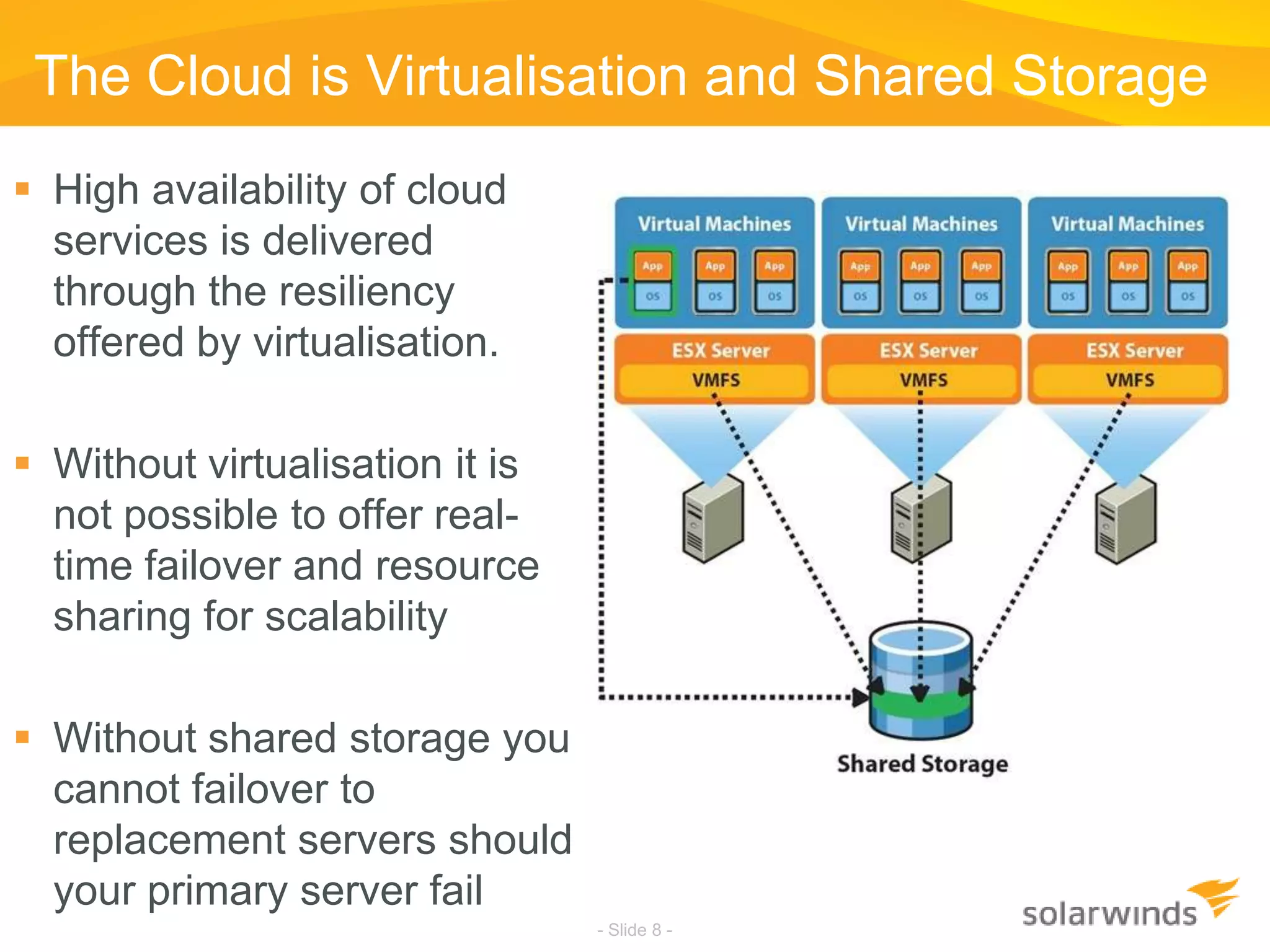
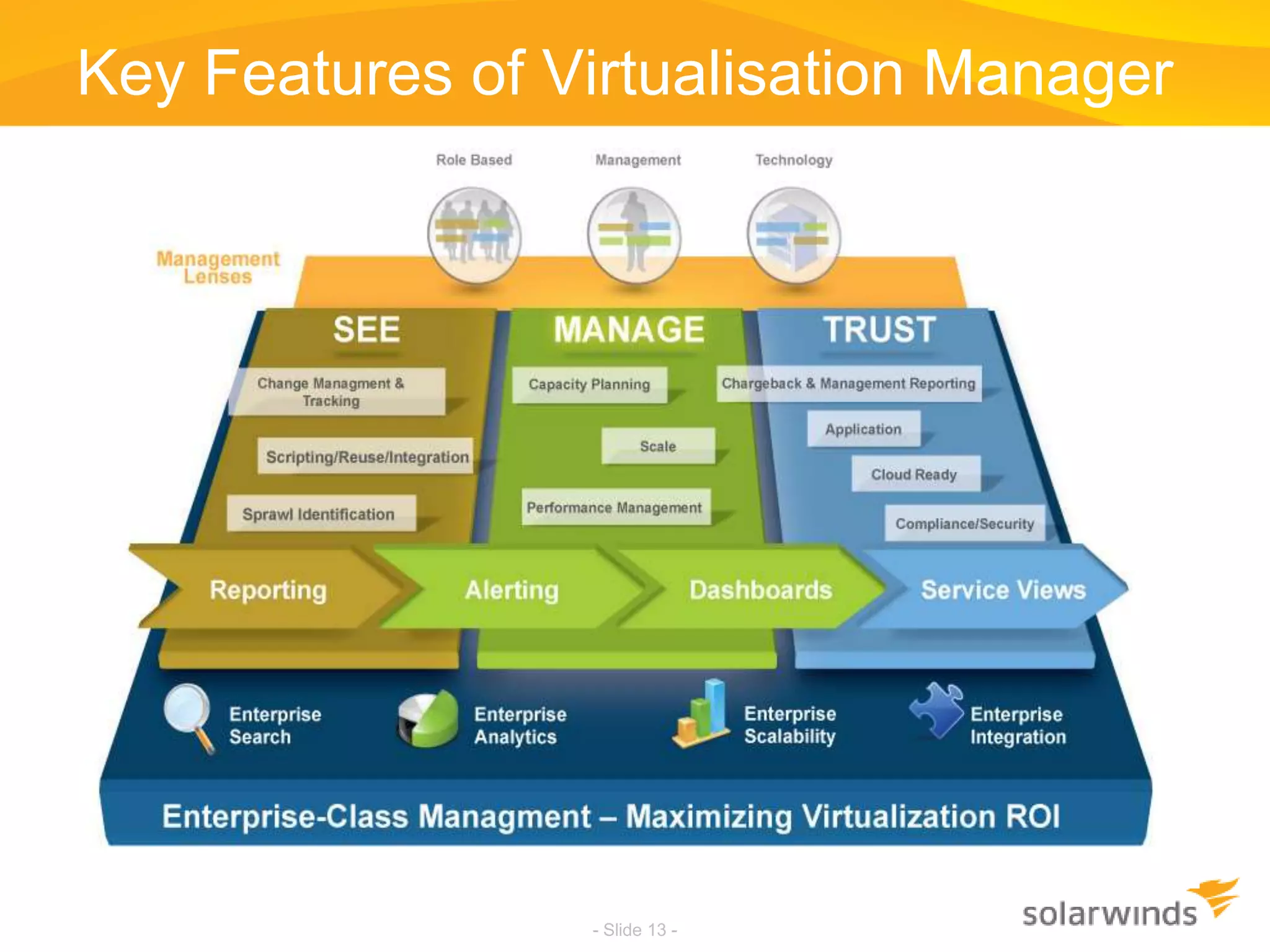
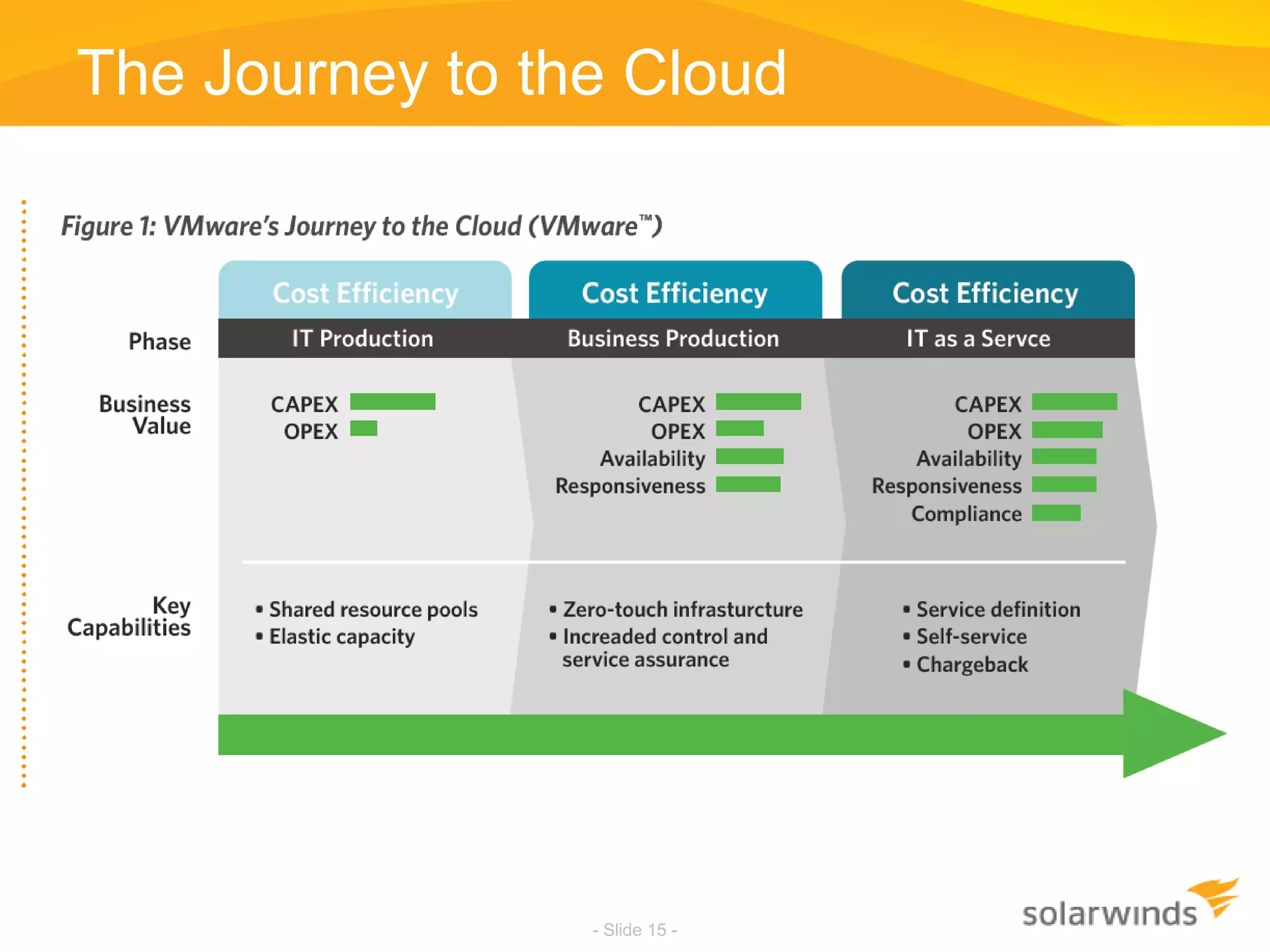
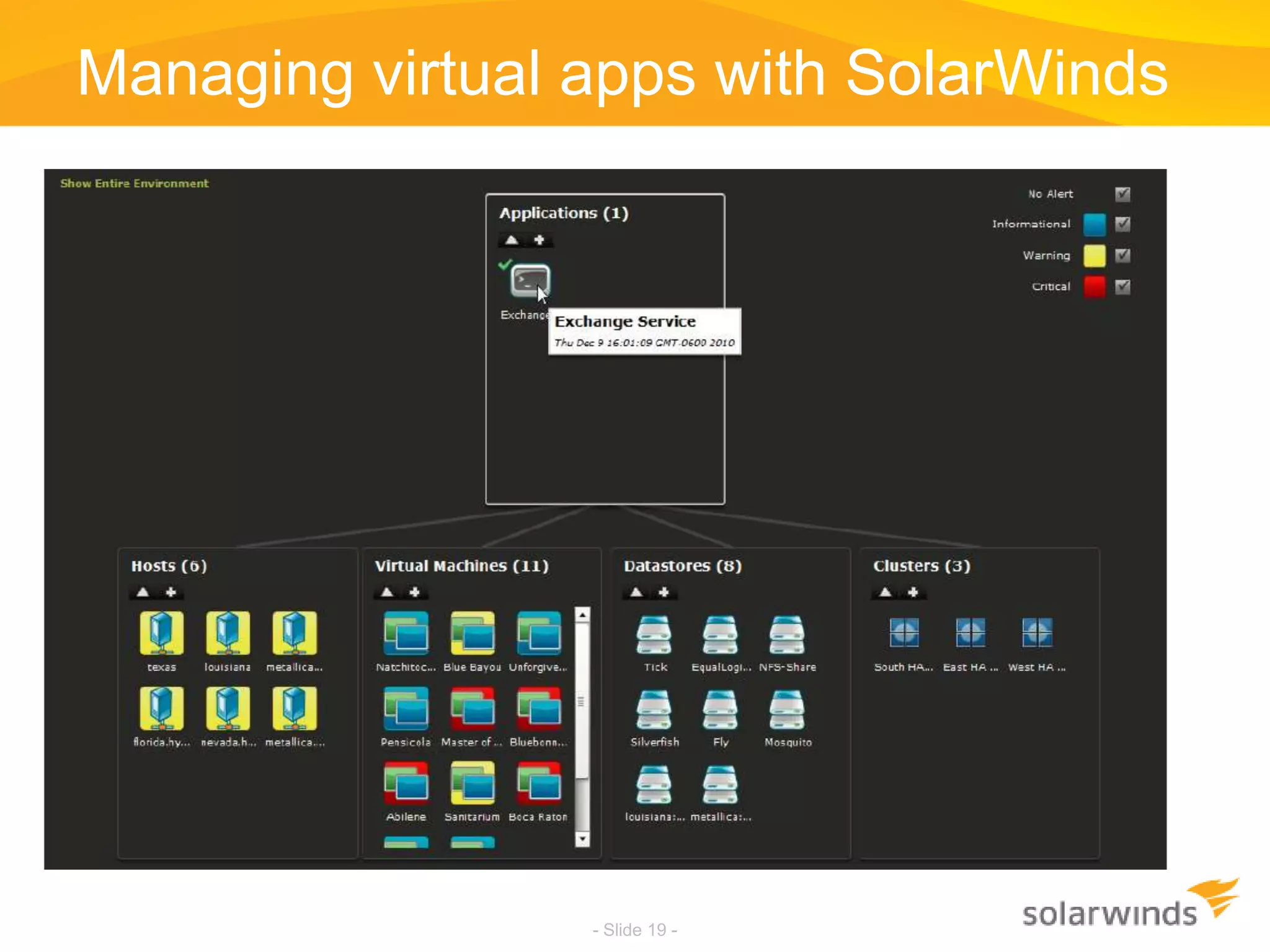
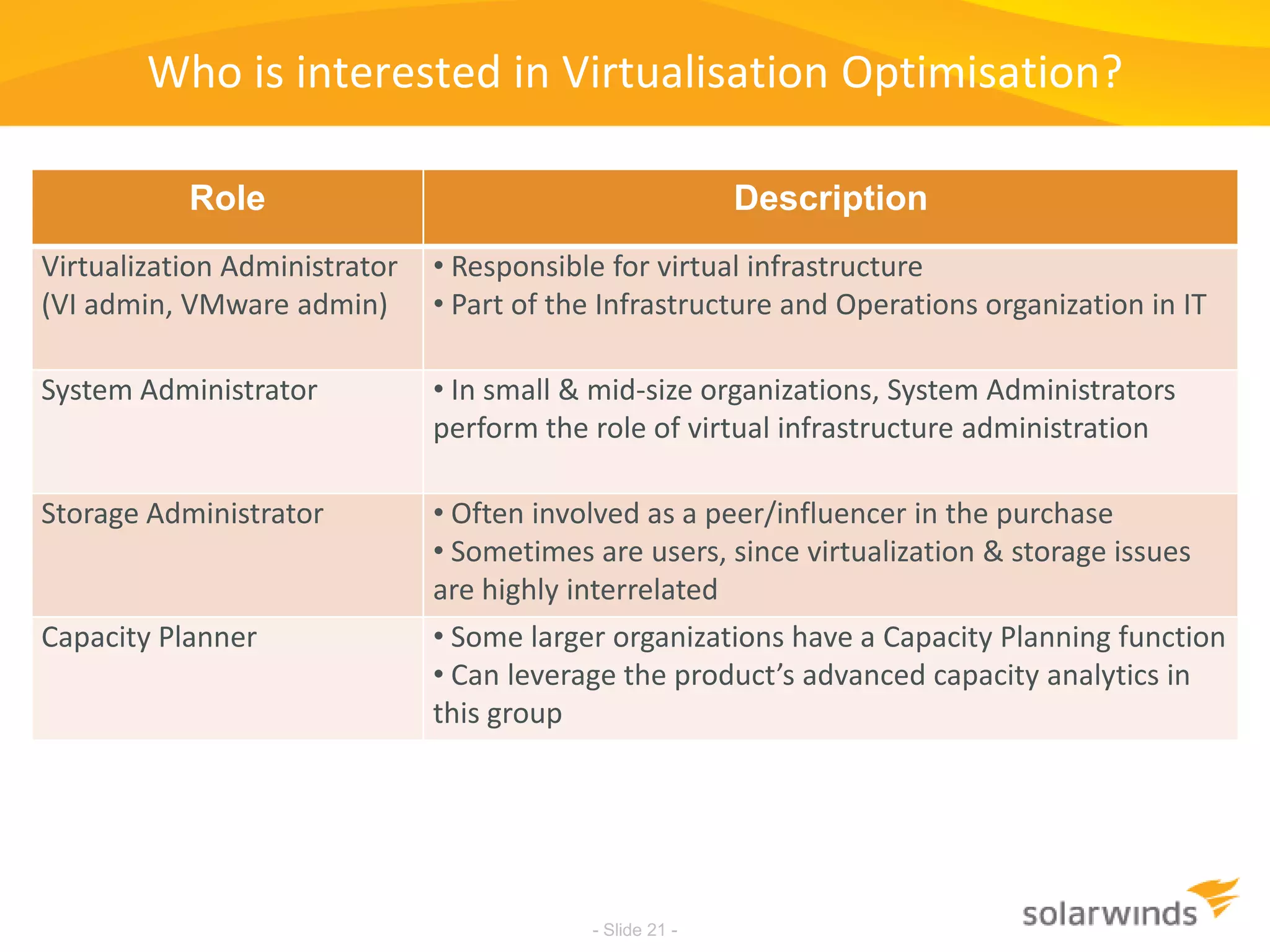
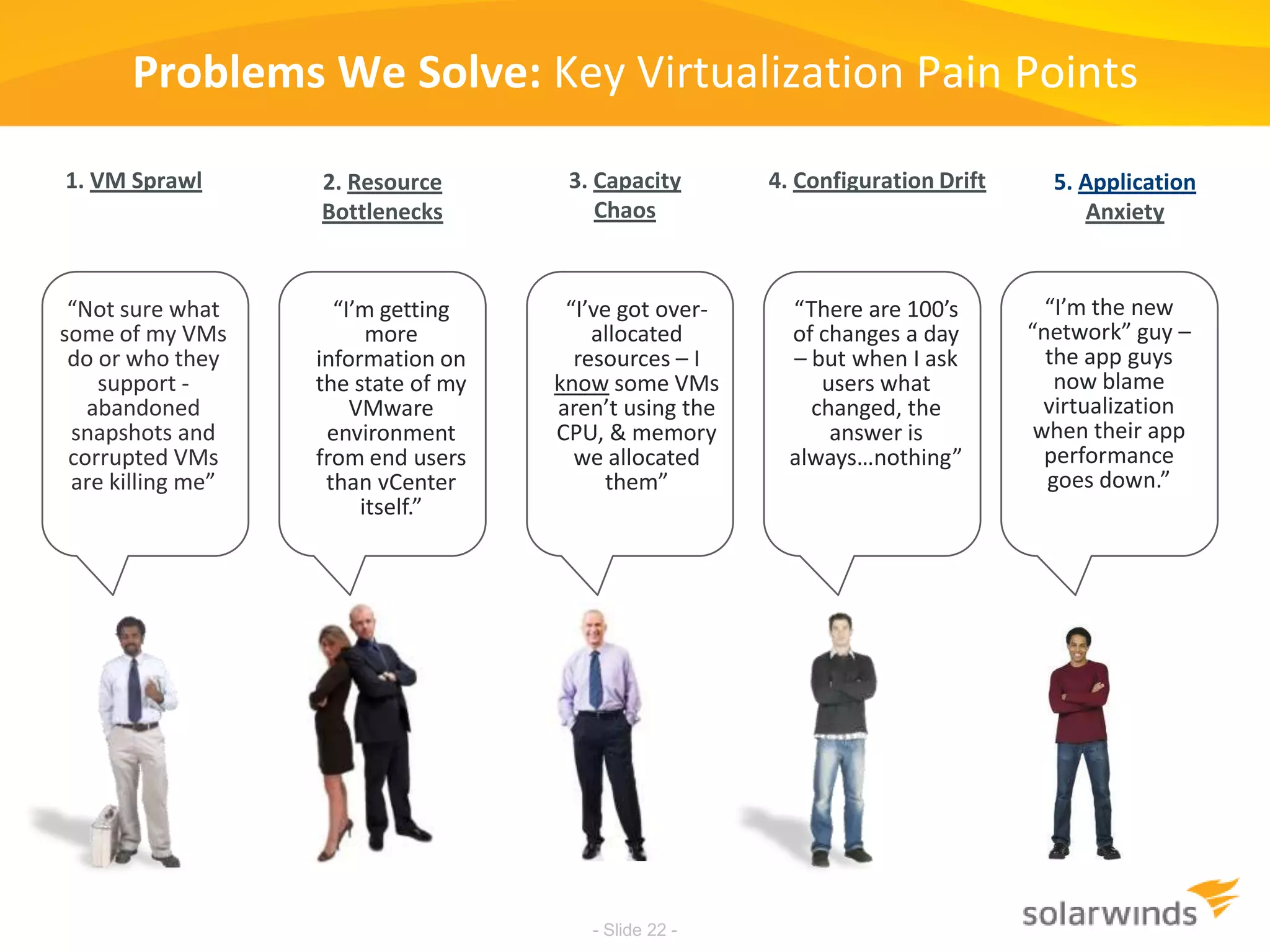
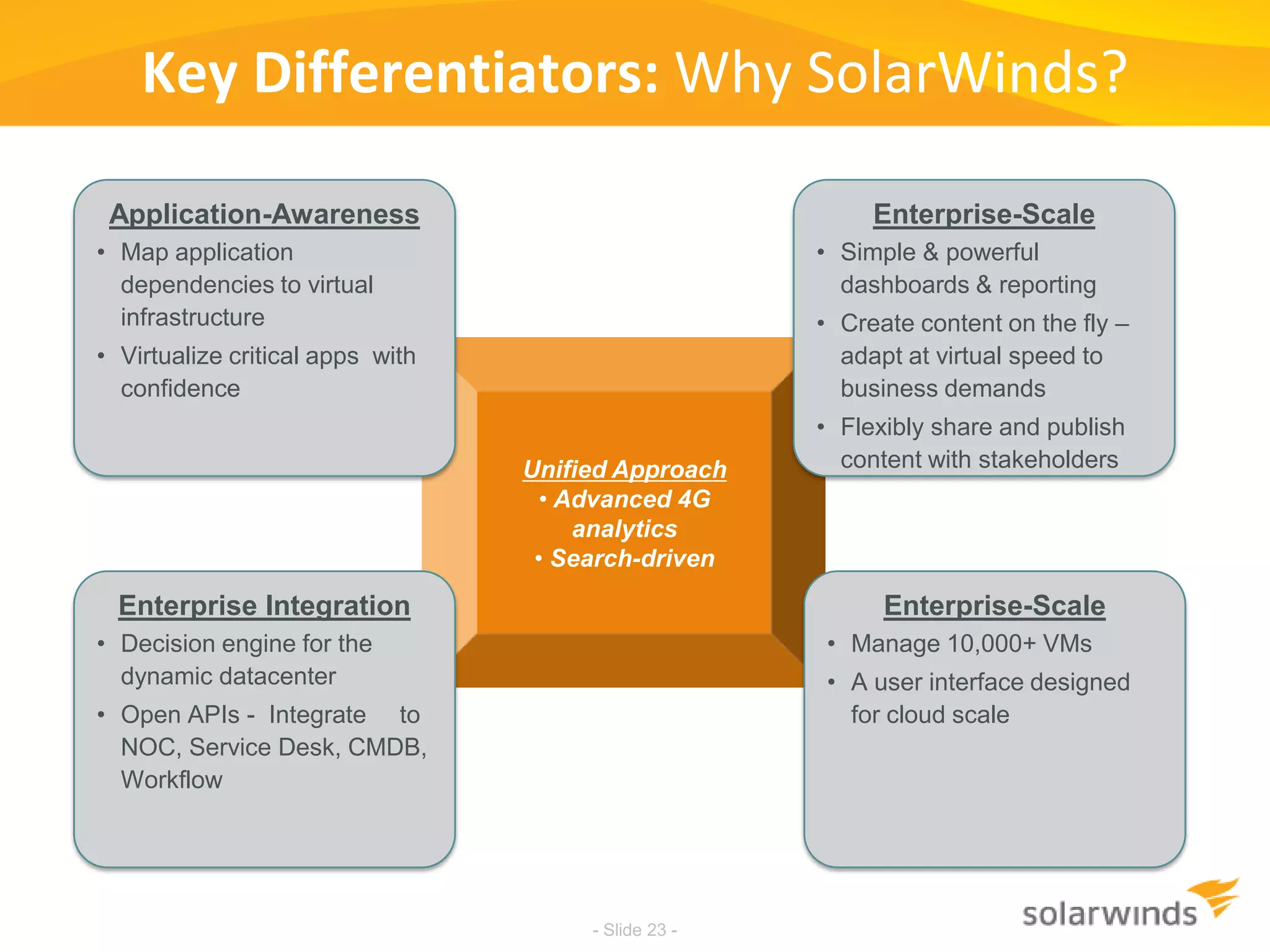
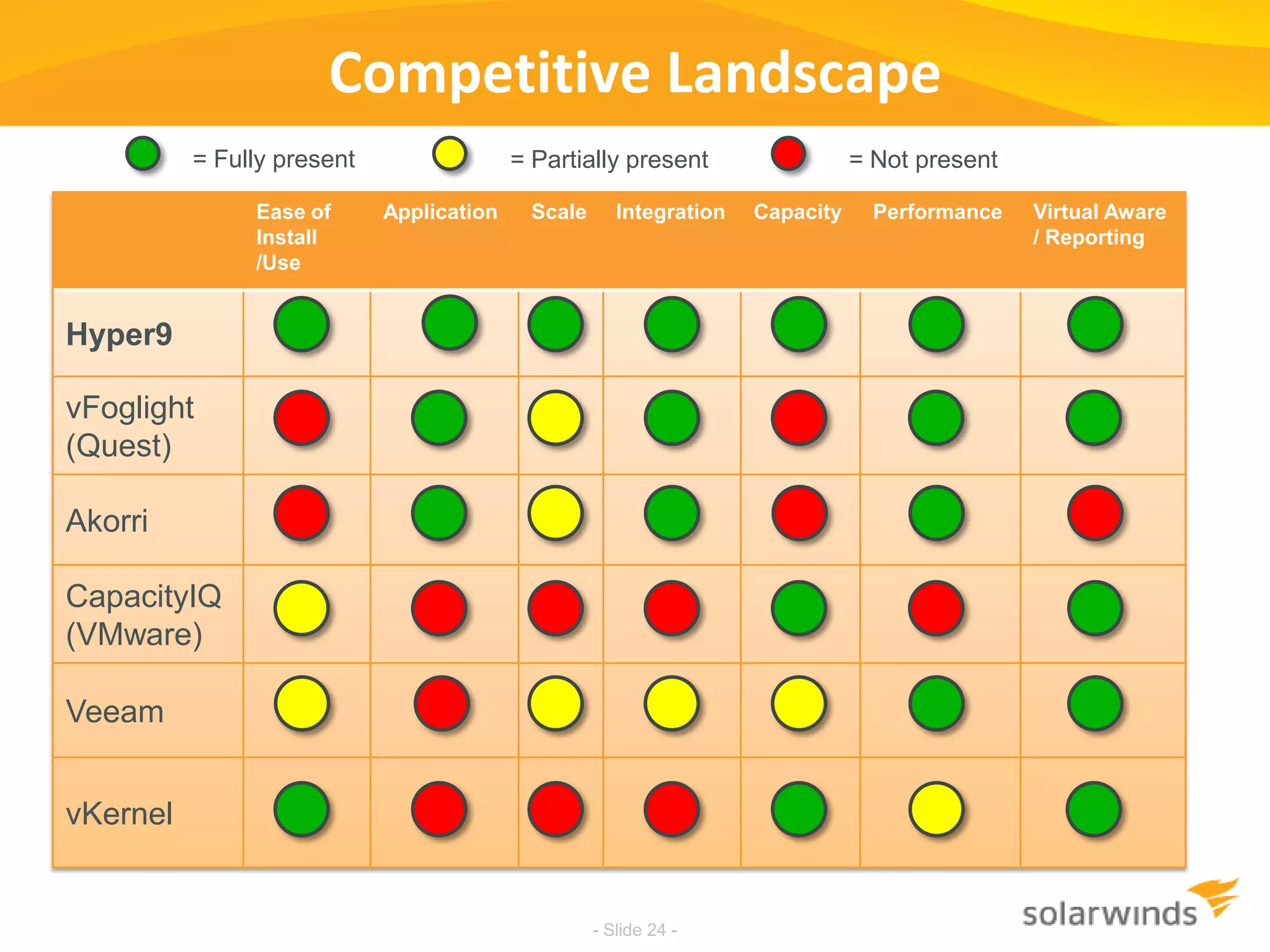
This document discusses virtualization and cloud computing. It begins by defining virtualization and describing its growth. It then discusses the benefits of virtualization like reduced costs and improved availability. The document notes that while virtualization adoption is growing, only about 18% of workloads have been virtualized. It introduces the SolarWinds Virtualization Manager product and describes how it can help organizations optimize their virtualized and cloud environments by addressing issues around visibility, capacity planning, and chargeback across three phases of cloud maturity. Key features and how it compares to competitors are outlined. In the end, the presentation argues SolarWinds Virtualization Manager is better suited than other products to manage end user environments cost-effectively.