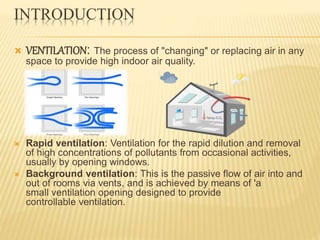
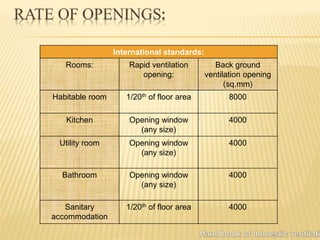
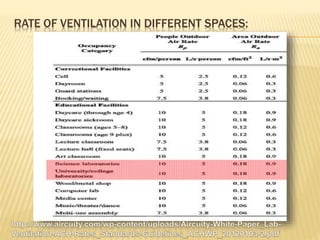
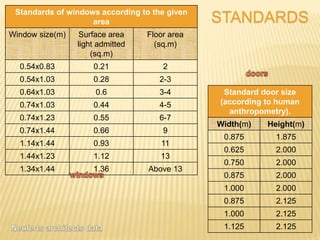
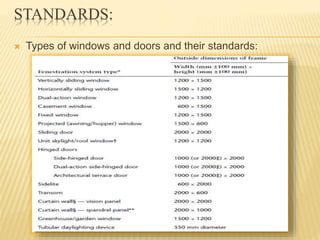
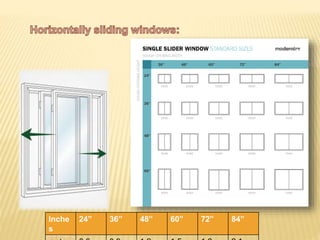
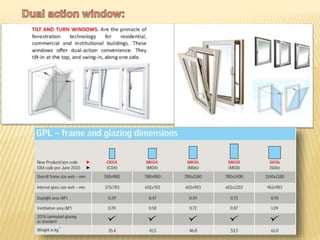
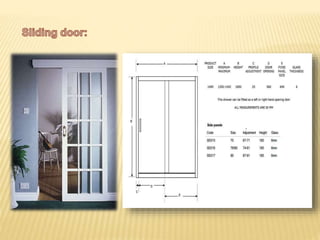
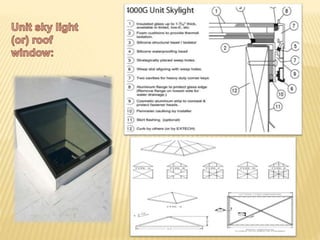
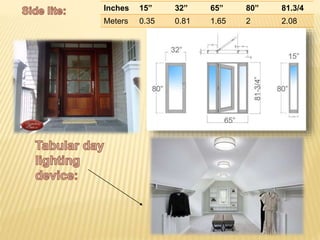
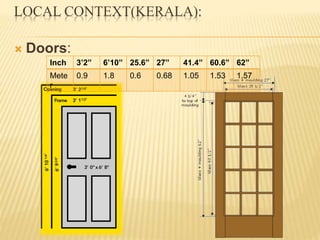
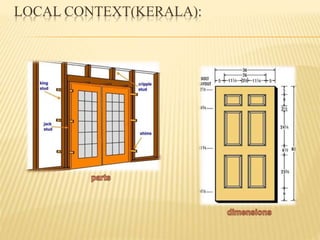
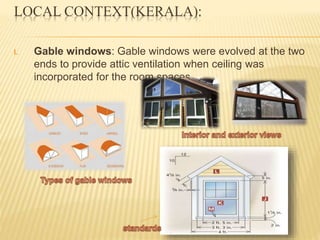
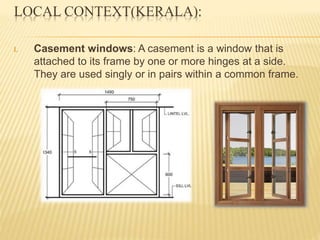
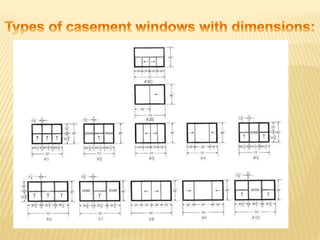
This document discusses ventilation requirements and standards for buildings. It defines ventilation as the process of changing air in a space to provide good indoor air quality. It discusses the rates of openings like windows and vents needed for different types of rooms according to international standards. Specific types of windows commonly used in Kerala architecture are also outlined, like gable windows, clerestory windows, and casement windows. Standards for window and door sizes are provided based on room area and human dimensions. Overall, the document provides information on calculating adequate ventilation openings and common ventilation installation features for buildings.