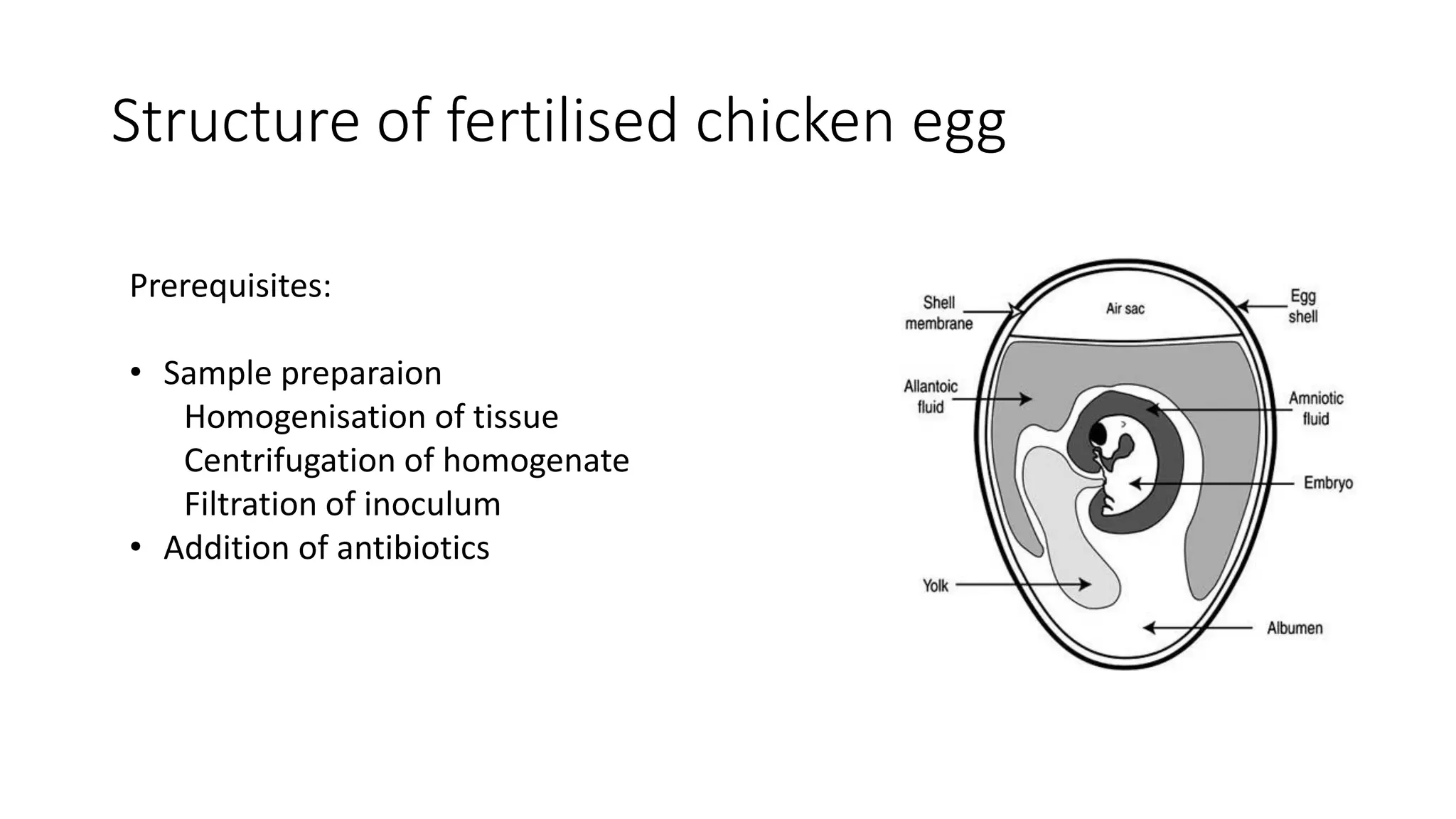
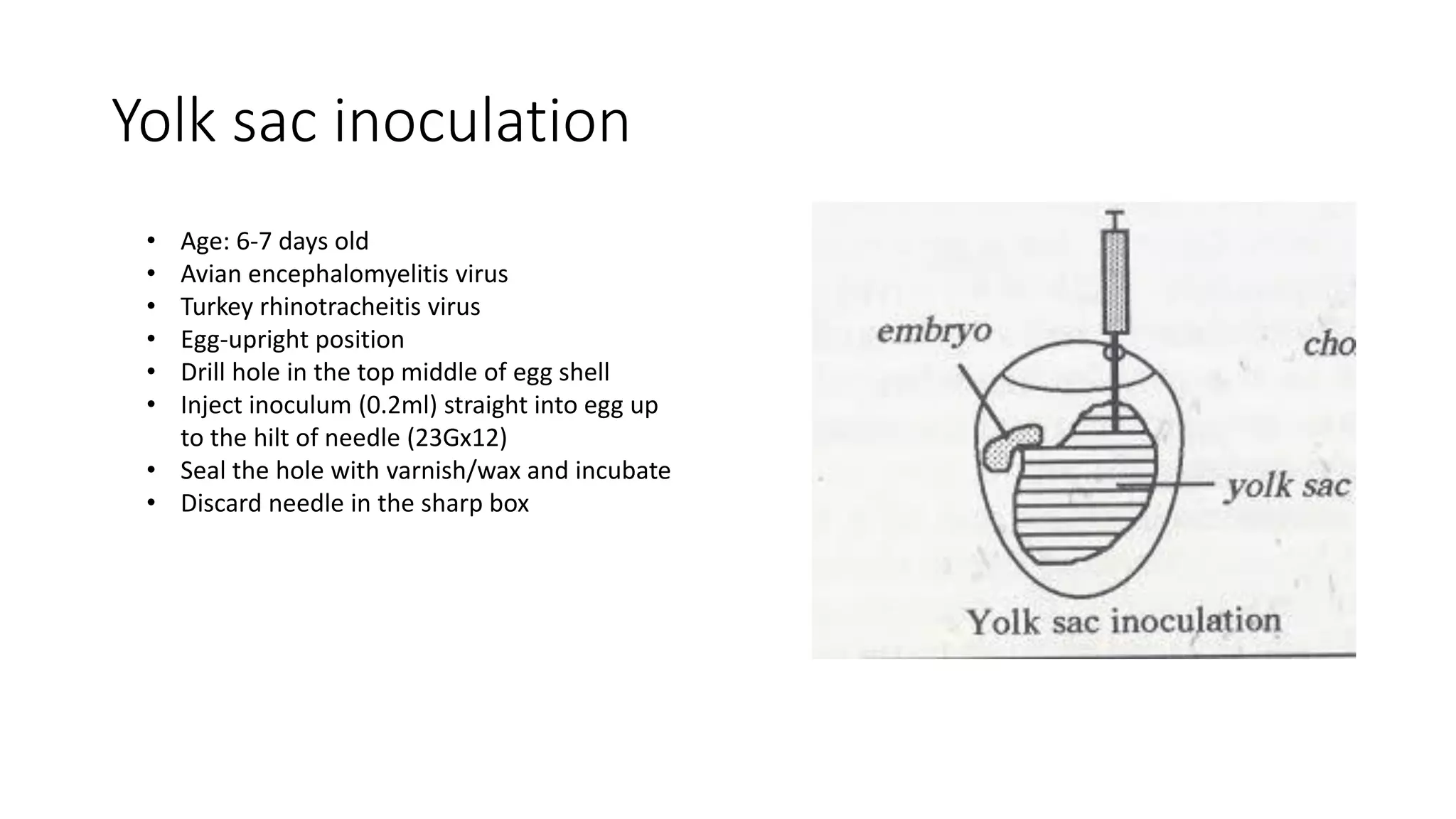
This document discusses viral inoculation methods using embryonated eggs. It provides advantages of using eggs such as their ability to isolate and cultivate avian and some mammalian viruses. It also discusses important considerations for the source of eggs including using specific pathogen free flocks to minimize risks. Different routes for inoculating viruses into eggs are described, including allantoic sac, chorioallantoic membrane, and yolk sac routes. Tools, procedures, and incubation conditions for successful egg inoculation are outlined.