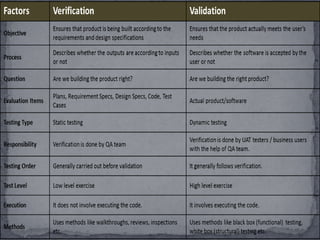
This document presents information on verification and validation, describing them as two types of testing. Verification ensures that the software conforms to its specifications by checking input/output and occurring during development. Validation checks that the software meets user needs and occurs after testing by getting user acceptance.
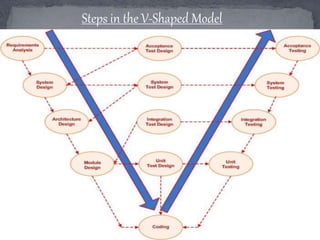
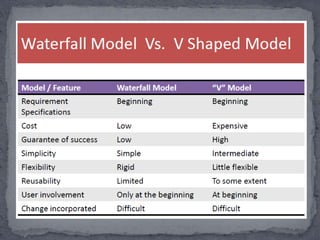
The document also discusses the V-model, a sequential software development process where testing is planned in parallel with development phases. Benefits are that testing planning occurs early, defects are found and fixed sooner, and it works for small, clearly-defined projects. Drawbacks are that it is rigid with no early prototypes and changes require updating all documents. The V-model is best for small to medium sized projects with set requirements and technical resources.