Vehicles are machines designed to transport people or cargo, and their evolution has been a primary driver of human progress, fundamentally reshaping societies, economies, and the very geography of our world. From the first wheel to the complex intelligent systems of today, vehicles represent humanity's enduring quest for mobility and connection.
### The Dawn of Mechanical Motion
For millennia, transportation was limited by the power of muscle, whether human or animal. The true revolution began with the Industrial Revolution and the harnessing of steam power, which gave rise to the first locomotives and steamboats. However, it was the development of the **internal combustion engine** (ICE) in the late 19th century that truly untethered humanity. Pioneers like Karl Benz and Henry Ford did not just invent a machine; they created a new paradigm of personal freedom. Ford's implementation of the moving assembly line made the automobile accessible to the masses, triggering a cascade of societal changes, including the growth of suburbs, the creation of vast road networks, and the birth of countless new industries.
### A World on Wheels
The concept of a vehicle extends far beyond the personal car. The specialization of vehicles has allowed humanity to conquer land, sea, and air, each designed for a specific purpose and environment.
* **Land Vehicles:** This is the most diverse category, including passenger cars, motorcycles for nimble transport, buses for public transit, and trucks that form the backbone of modern logistics. Trains continue to be a vital mode of transport for both passengers and heavy freight over long distances.
* **Watercraft:** Ships and boats have been essential for trade and exploration for centuries. Modern watercraft range from massive container ships and oil tankers that carry global trade to sophisticated submarines and personal leisure boats.
* **Aircraft:** The 20th century saw humanity take to the skies. Airplanes have made the world smaller, enabling rapid long-distance travel and air freight. Helicopters offer unique vertical takeoff and landing capabilities, crucial for emergency services, construction, and military operations.
* **Specialized Vehicles:** This category includes everything from agricultural tractors and combines that feed the world to heavy construction equipment that builds our cities. At the pinnacle of vehicle engineering are spacecraft, which have carried humans to the Moon and probes to the far reaches of our solar system.
### The Digital Transformation
In recent decades, vehicles have transformed from purely mechanical constructs into sophisticated electronic systems on wheels. The integration of computers began with engine control units (ECUs) to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. This digital foundation has paved the way for a new era of automotive technology defined by safety, connectivity, and autonomy.
Modern vehicles are equipped with an array of advanced driver-assistan








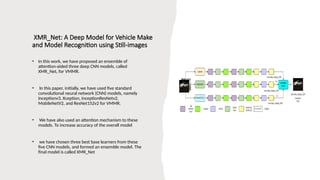
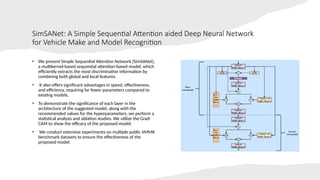
![A Feature Fusion based Custom Deep Learning
Model for Vehicle Make and Model Recognition
• Deep Feature Fusion: It fuses two feature maps
that are extracted from input images in two parallel
paths containing two different base models.
• Modified CBAM: Taking inspiration from the
original CBAM attention [14], a modified attention
mechanism is used, which extracts channel and
spatial information in parallel and combines them
with input feature maps.
• Generalized Approach: Our model is evaluated on
two VMMR datasets, namely Stanford Cars and
Comp-CarsSV, and achieved 93.51% and 99.03%
test accuracies, respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vehiclerecognisationusingdeeplearningcnn-251010035703-fbe86568/85/vehicle-recognisation-using-deep-learning-cnn-pptx-14-320.jpg)