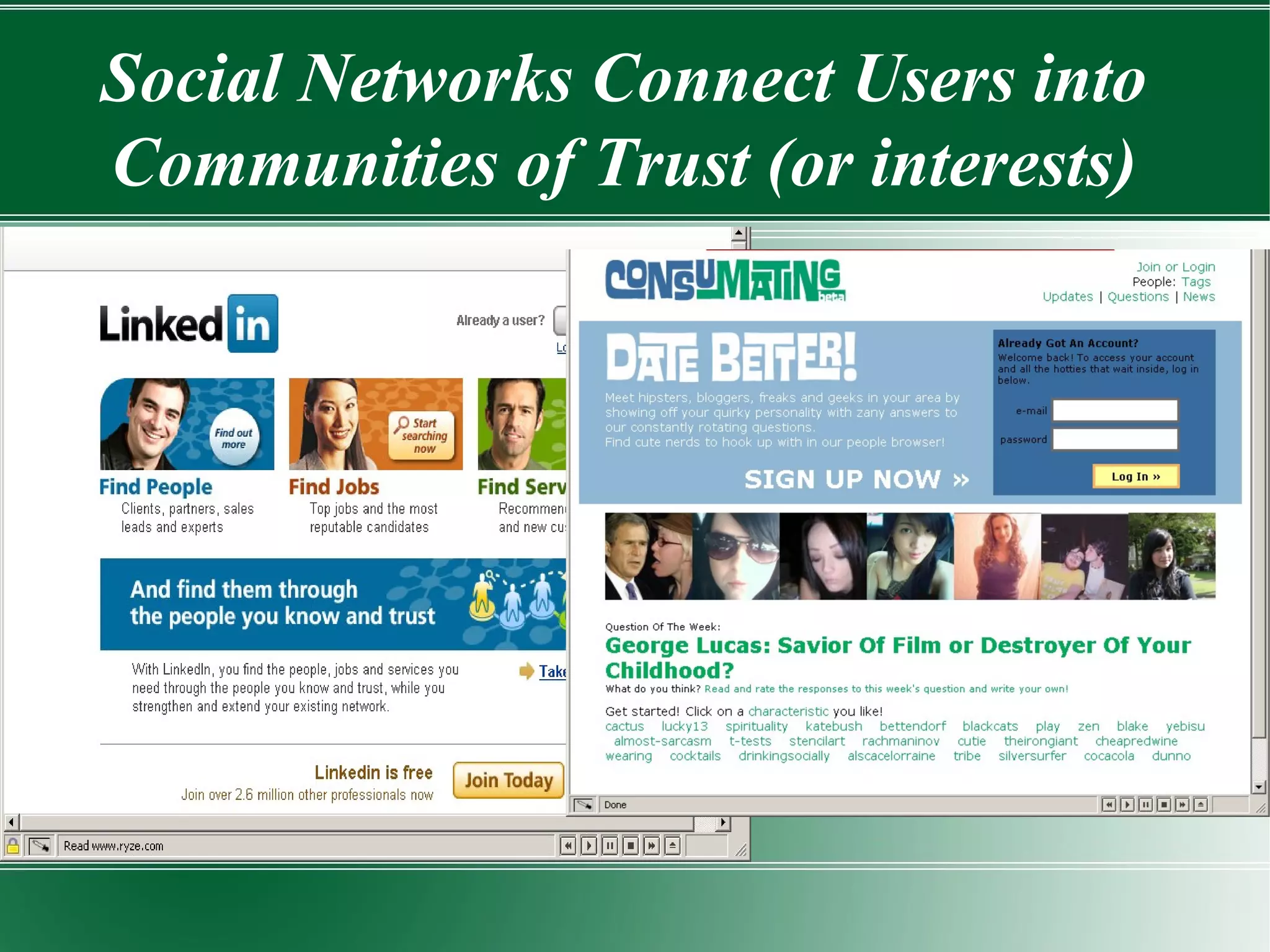
Web 2.0 represents the evolution of the internet into a more interactive and collaborative platform, characterized by user-generated content and social networking. It leverages technologies such as AJAX, mashups, and RSS, shifting from static web pages to dynamic web applications that engage users in real-time. However, while it offers opportunities for enhanced user engagement and community building, it also raises security challenges and requires effective content management strategies.