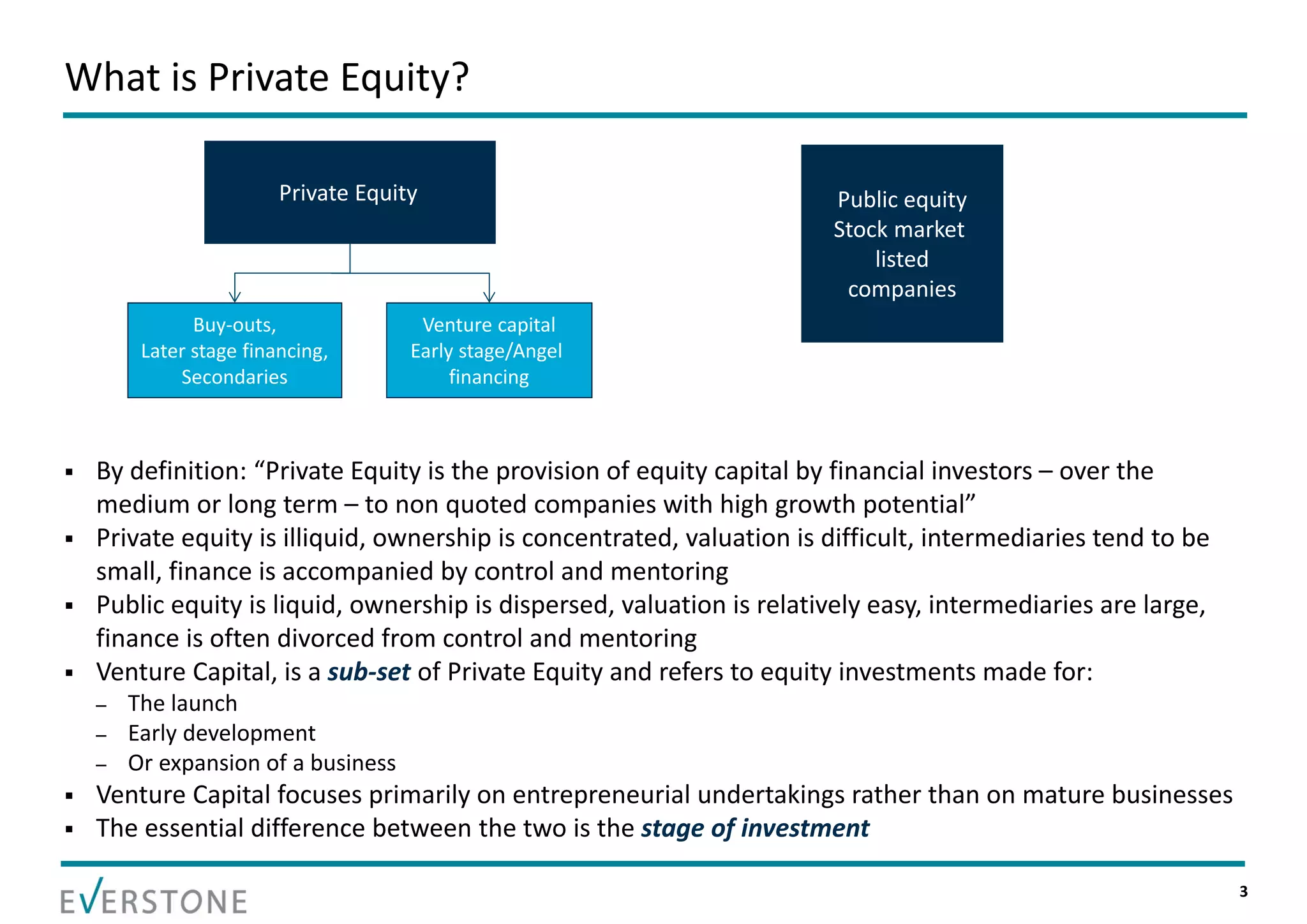
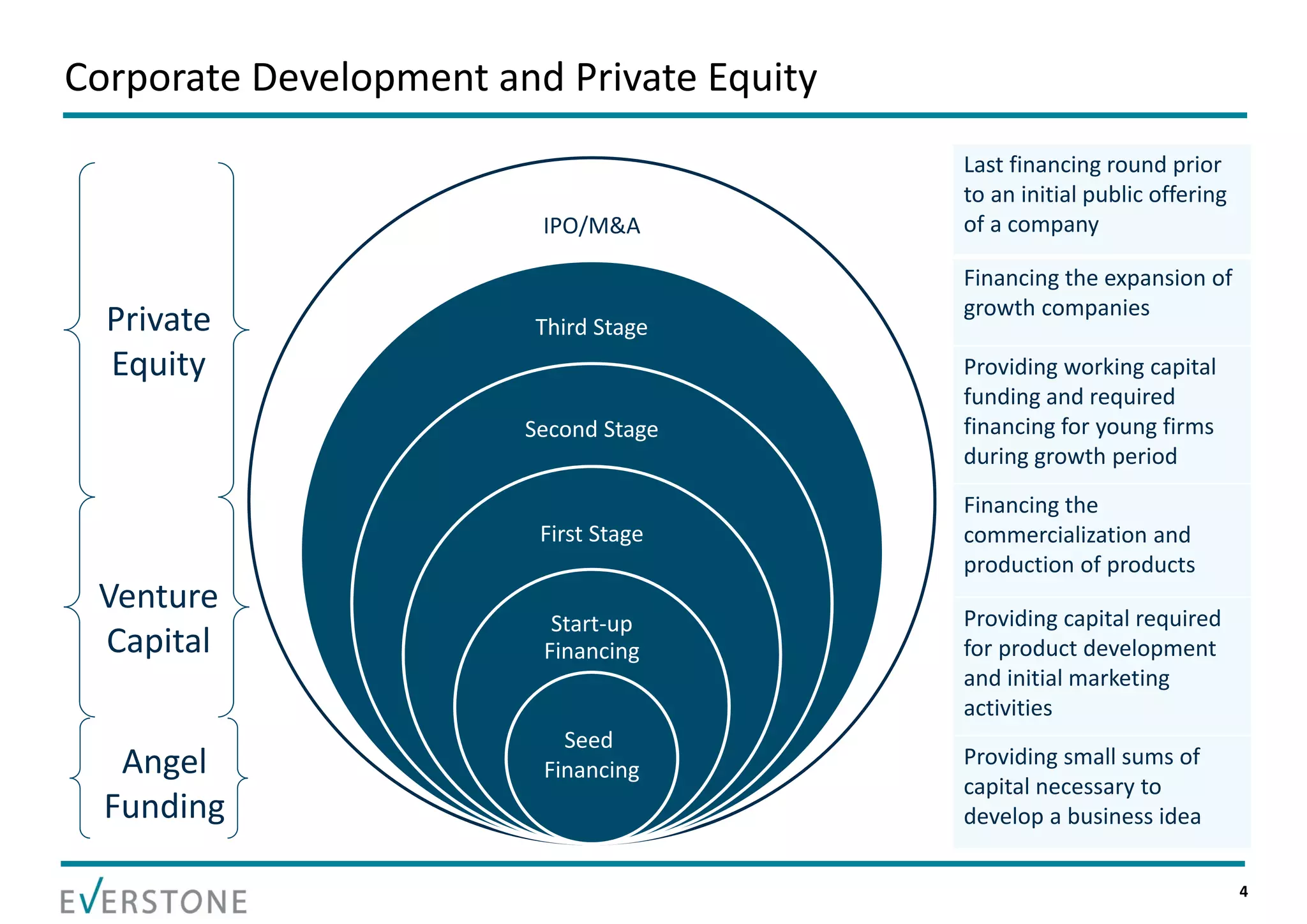
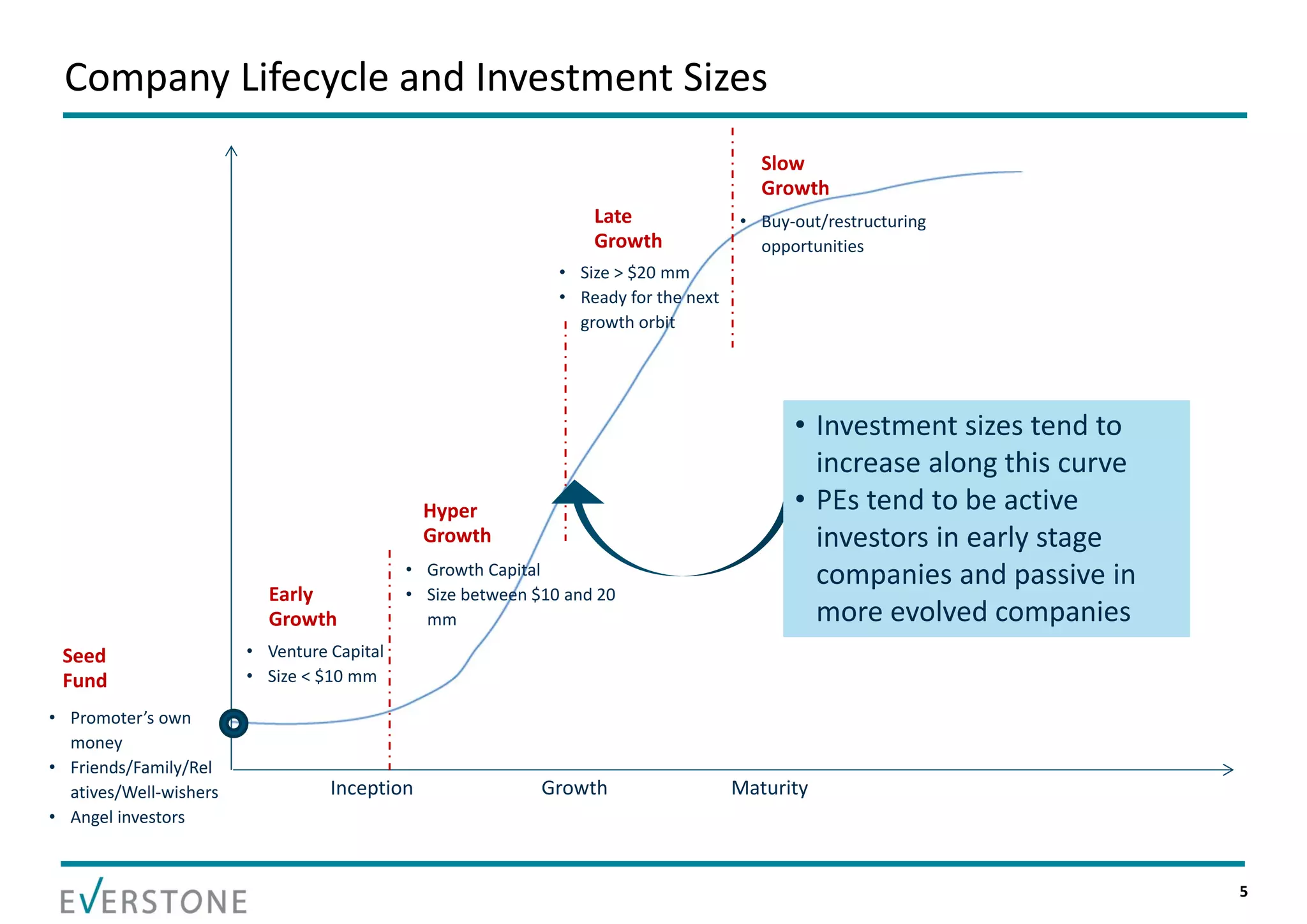
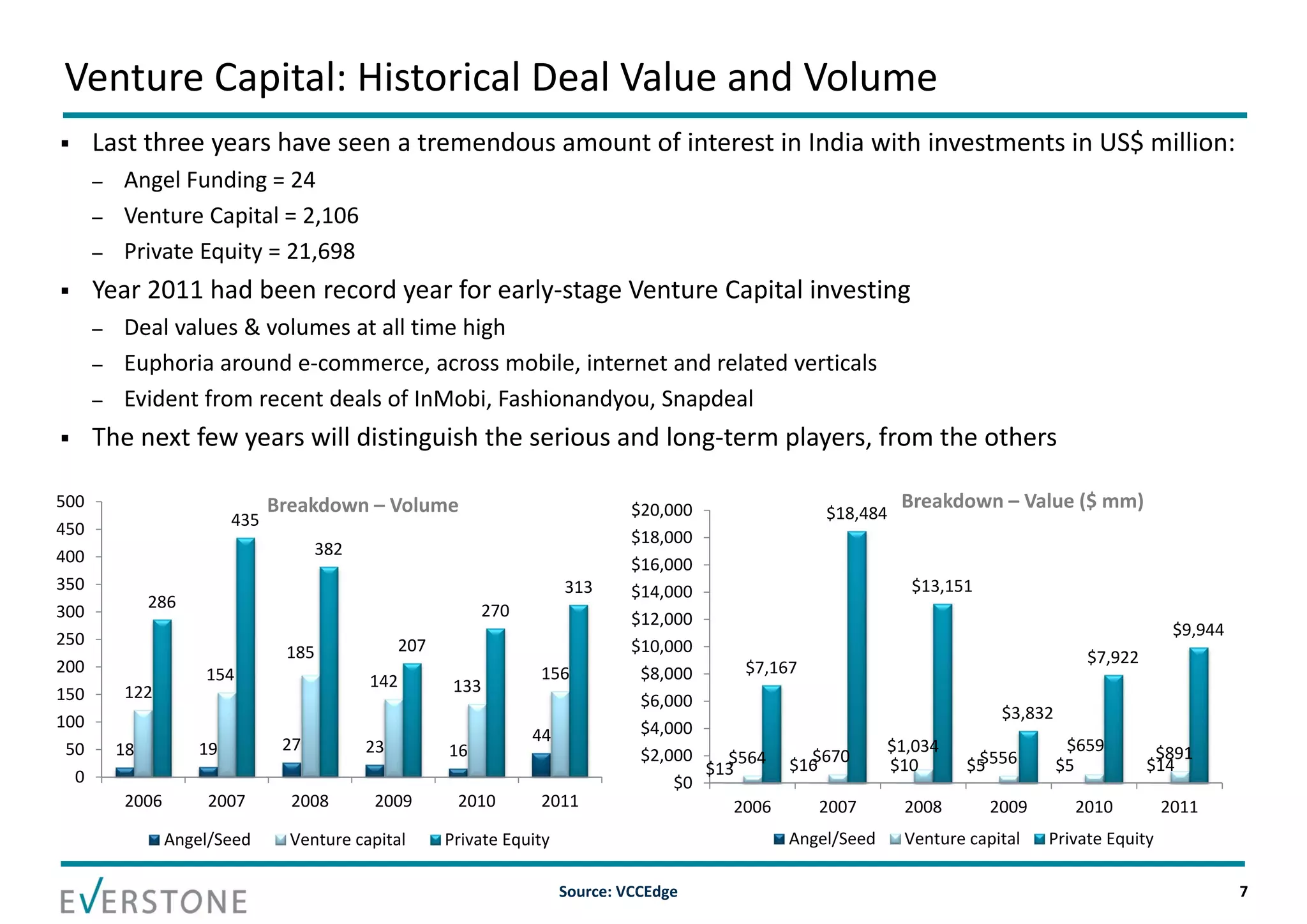
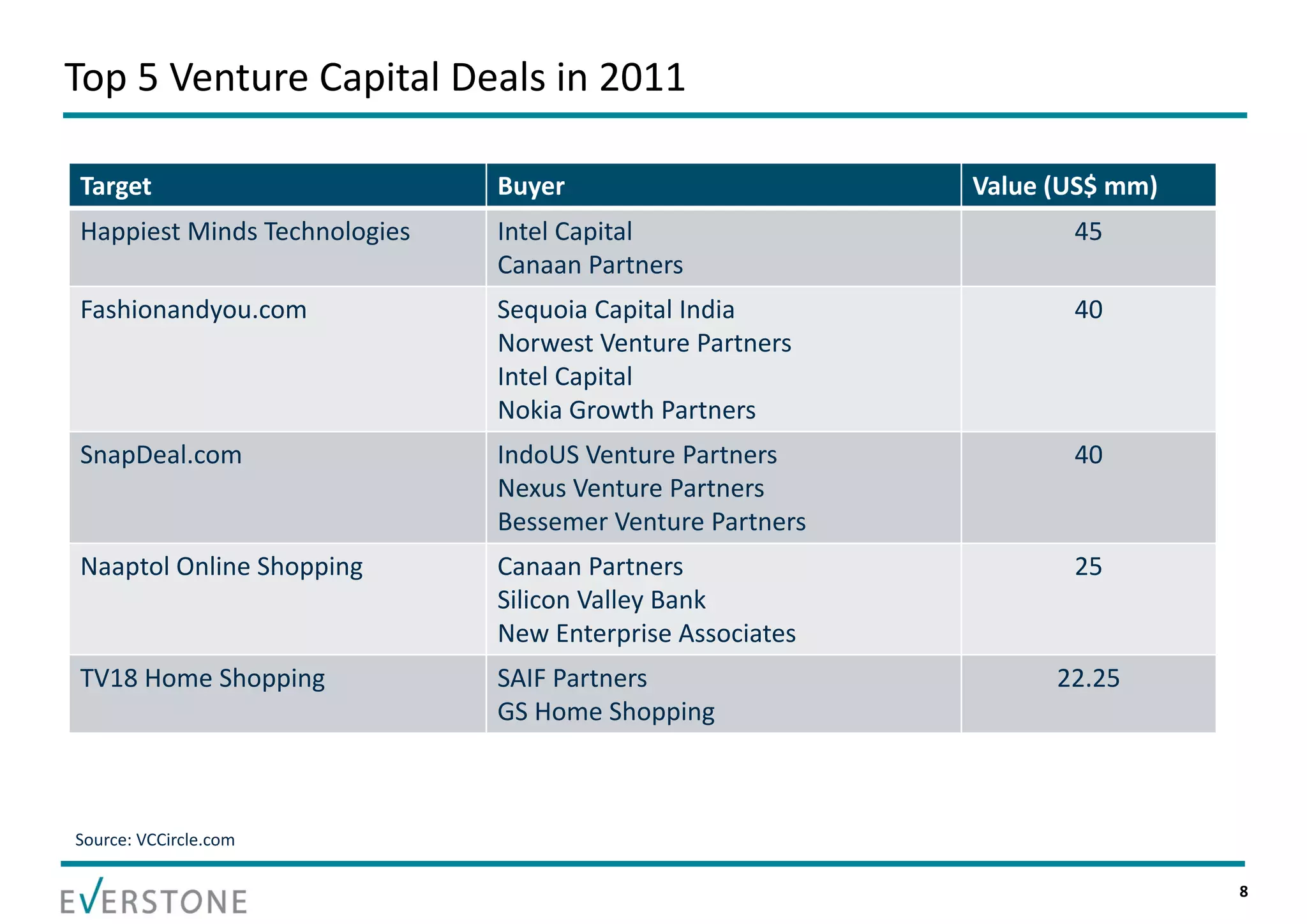
The document summarizes key topics relating to private capital and venture capital in India. It discusses the evolution of private capital in India from the 1980s onward. It provides data on historical venture capital deal value and volume in India, with 2011 being a record year. The top 5 venture capital deals of 2011 are listed. The rest of the document outlines various aspects of the venture capital process, including the pre-investment and post-investment phases, managing exits, tips for a successful partnership between entrepreneurs and investors, and challenges that can arise.