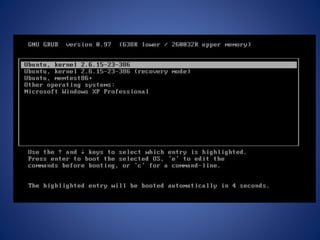
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on the same hardware. It saves money by improving hardware utilization. A virtual machine uses software to simulate a physical computing system with its own virtualized hardware resources, like memory, storage, and network interfaces. There are two main types of hypervisors - Type 1 hypervisors run directly on the hardware while Type 2 hypervisors run within a conventional operating system environment. Virtualization provides benefits like server consolidation, easier development and testing environments, and cloud computing capabilities.