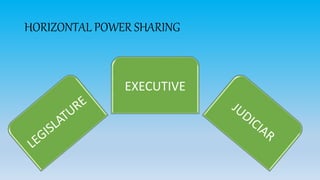
Power sharing is a technique used in India to distribute power across different levels and groups to prevent concentration of power. It takes various forms, including horizontal power sharing between the legislature, executive, and judiciary branches of government. Vertically, power is shared between federal, state, and local levels of government. Power is also shared among different social communities through representation and reservation. Coalition governments represent another form of power sharing, with ruling and opposition political parties each wielding influence.