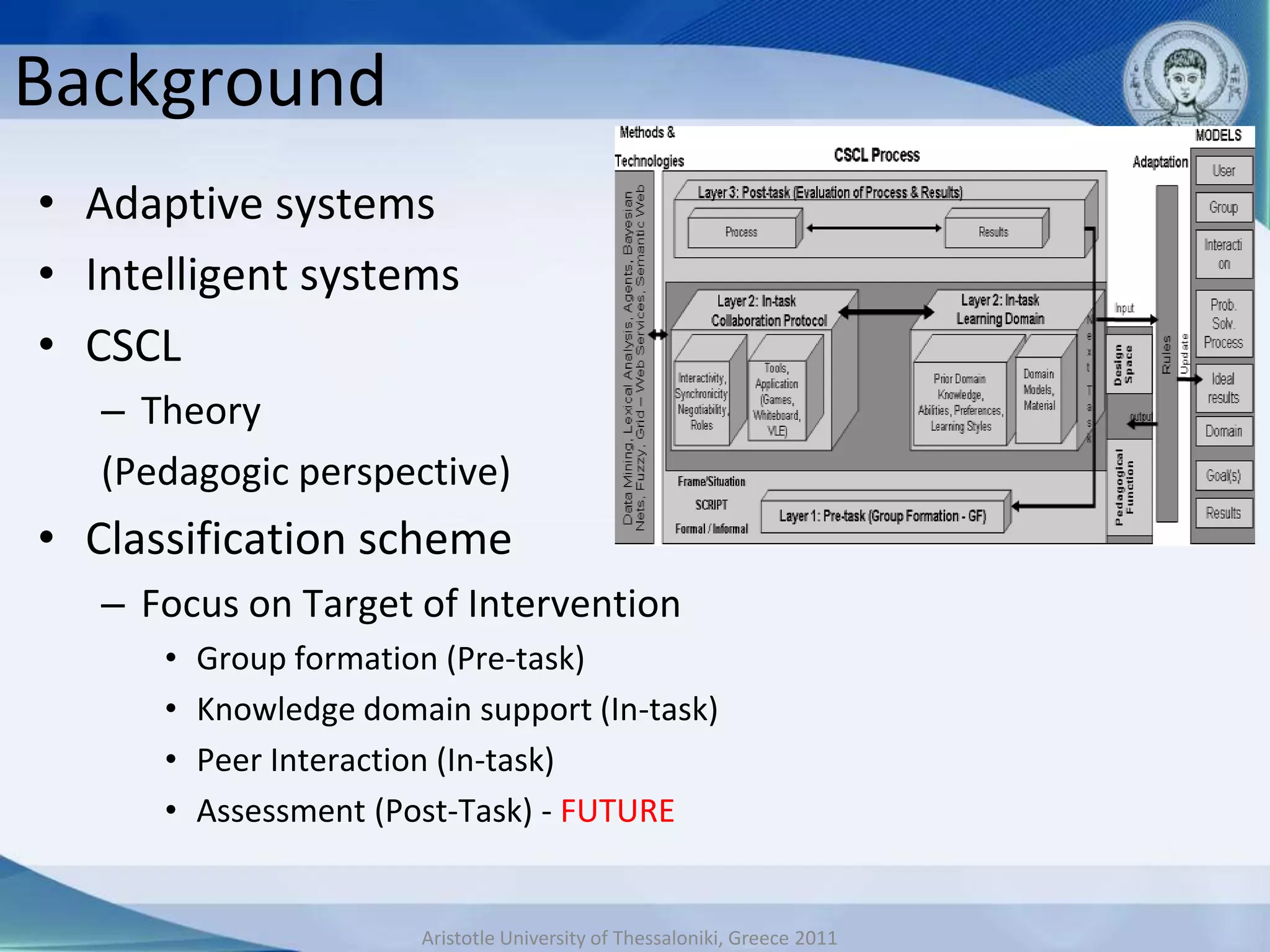
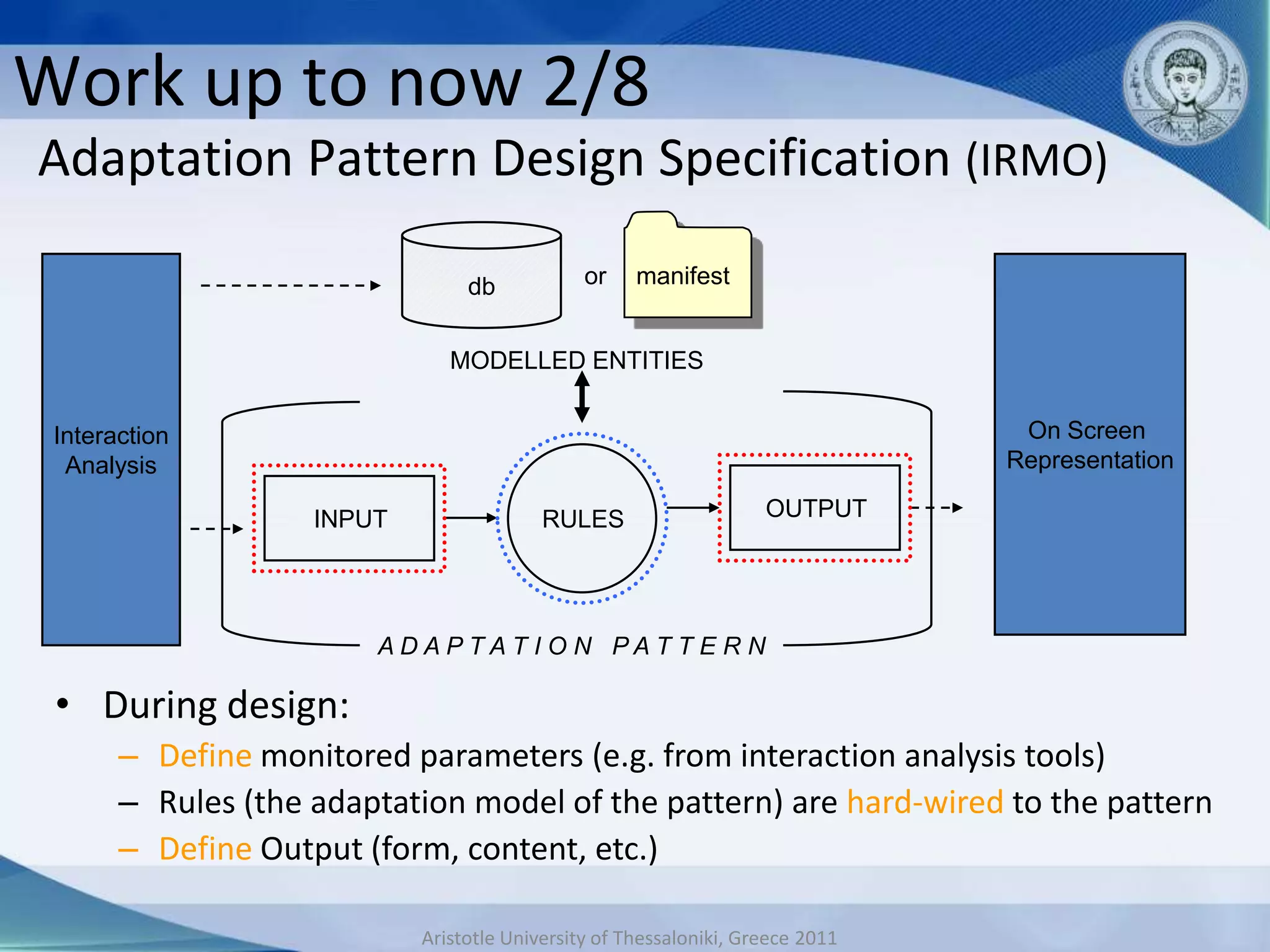
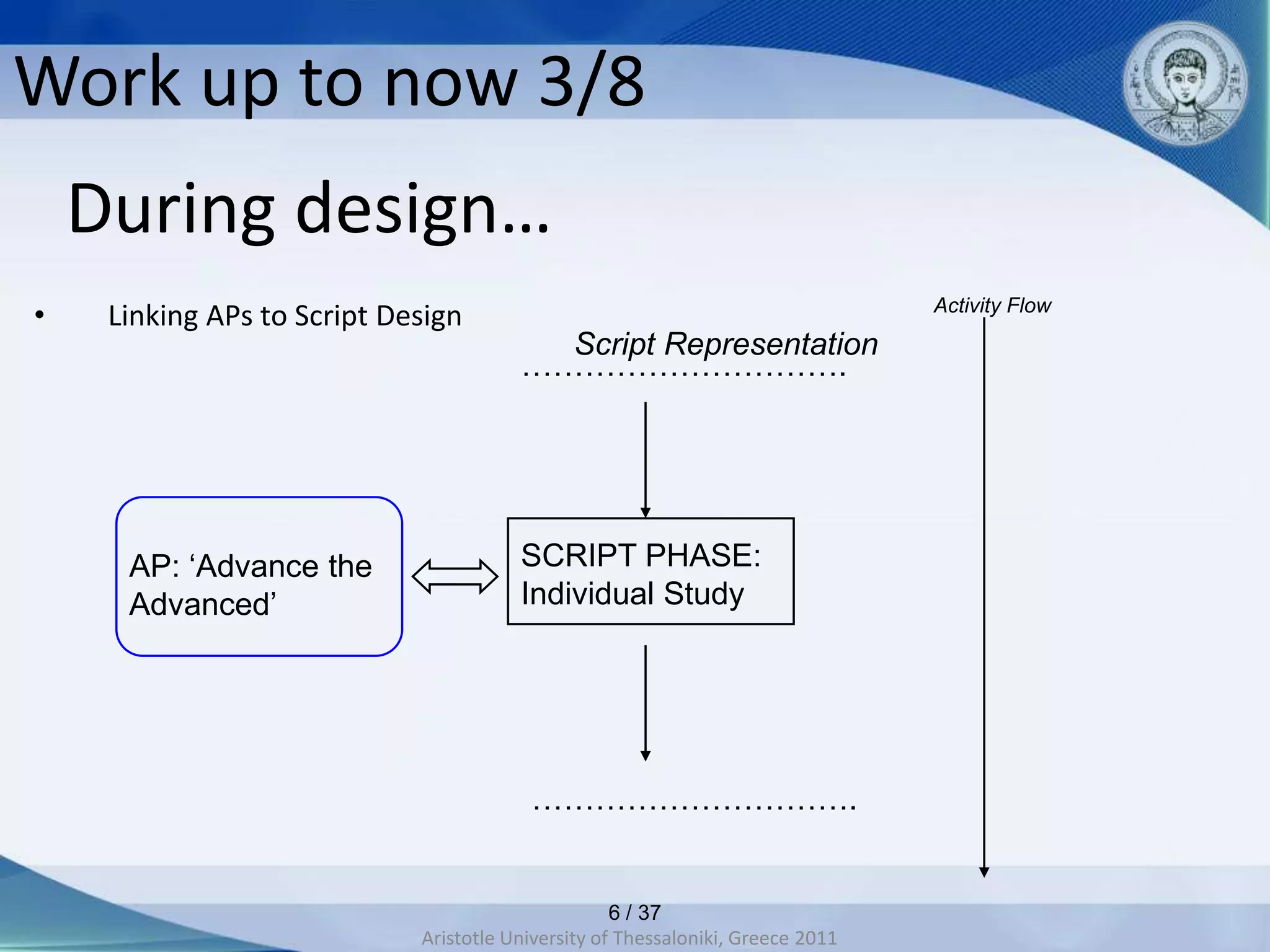
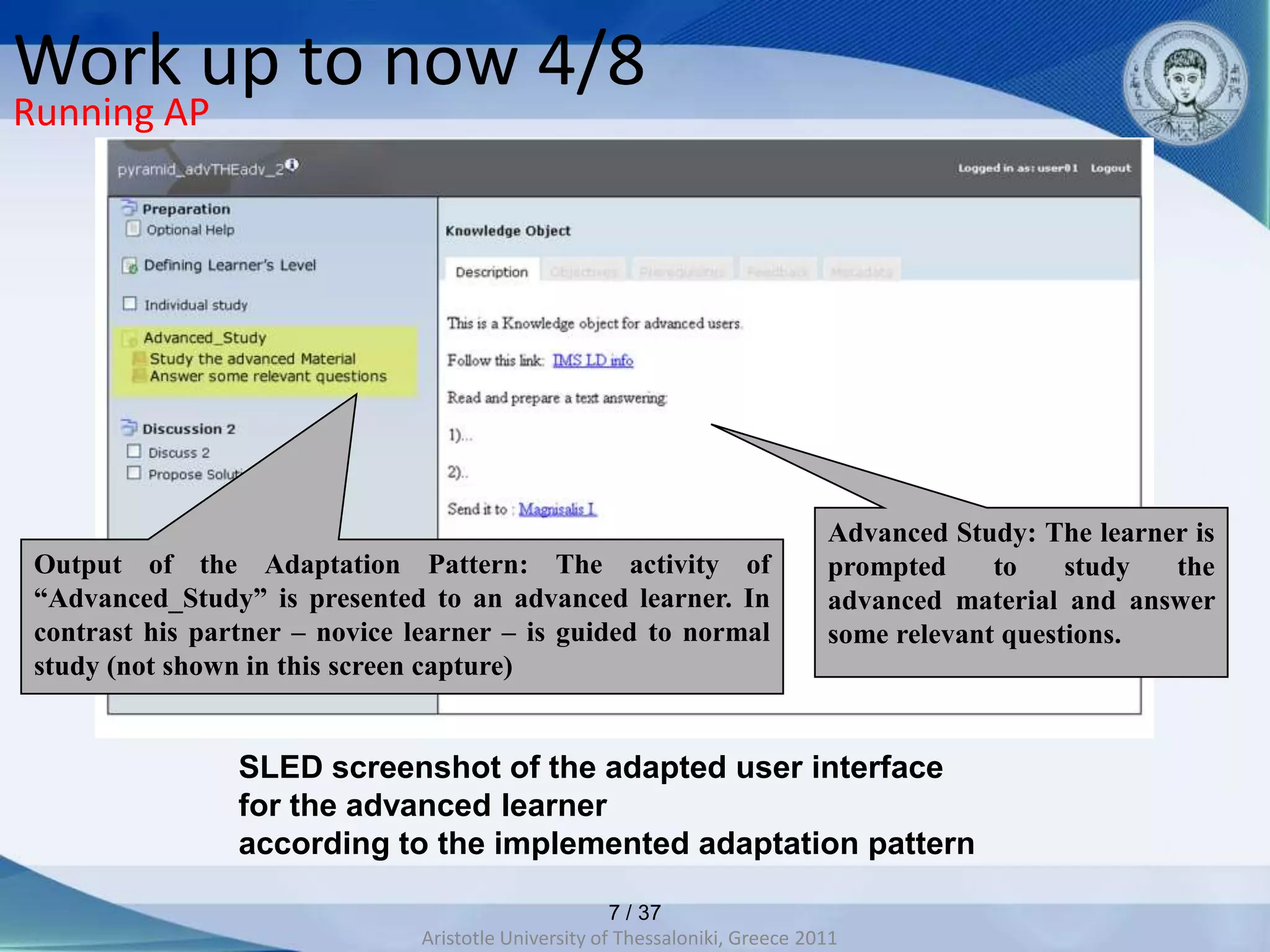
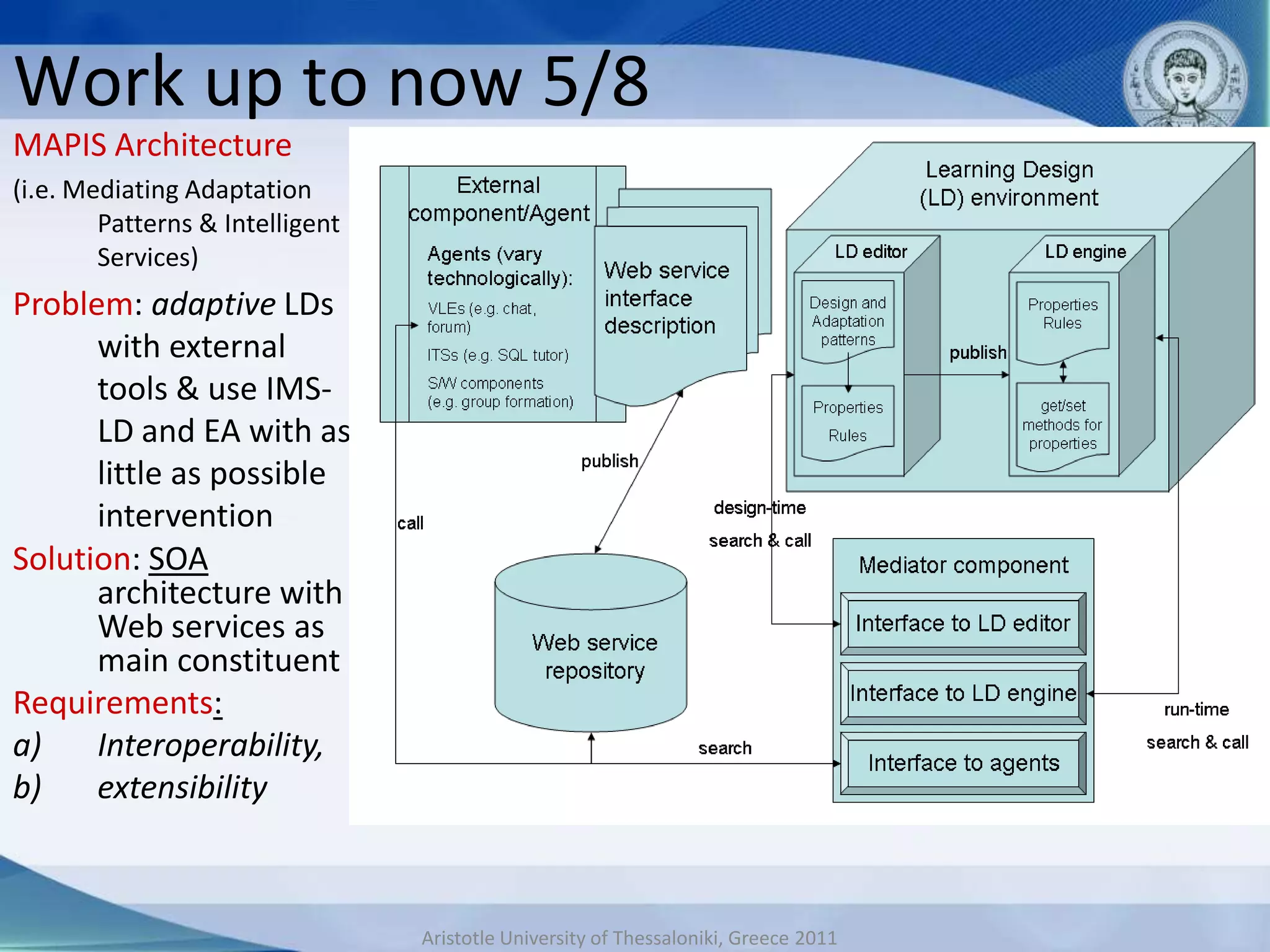
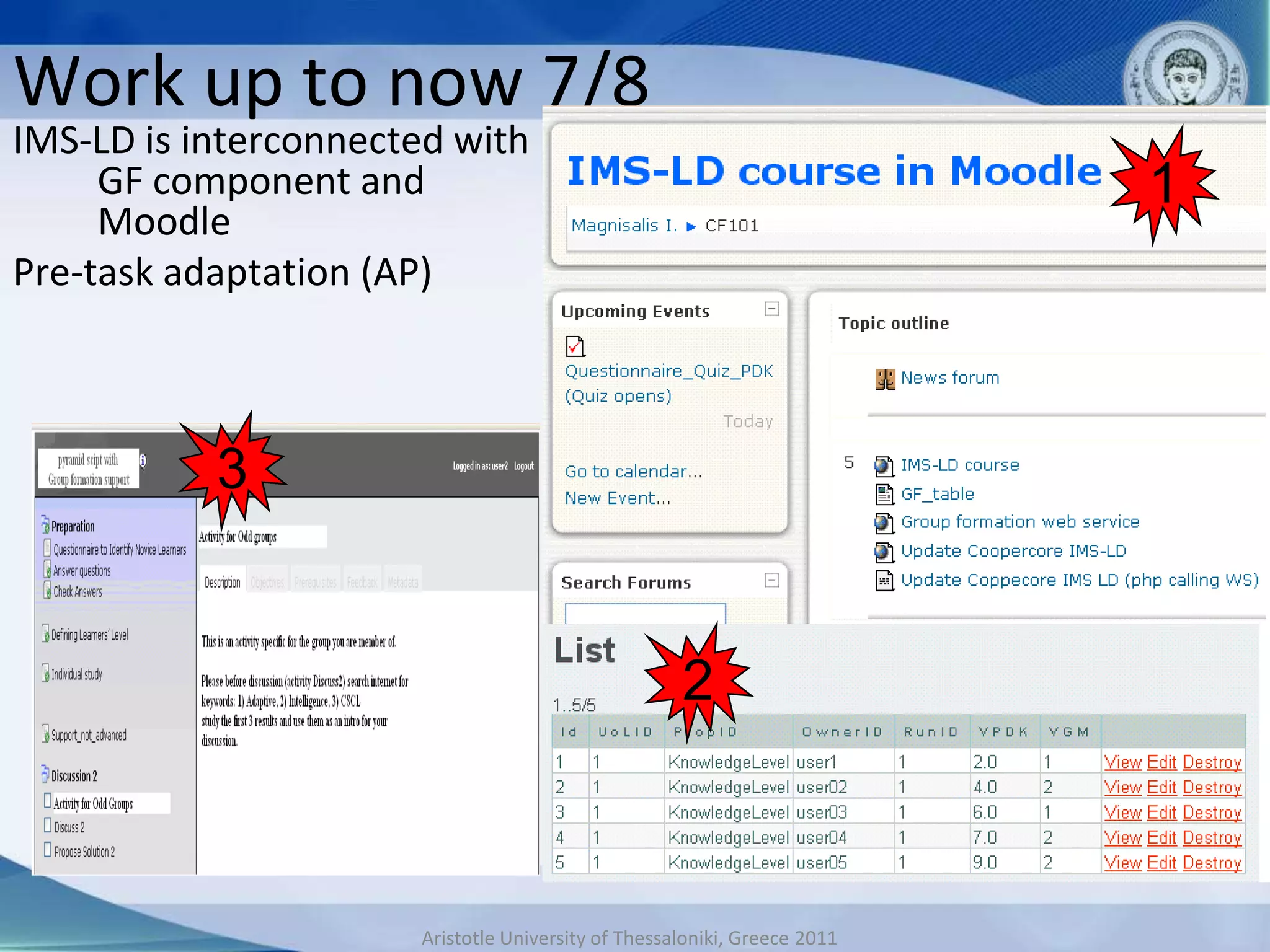
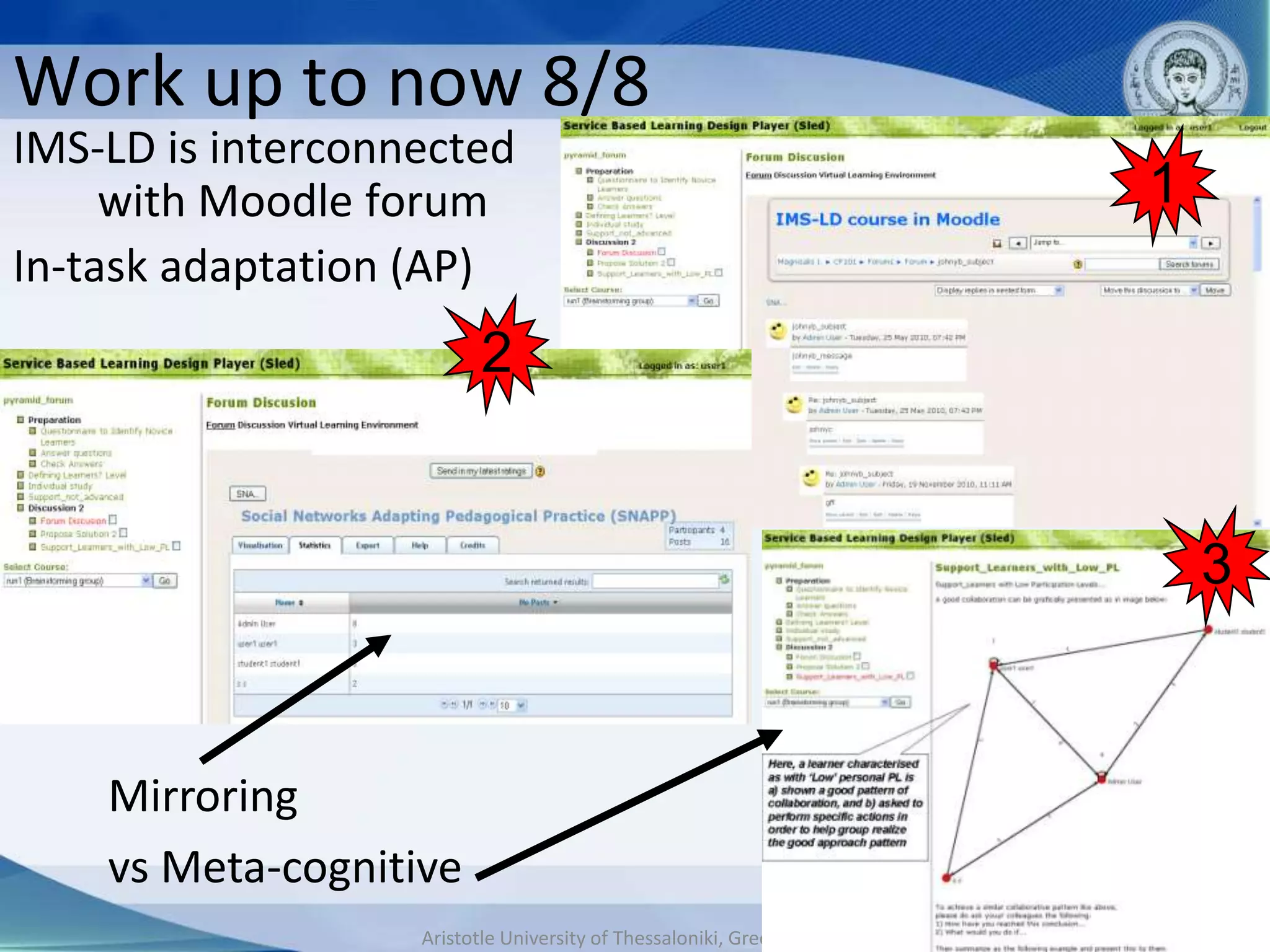
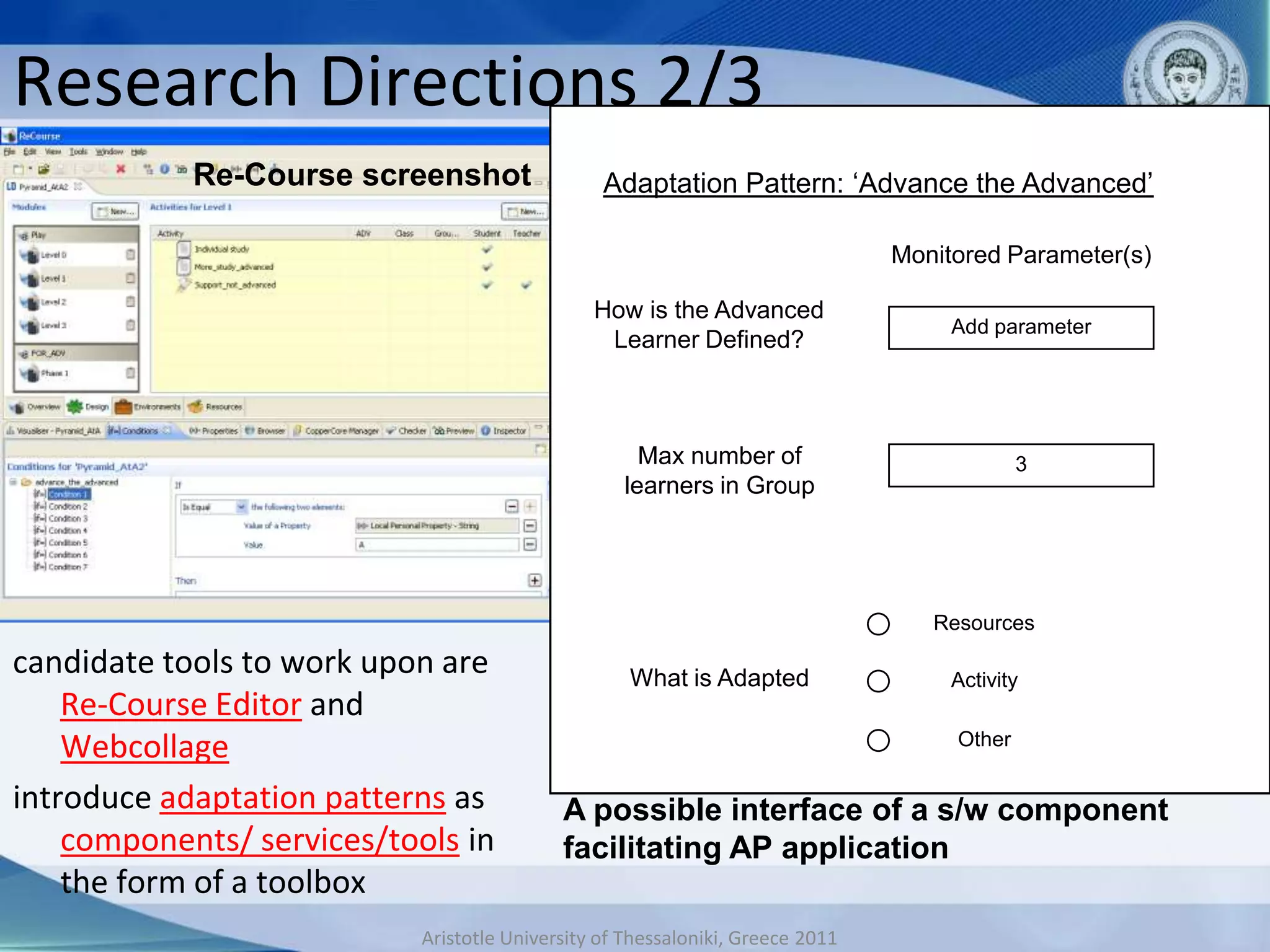
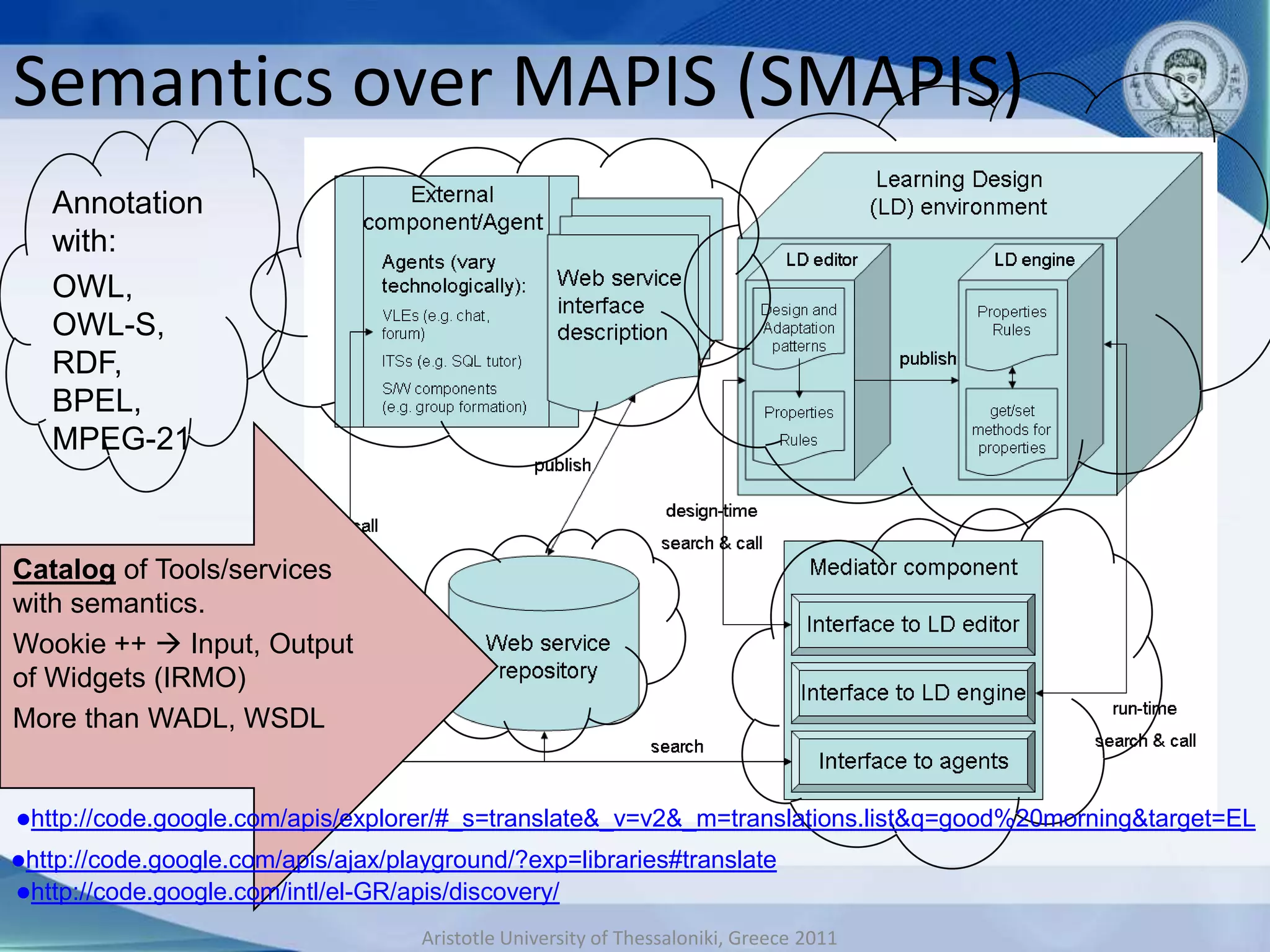
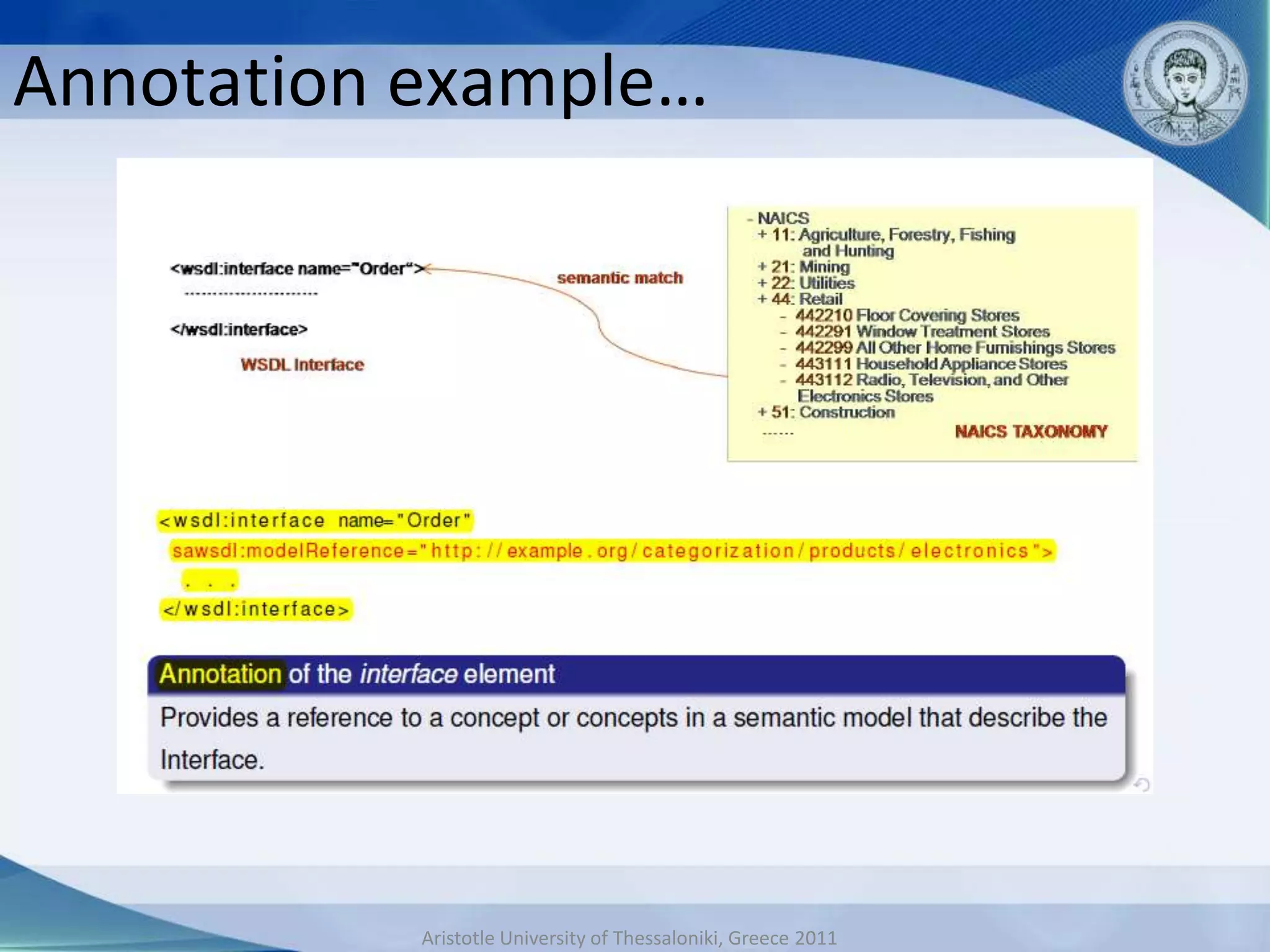
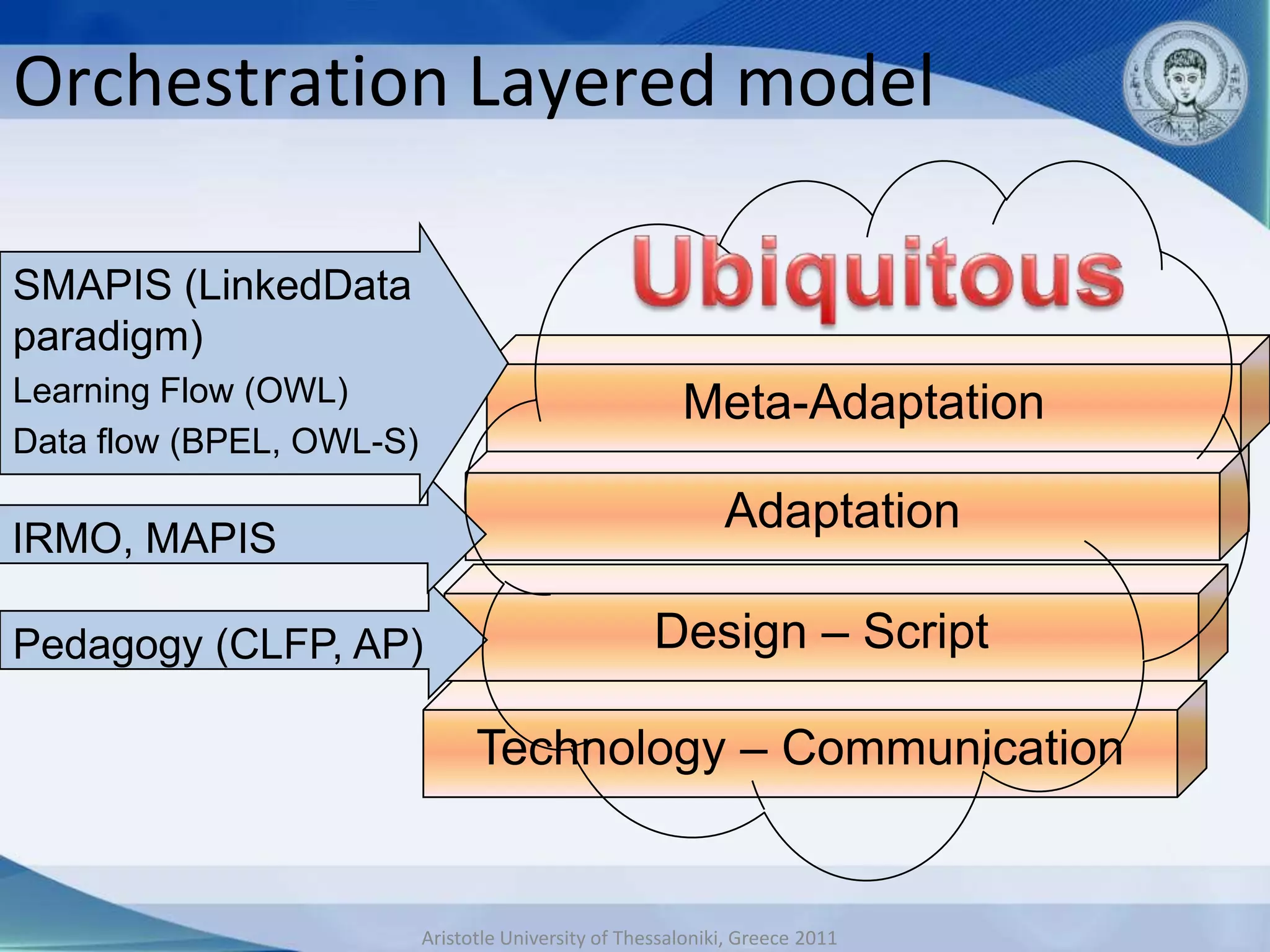
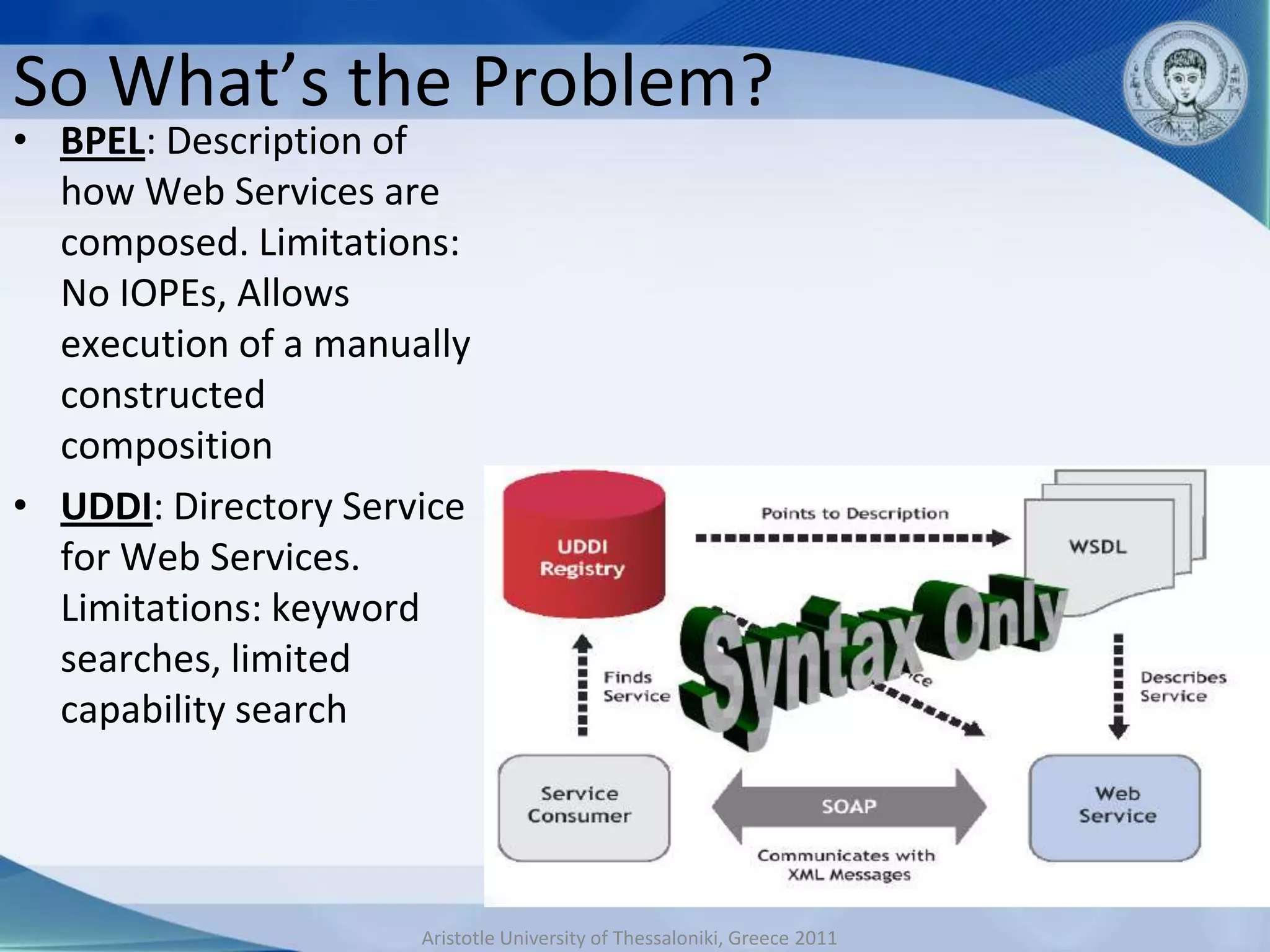
This document discusses adaptive and intelligent collaborative learning support systems (AICLS). It provides background on related fields and outlines a classification scheme for AICLS focusing on the target of intervention. It describes work done to model adaptation patterns, develop an AICLS architecture, and implement case studies. Future research directions are proposed, including implementing complete courses with adaptive support at different levels and evolving systems based on assessment. Key publications in the field are also listed.