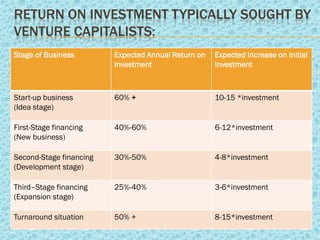
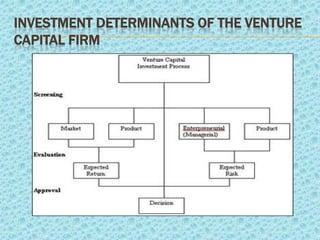
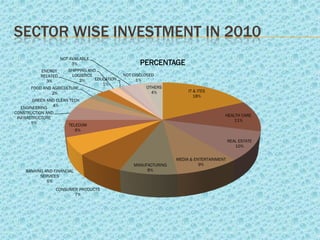
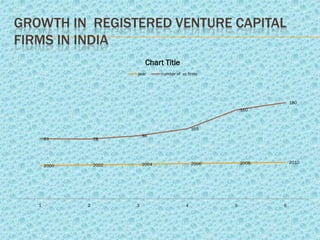
Venture capital refers to investments made in startup companies and small businesses with long-term growth potential. Venture capitalists provide funding to companies that do not have access to capital markets in exchange for equity ownership. They carefully evaluate founders and business concepts before investing and remain actively involved after by monitoring portfolio companies and participating at the board level. India has significant potential for venture capital investment due to its success in technology industries. Several government programs and private funds have helped promote venture capital in India since the 1970s, focusing on technology and manufacturing sectors. Typical returns sought by venture capitalists range from 30-60% depending on the business stage.