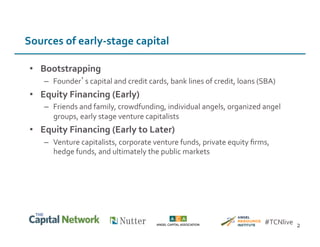
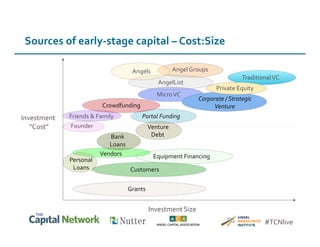
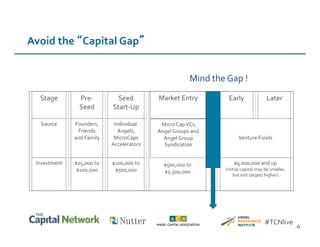
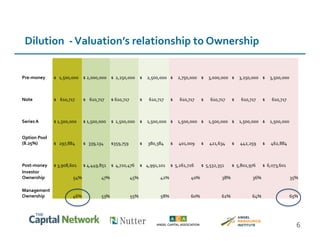
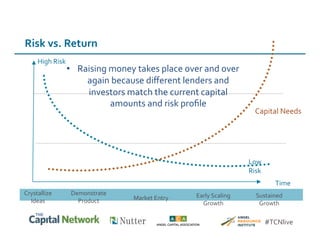
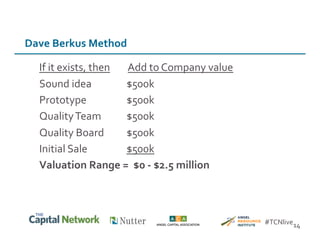
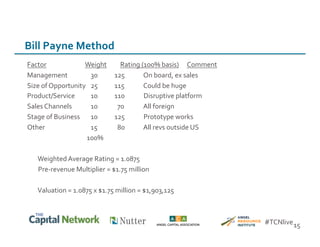
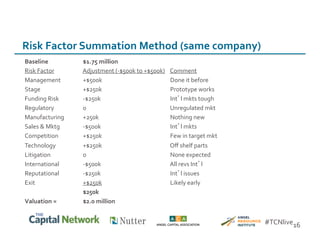
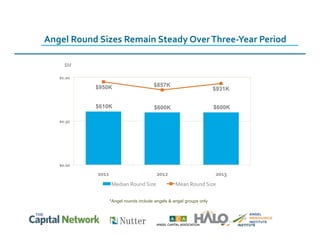
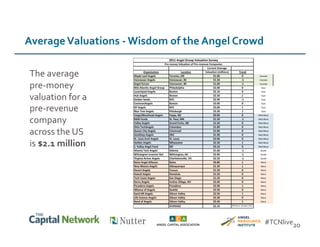
This document discusses sources of early-stage capital for startups and methods for valuing early-stage companies. It provides an overview of common sources of funding for startups at different stages, including bootstrapping, equity financing from friends/family and angels, and later stage funding from VCs. It also discusses tools for valuing early companies, including common equity, debt/convertible notes, and preferred equity. Dilution as it relates to company valuation and ownership is demonstrated through an example.