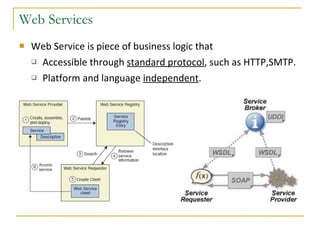
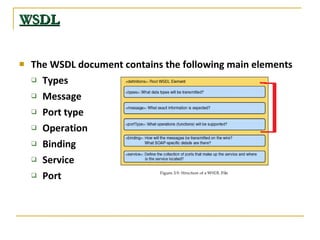
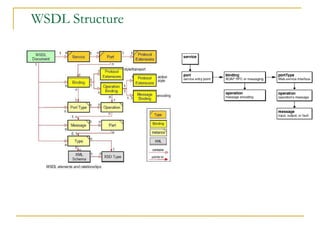
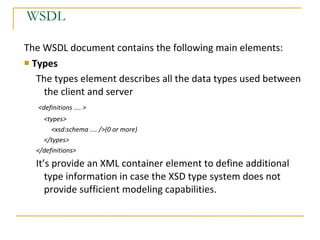
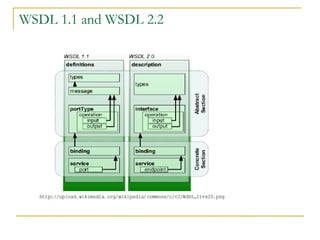
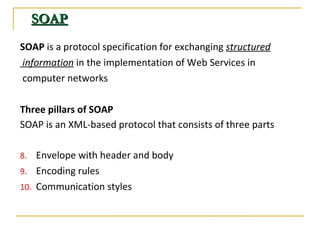
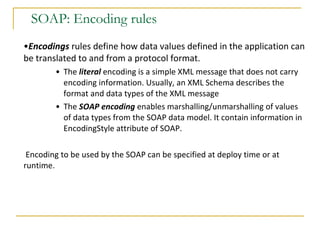
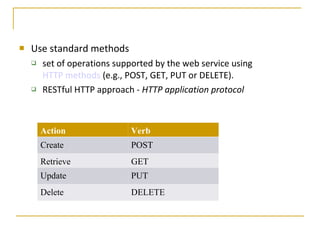
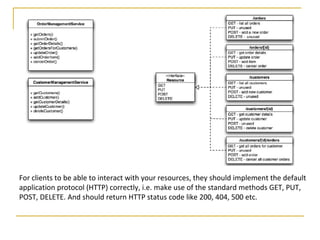
Web services allow for platform and language independent access to business logic through standard protocols like HTTP. Core technologies include XML, SOAP, WSDL, and UDDI. WSDL defines services using messages, port types, bindings and ports. SOAP is an XML-based protocol for exchanging structured data with envelopes containing headers and bodies. RESTful web services use standard HTTP methods to operate on resources identified by URIs in a stateless manner.