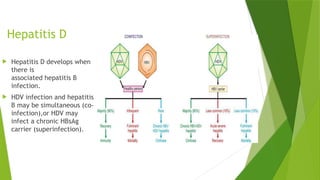
The document discusses viral hepatitis, detailing five main types caused by specific viruses: A, B, C, D, and E, each with distinct modes of transmission, incubation periods, and clinical implications. Hepatitis A primarily spreads through the faeco-oral route and is generally self-limiting, while Hepatitis B and C can lead to chronic conditions and severe liver damage. Hepatitis D occurs in conjunction with Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis E is primarily waterborne, posing high risks to pregnant women, but typically resolves without chronic complications.