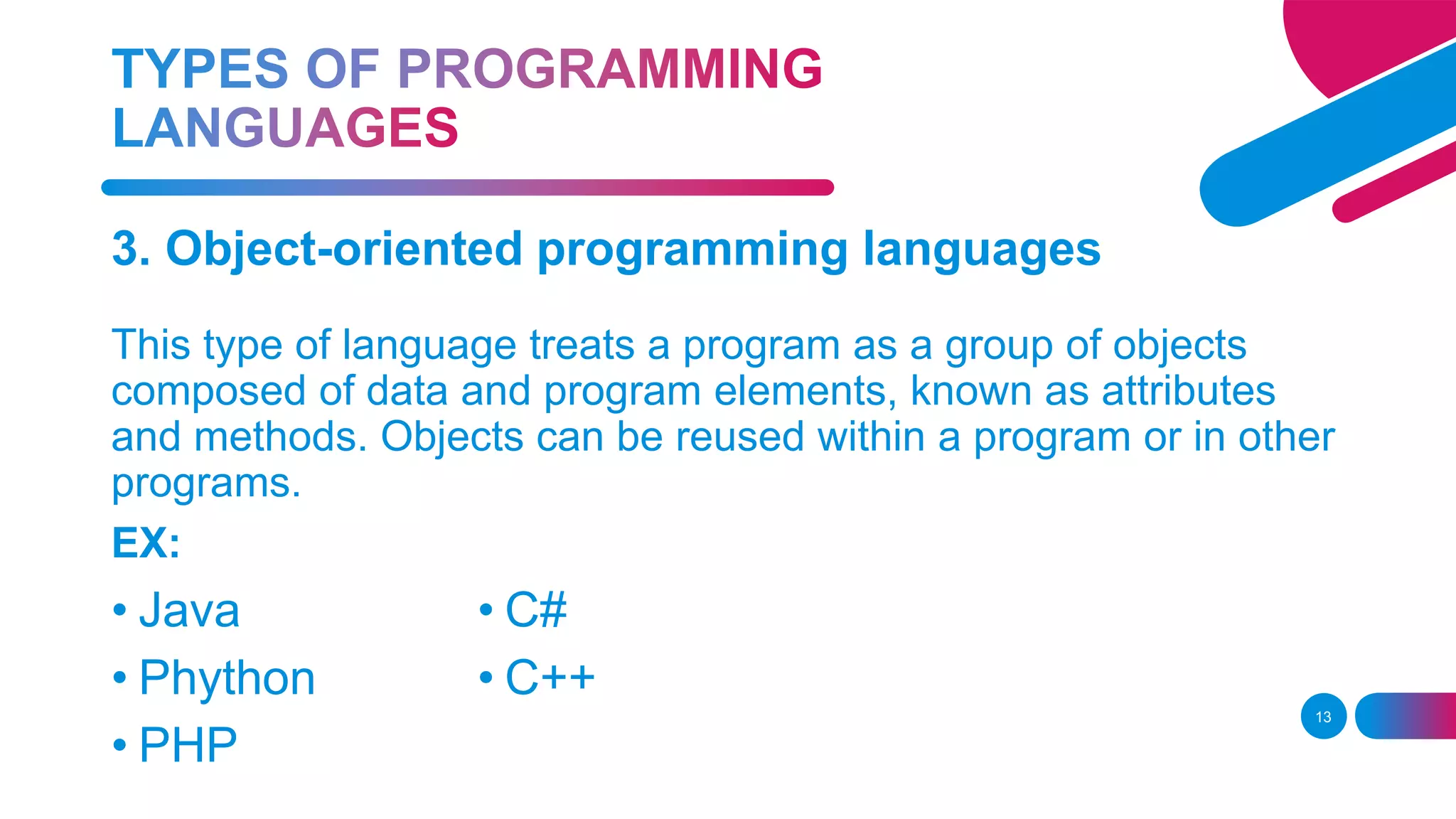
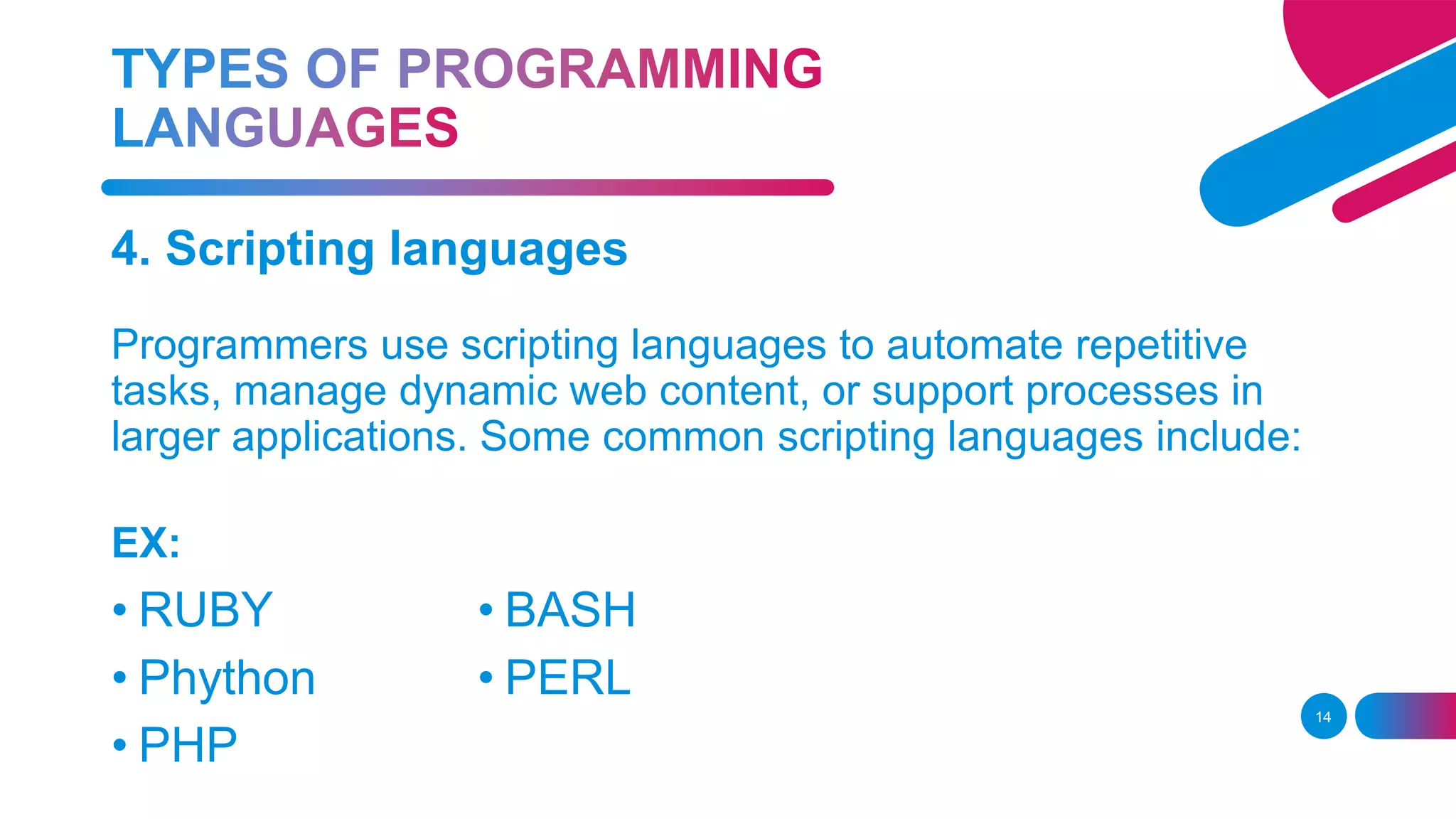
Visual Basic is an event-driven programming language and environment from Microsoft that provides a graphical user interface (GUI) which allows programmers to modify code by simply dragging and dropping objects and defining their behavior and appearance. The document discusses programming languages, including procedural languages like C and C++, functional languages like Haskell, object-oriented languages like Java and C++, scripting languages like PHP and Python, and logic programming languages like Prolog. It also defines key terms like applications, class, coding, computer programs, debugging, IDE, instance, object, object-oriented programming language, and user interface.