The document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses that C is a general purpose, procedural language developed in 1972 at Bell Labs. C is a middle-level language as it allows programming at both high-level and assembly-level. Key aspects of C covered include data types, variables, operators, functions, arrays, pointers, memory management, and file handling. The document also provides examples of various C programming concepts.













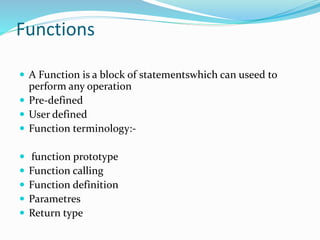
![Tokens type in c
Constants:-
Integer Constants – Refers to sequence of digits such as
decimal integer, octal integer and hexadecimal integer. –
Some of the examples are 112, 0551, 56579u, 0X2 etc.
• Real Constants – The floating point constants such as
0.0083, -0.78, +67.89 etc.
• Single Character Constants – A single char const contains a
single character enclosed within pair of single quotes [ ‘ ’ ].
For example, ‘8’, ‘a’ , ‘i’ etc.
• String Constants – A string constant is a sequence of
characters enclosed in double quotes [ “ ” ]; For example,
“0211”, “Stack Overflow” etc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/venkatesh-230725142844-e2612f1e/85/venkatesh-pptx-14-320.jpg)



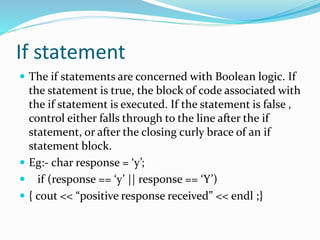


![Arrays in c
Array is a collection of data items all of same types
Three types of array
1.one dimensional array
2. two dimensional array
3. multi dimensional array
Array declaration syntax: data type arr_name[array_size];
Learnt how to declare and initialize at compile time and run time
STRING IN C
A string in C is merely an array of characters
The length of a string is determined by a terminating null character:
'0‘
String has some in built functions so it can save our time space and
efficient](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/venkatesh-230725142844-e2612f1e/85/venkatesh-pptx-22-320.jpg)