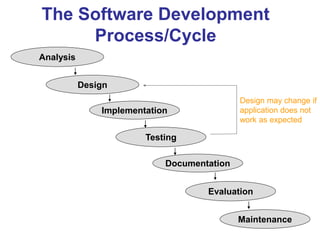
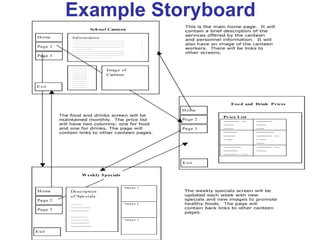
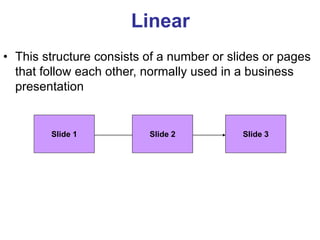
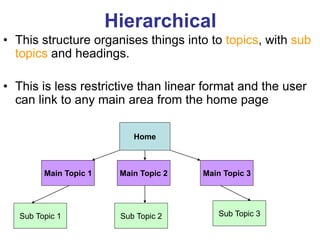
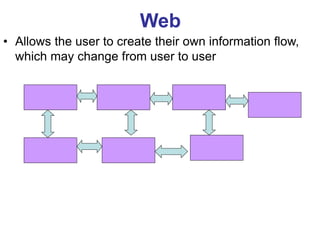
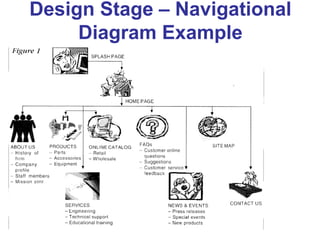
This document provides an overview of the website development process, including defining what a website is and what makes a good or bad website. It then discusses the typical software development process/cycle of analysis, design, implementation, testing, documentation, and evaluation. Each stage of the process is described in 1-2 sentences. The document includes examples of a storyboard and navigational diagrams to illustrate the design stage.