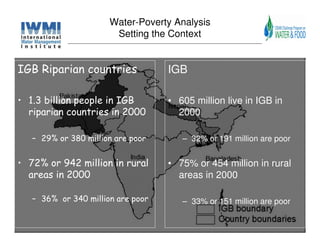
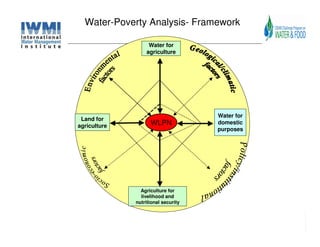
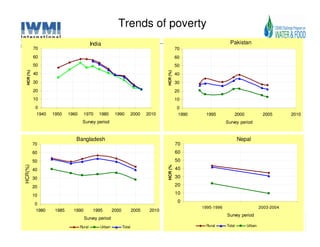
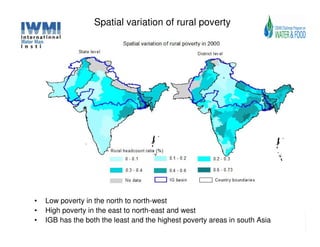
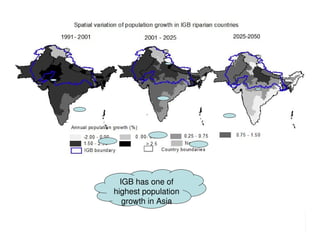
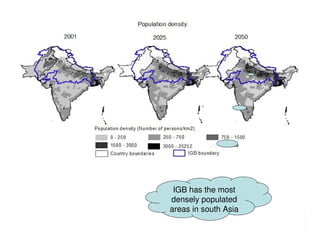
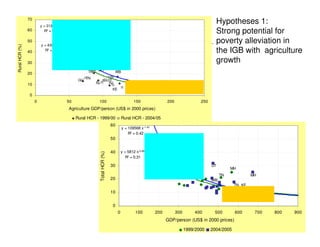
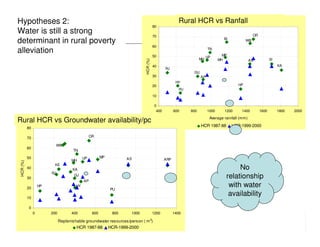
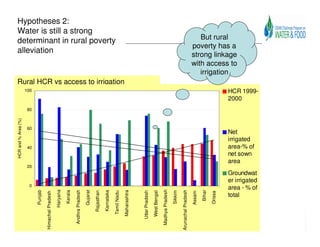
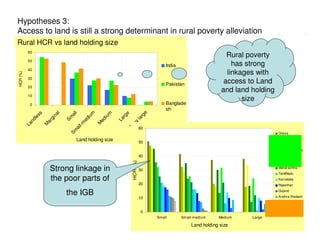
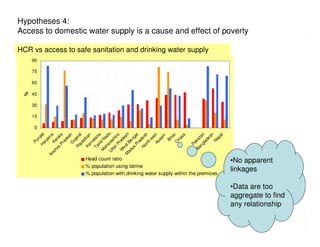
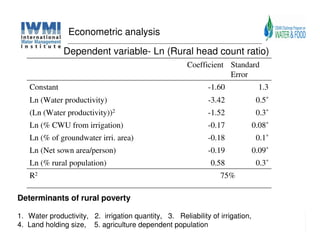
The document analyzes water poverty in the IGB basin, where 1.3 billion people are affected, with significant rural poverty linked to inadequate access to water and land resources. Objectives include mapping sub-national poverty, identifying determinants related to water-land-poverty, and exploring coping mechanisms of affected communities. Ongoing efforts encompass literature synthesis, poverty mapping, and econometric analyses to understand the complex interrelations between agriculture, water resources, and poverty alleviation strategies.