This document summarizes key concepts about weathering and soil formation:
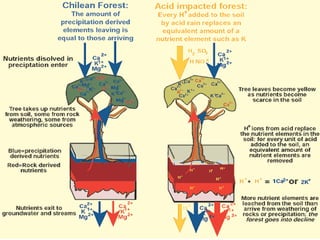
1. Weathering is the process that breaks down rock into smaller fragments through mechanical and chemical processes. Chemical weathering causes chemical changes through reactions with water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, living organisms, and acid rain. Mechanical weathering breaks rock into pieces through processes like freezing and thawing.
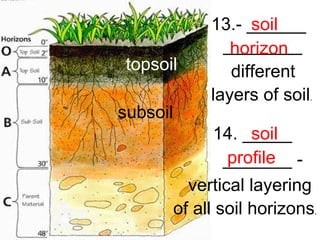
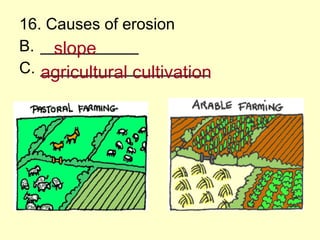
2. Soil is formed over long periods of time as weathered rock and organic matter accumulate and layer. Factors like climate, vegetation, rock type, slope, and time influence soil formation.
3. Soil conservation techniques help reduce erosion, including contour plowing, terracing, crop rotation, shelter belts, proper grazing, no