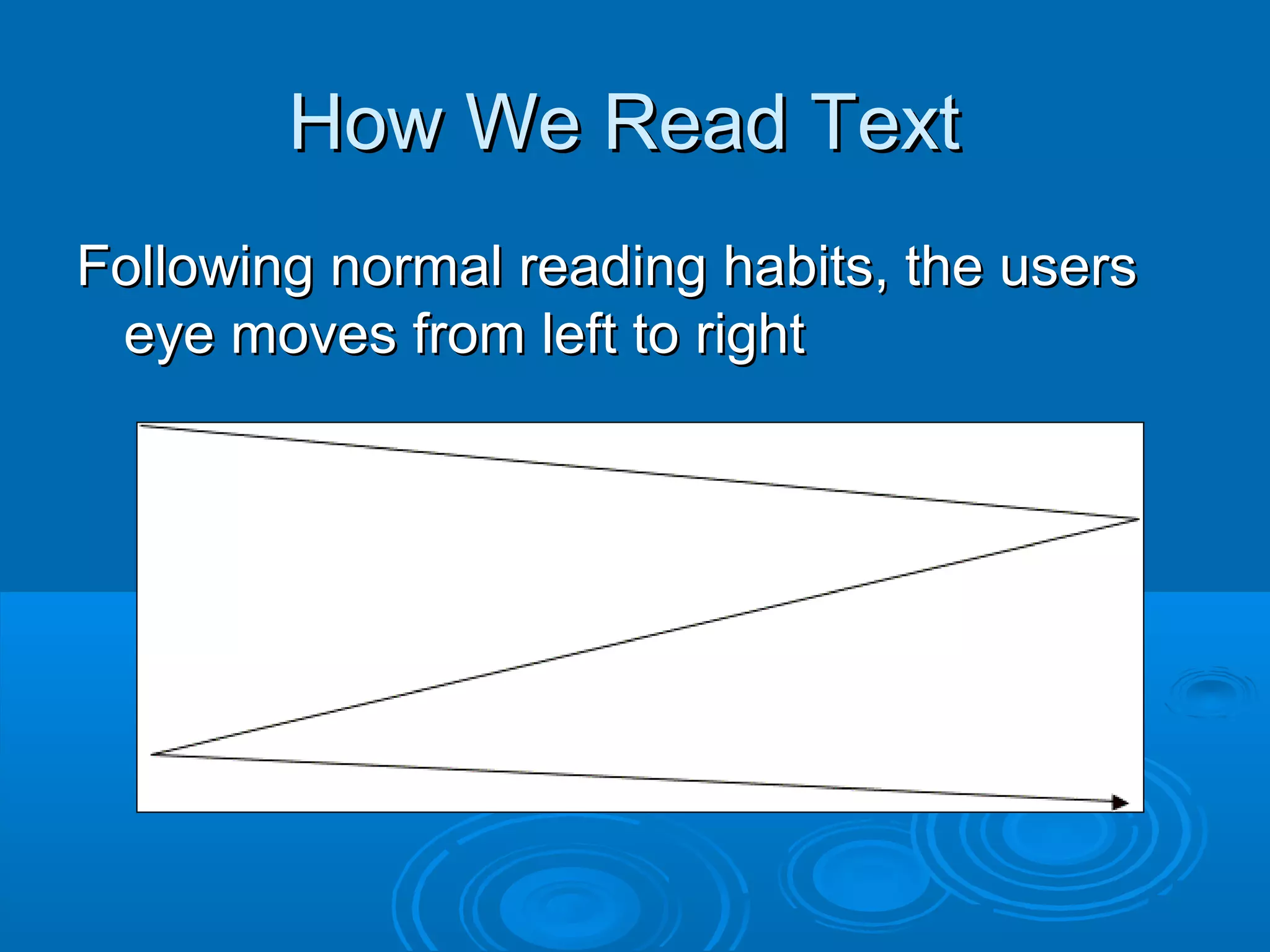
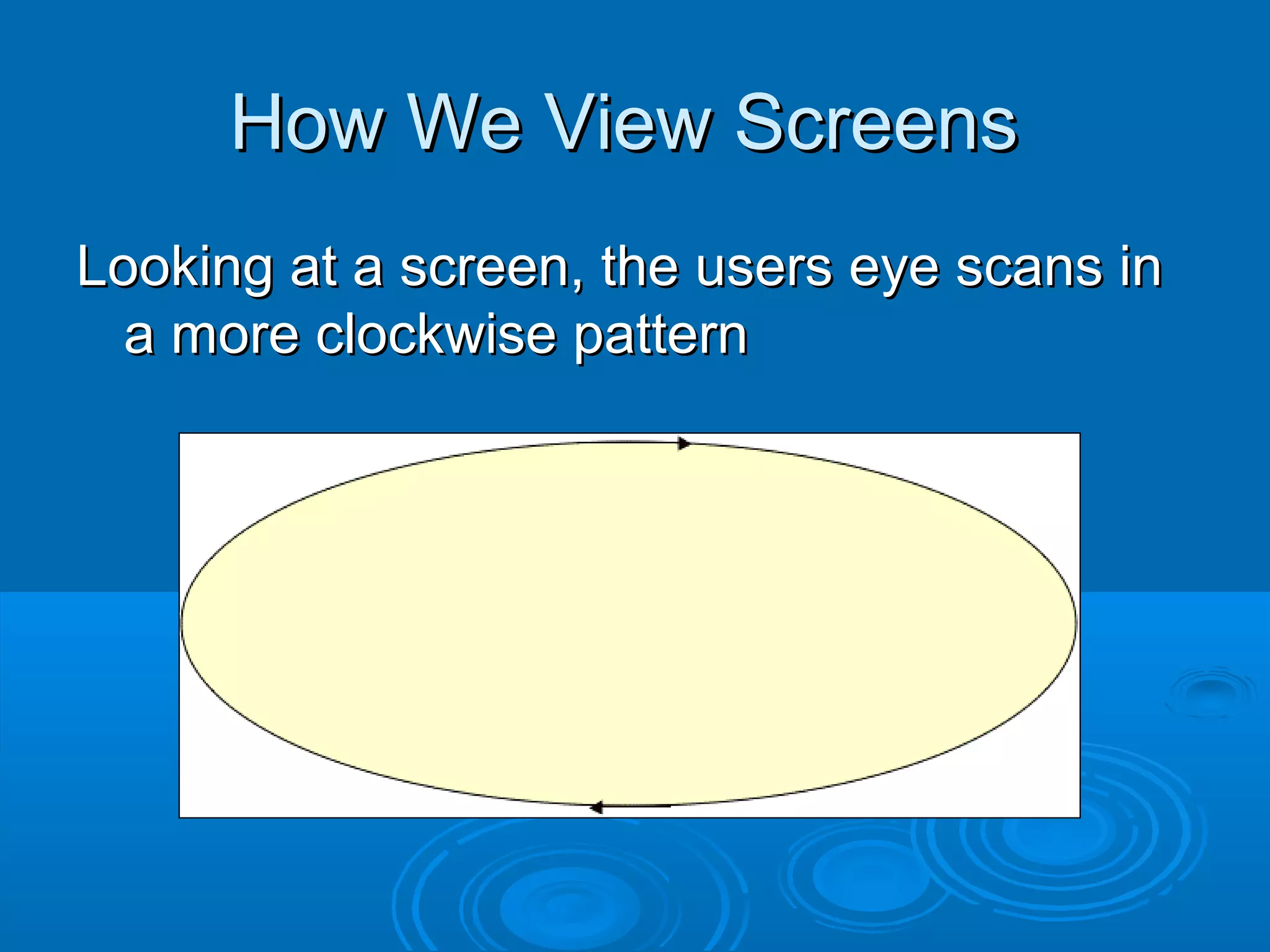
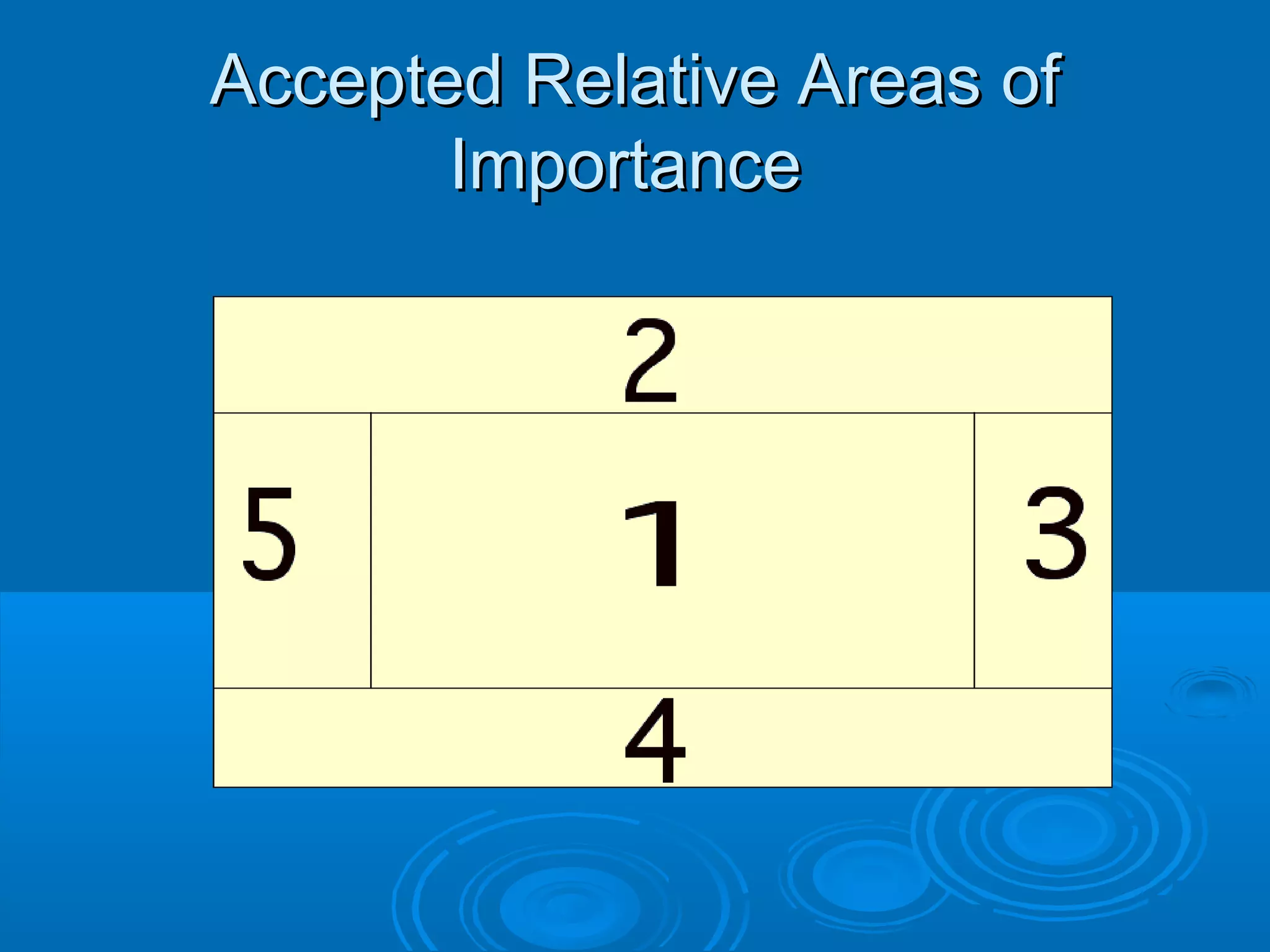
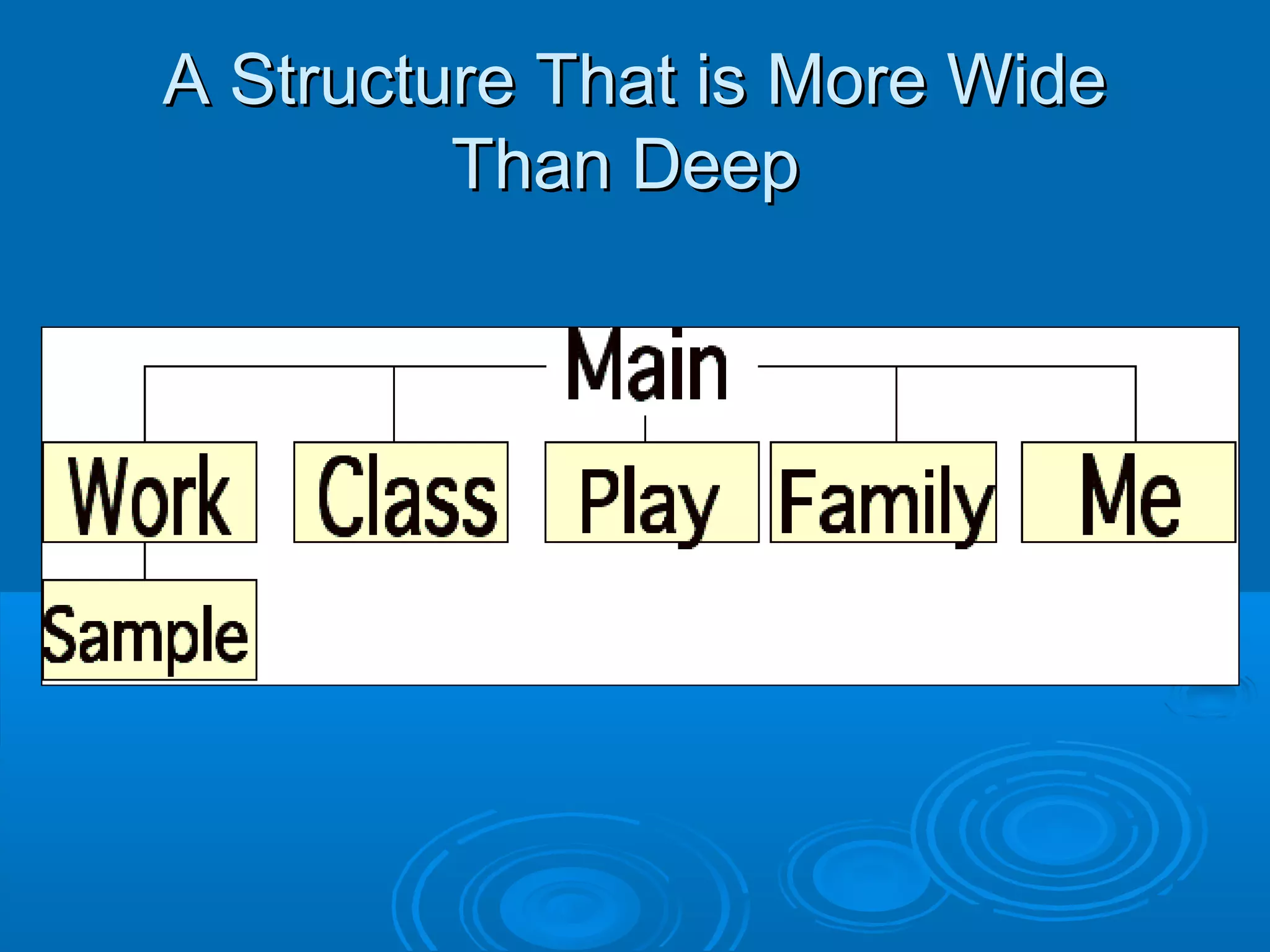
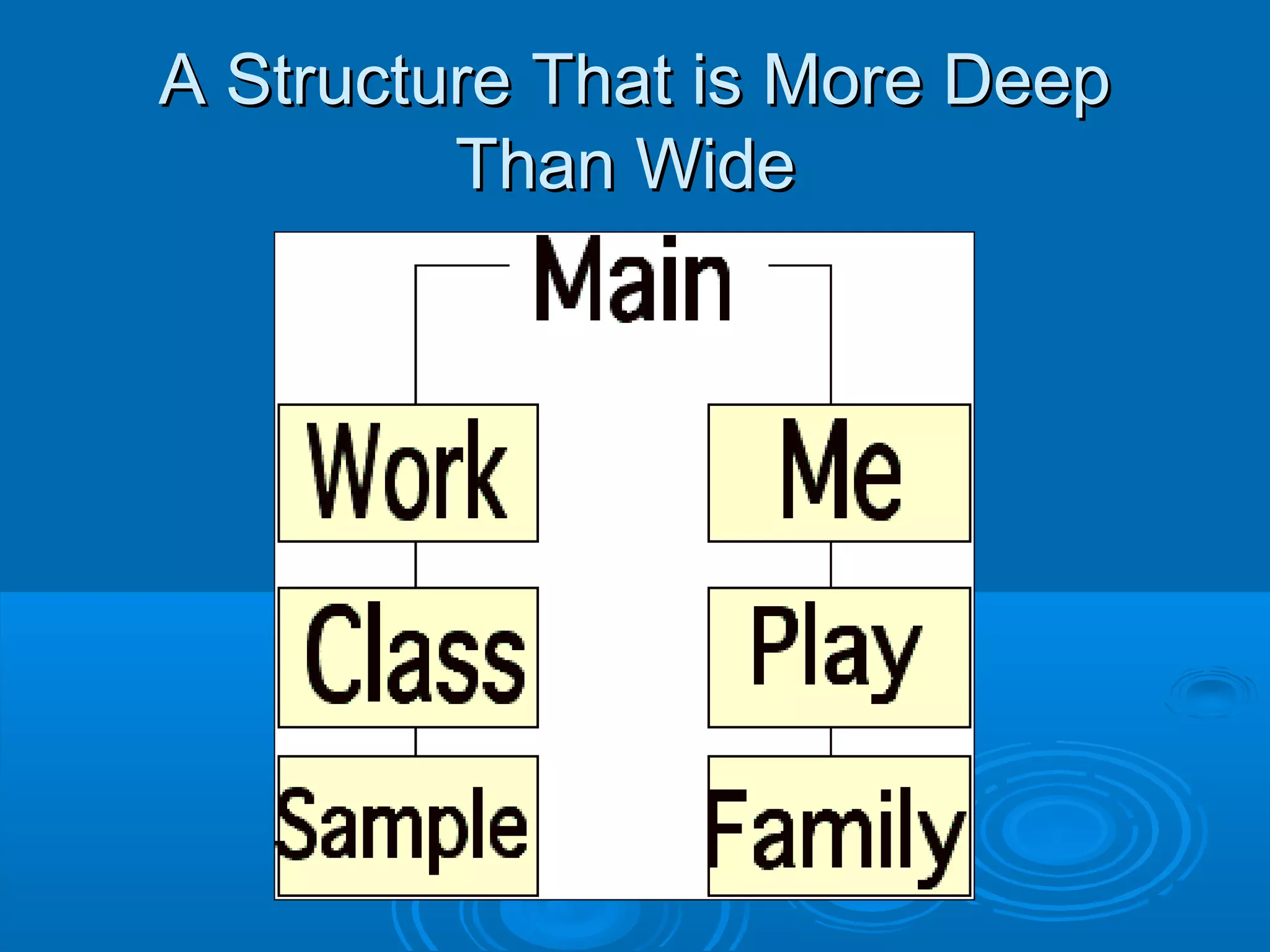
This document provides guidance on designing effective web pages. It discusses how to design for the computer medium by considering readability across different browsers and screens. It recommends planning page hierarchy by determining how pages are linked and where users will navigate next. The document also offers tips on designing content, such as naming files logically, using consistent design, and avoiding excessive scrolling. Overall, it outlines important steps and best practices for web page design.