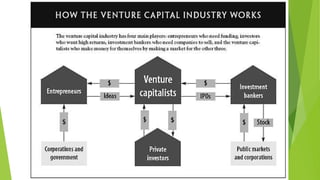
Venture capital is funding provided to startup companies that are attempting to develop a new product or service. It allows these companies to begin and build operations by providing necessary funding in exchange for equity. Venture capital firms also provide business expertise to help startups succeed.
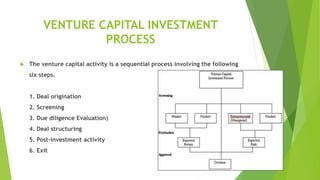
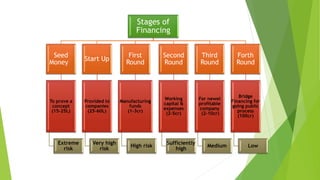
The venture capital process involves six sequential steps - deal origination, screening, due diligence, deal structuring, post-investment activity, and exit. Venture capital in India comes from government development institutions, public/private banks, private sector companies, and overseas funds. Micro venture capital provides smaller seed investments of 50 lakhs to 1.5 crore rupees to startups that have yet to gain traction, compared to larger traditional venture