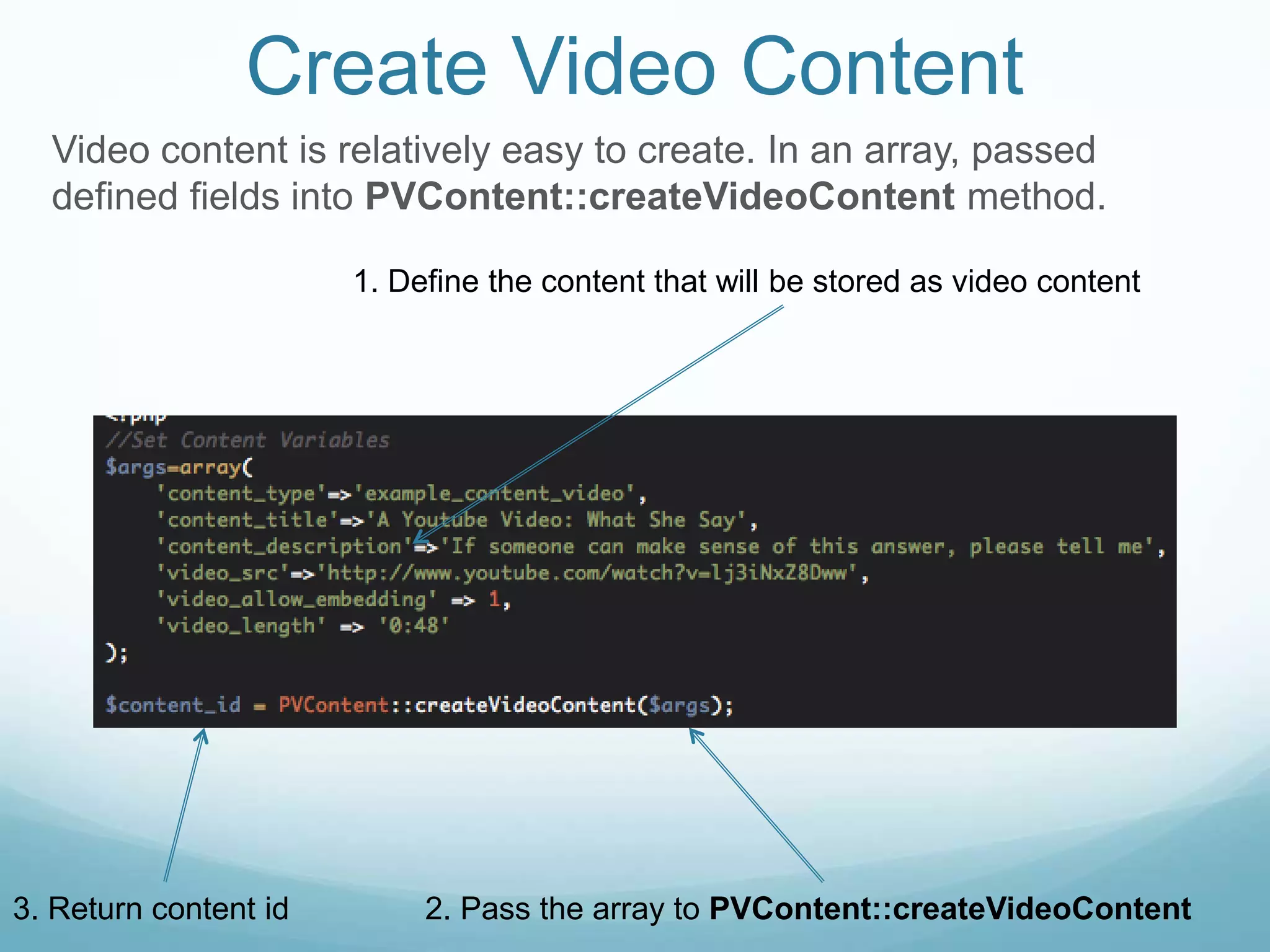
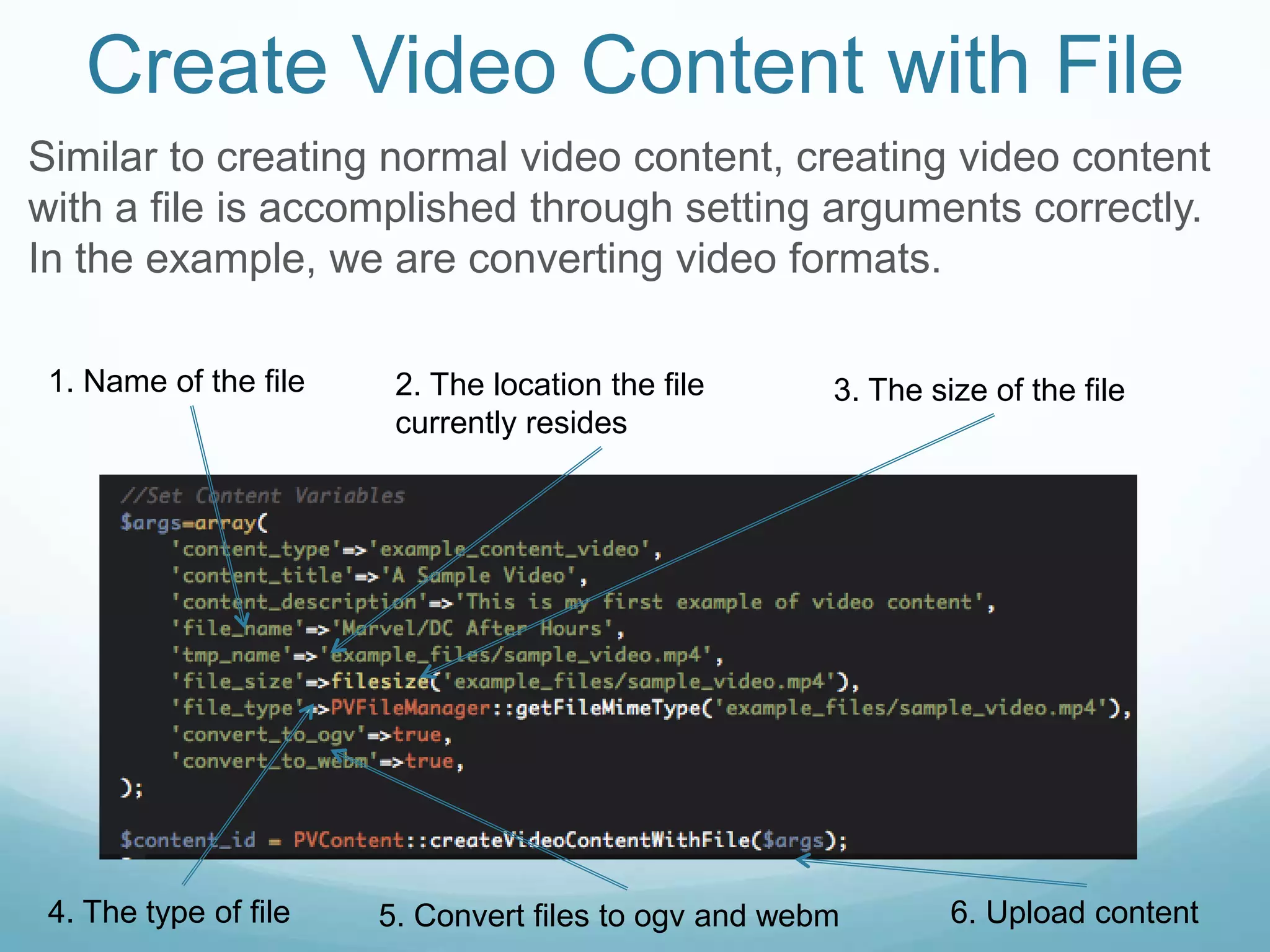
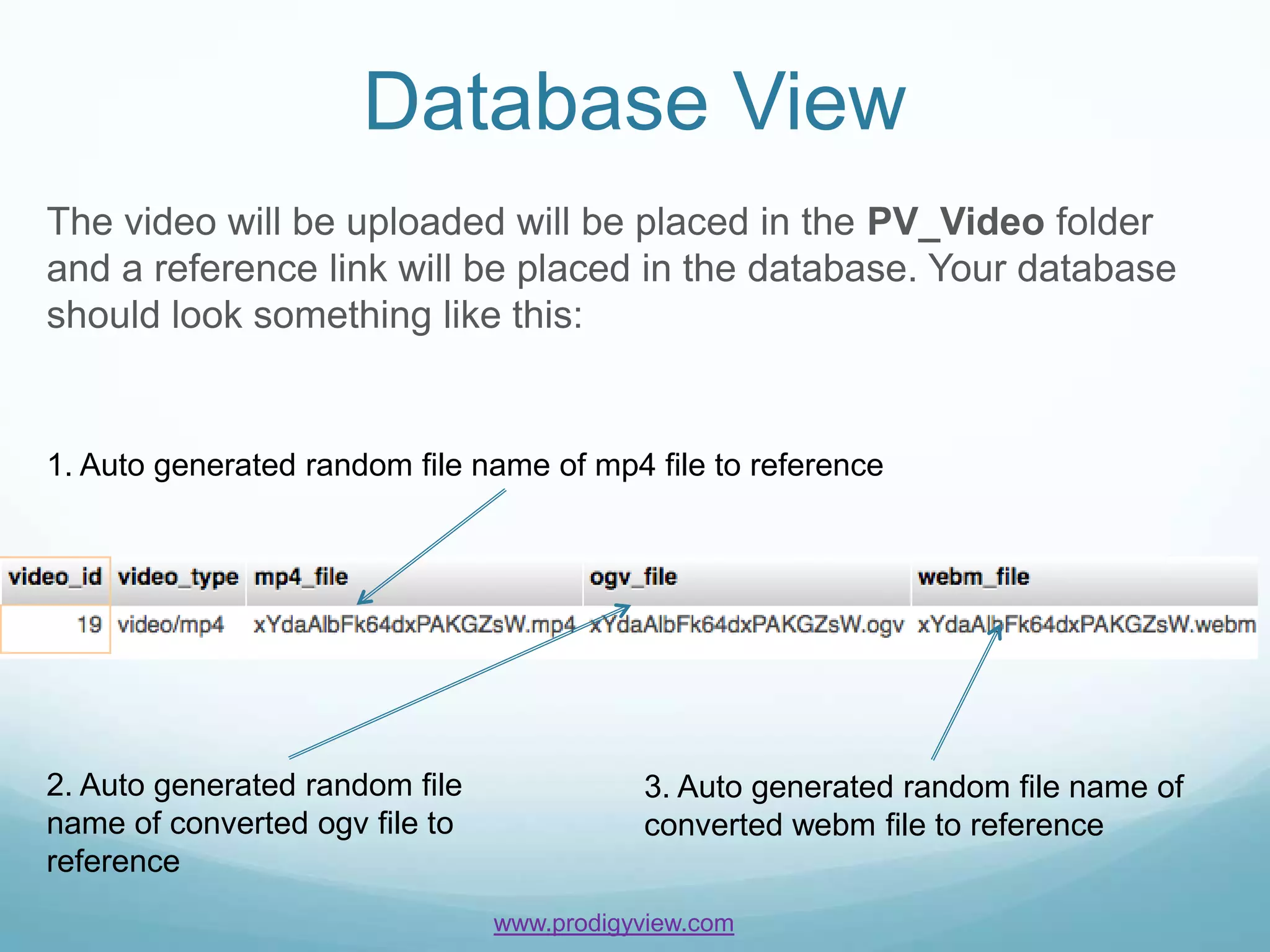
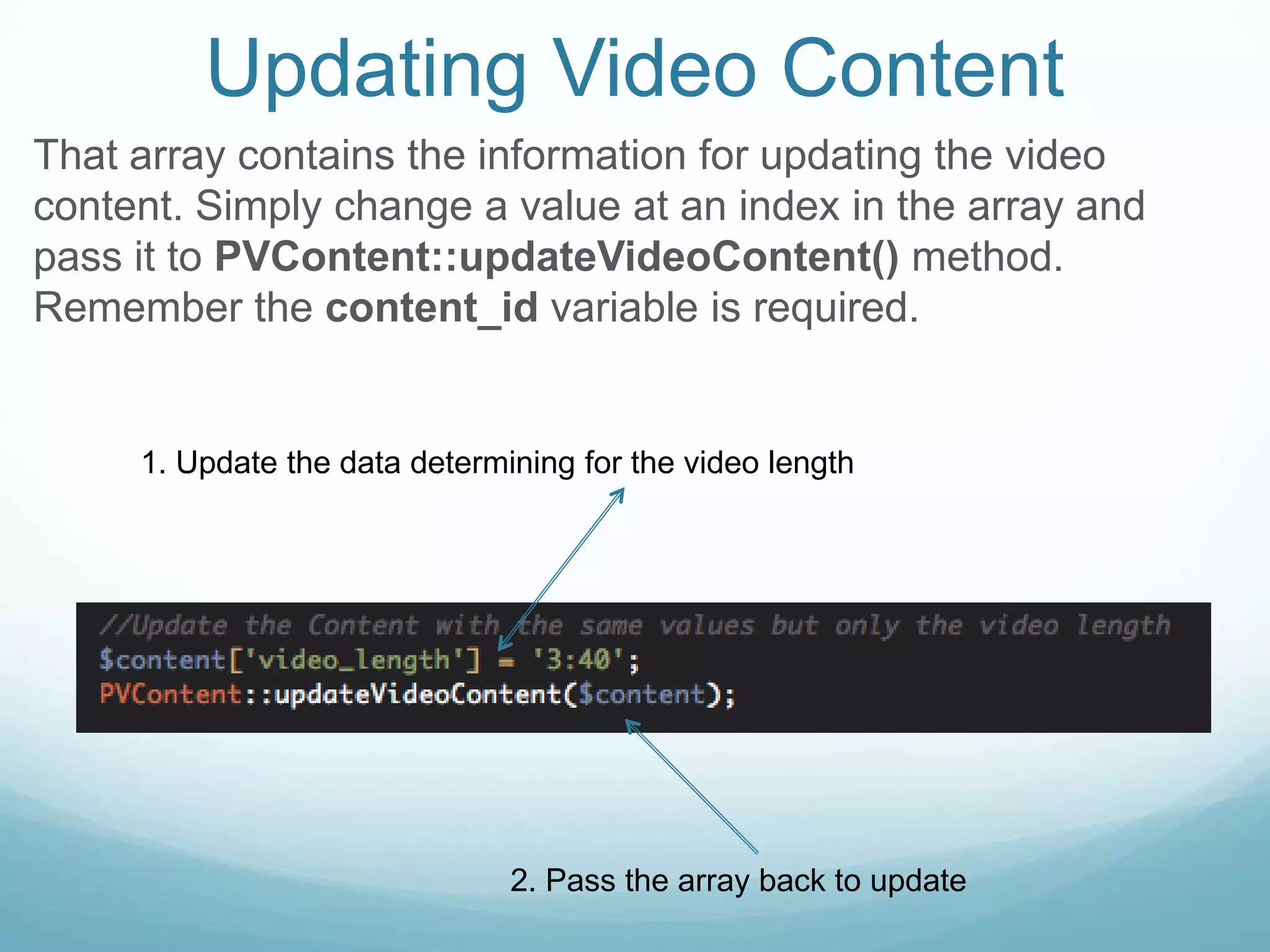
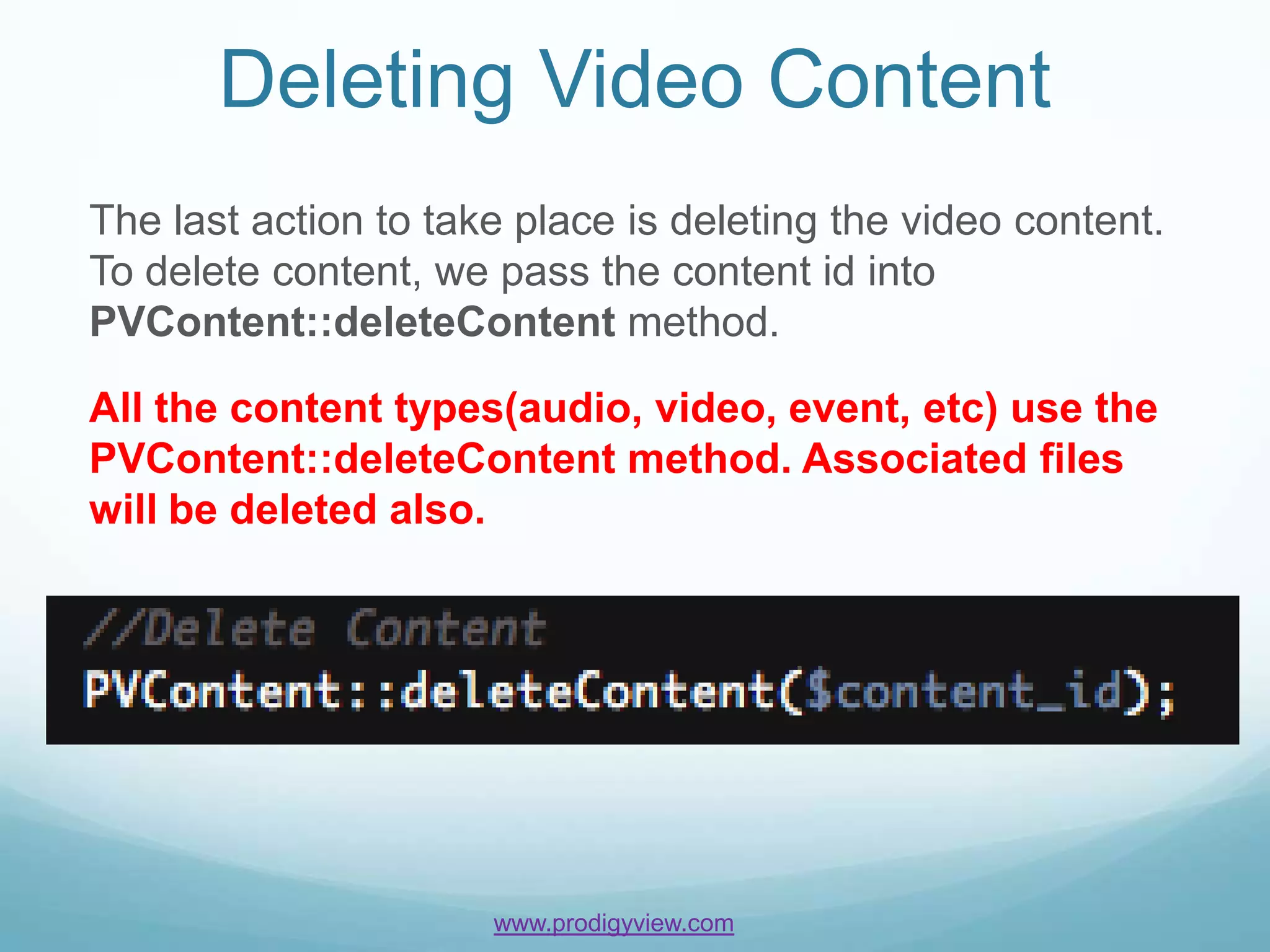
The document provides an overview of how to manage video content using ProdigyView's content management system, including uploading and converting video files. It outlines the requirements, methods for creating, updating, and deleting video content, and offers examples of usage as well as API references. Users can create video content by passing arguments into specific methods and search or retrieve information based on content IDs.