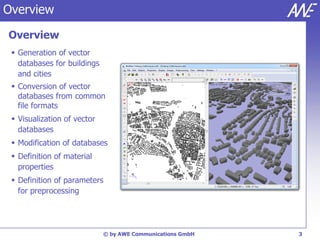
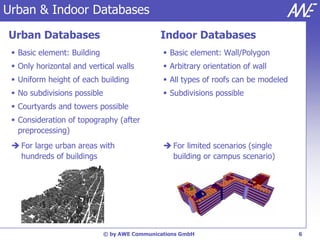
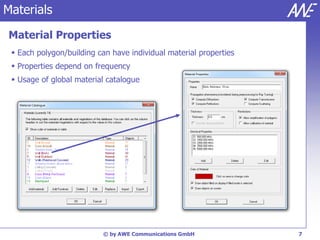
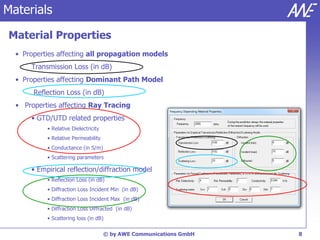
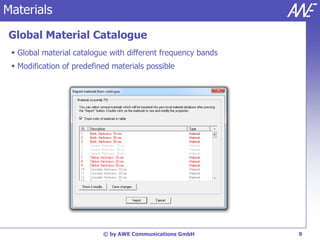
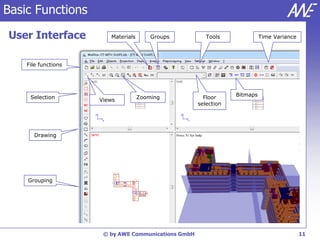
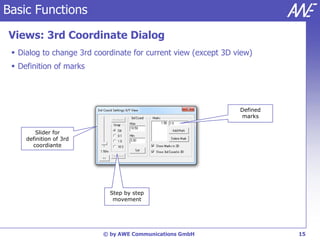
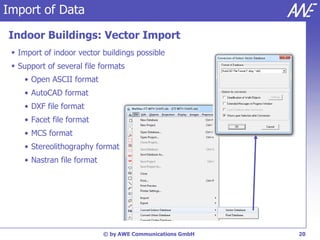
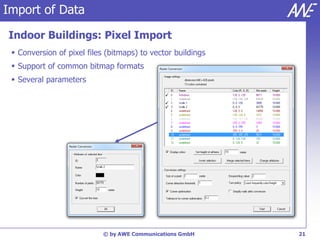
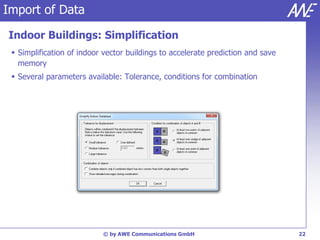
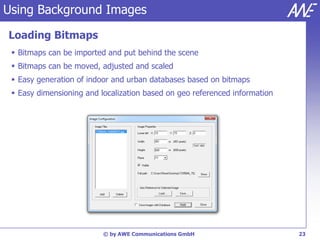
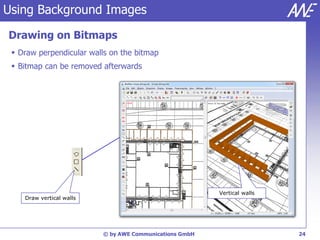
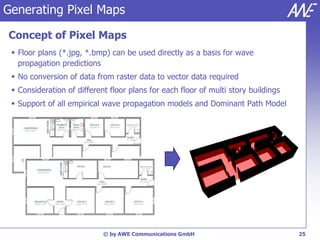
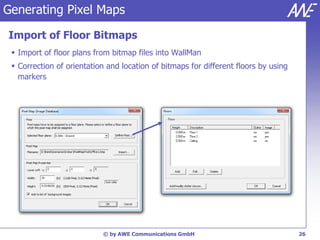
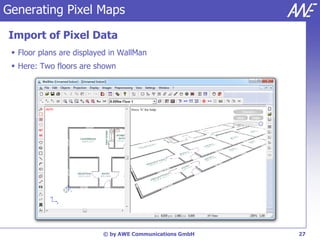
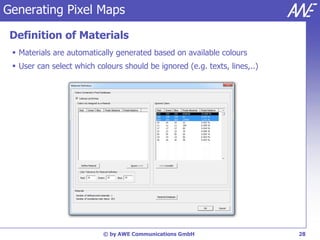
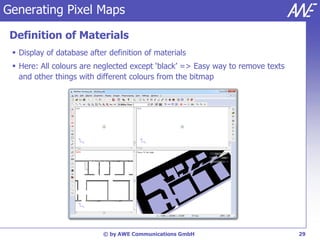
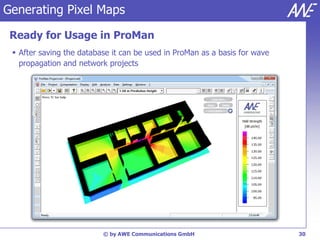
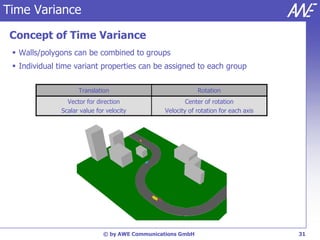
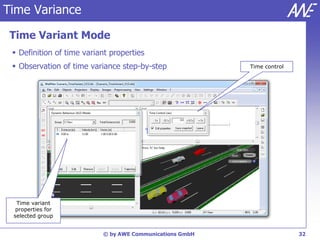
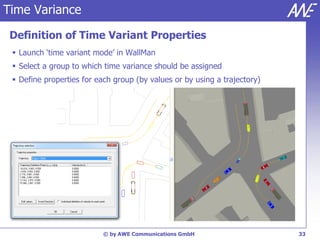
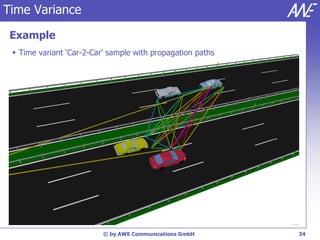
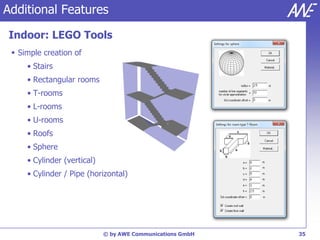
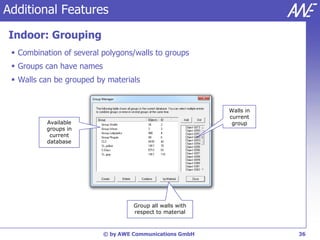
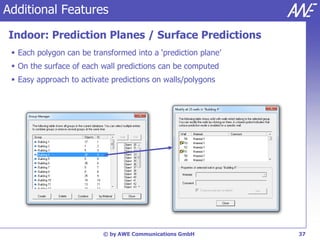
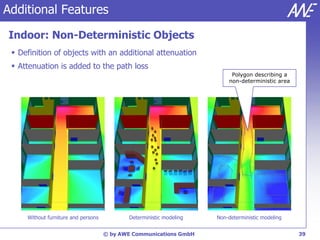
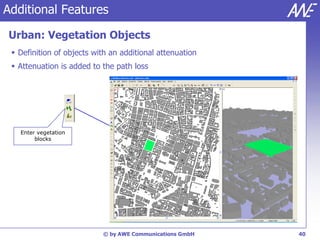
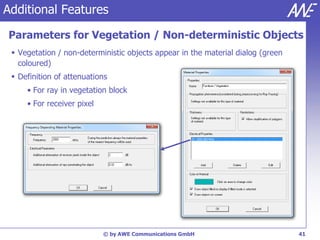
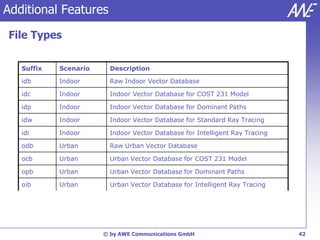
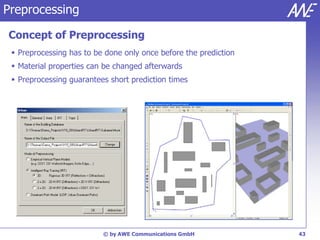
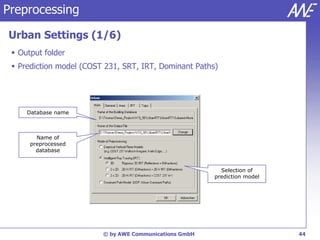
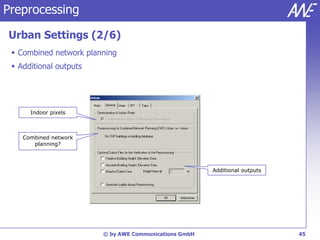
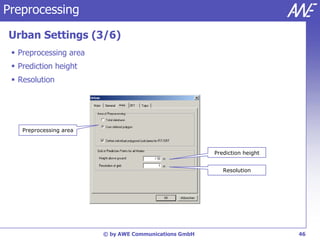
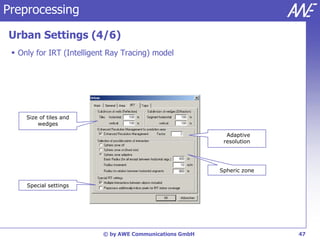
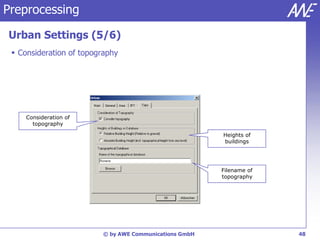
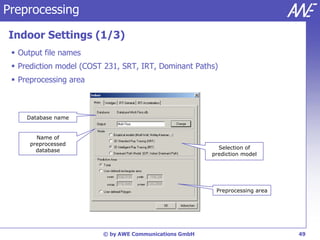
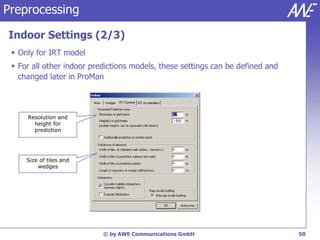
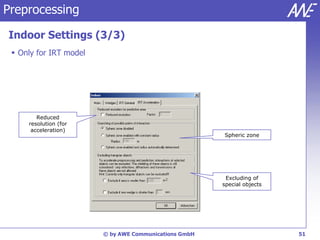
The document describes the WallMan software for generating and editing 3D vector databases of indoor and urban environments. It allows the import of common file formats, definition of material properties, and preprocessing of data. Key features include generation of databases from background images, working with pixel maps directly for propagation predictions, and time variance modeling.