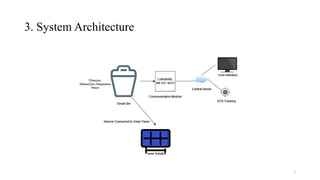
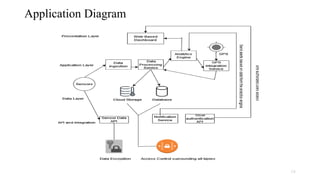
The document outlines the development of a smart waste management system utilizing IoT technology to address issues like waste overflow, high operational costs, and public health concerns. It details objectives such as timely waste disposal and data analysis, along with an implementation plan, budget estimation, and ongoing maintenance strategies. The integration of IoT sensors is expected to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and promote environmental sustainability.