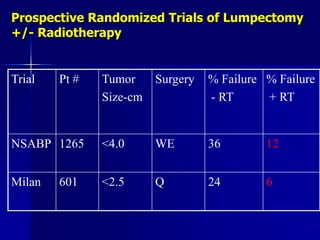
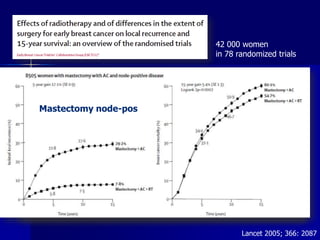
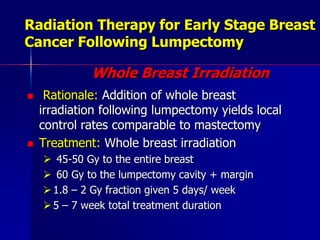
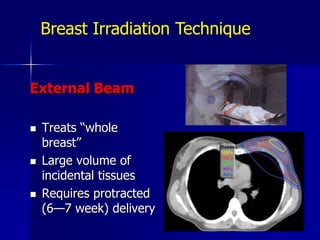
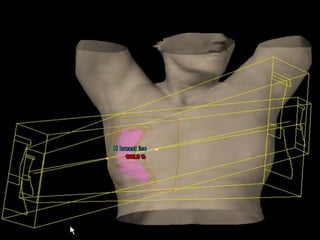
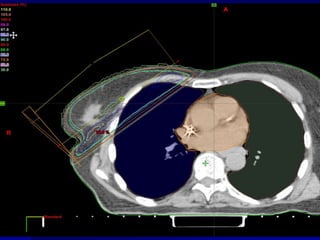
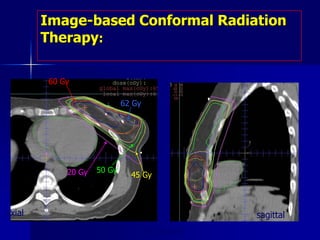
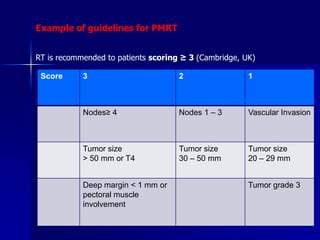
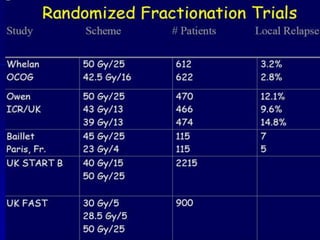
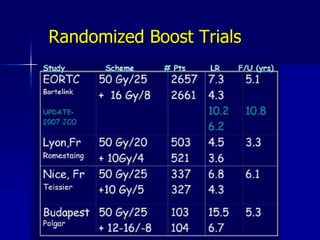
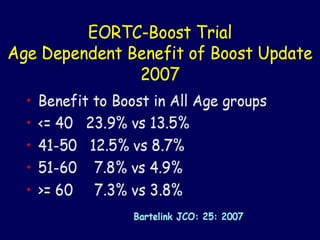
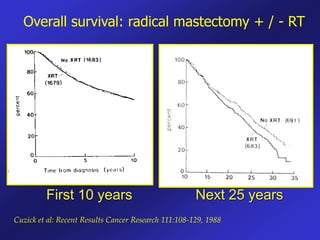
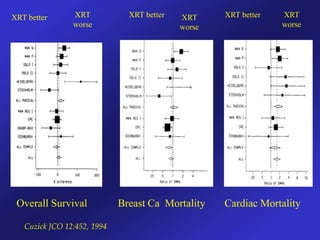
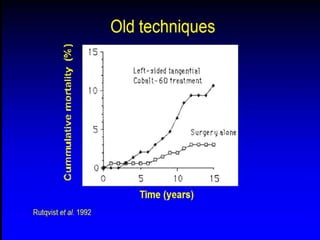
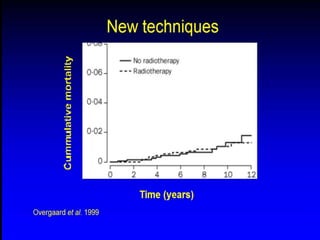
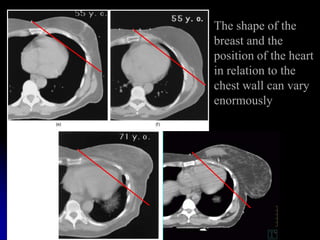
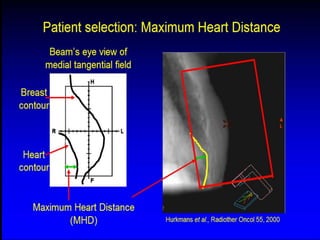
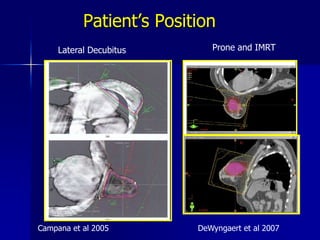
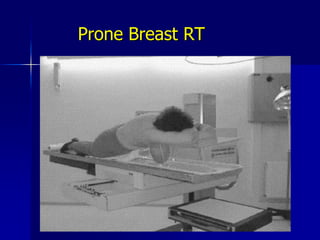
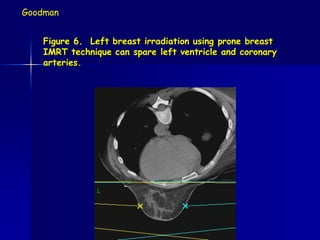
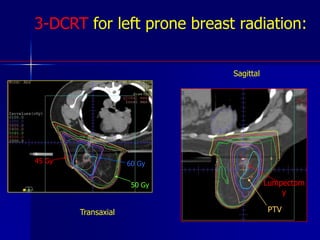
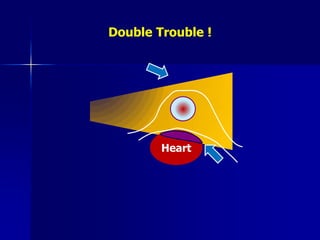
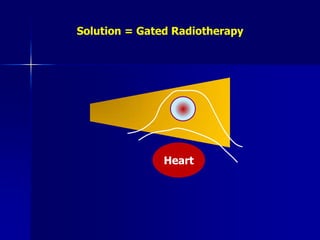
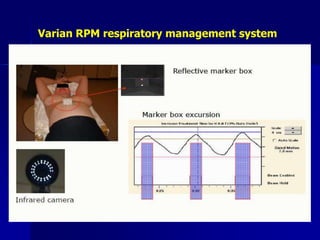
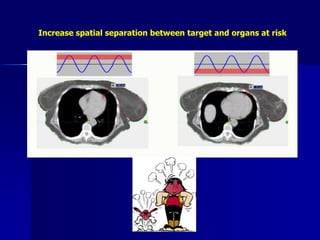
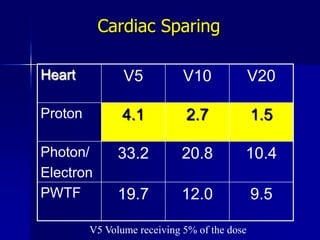
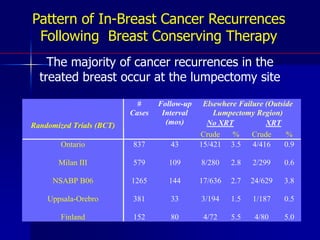
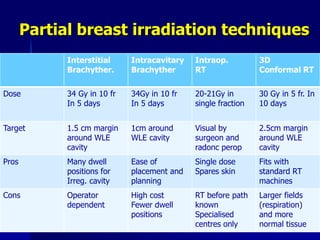
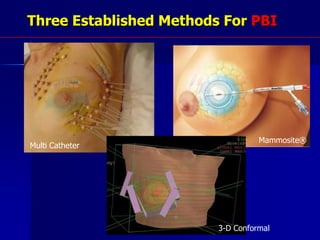
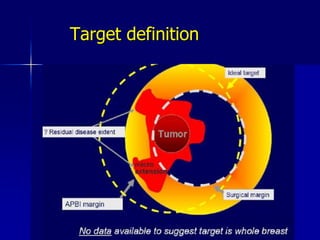
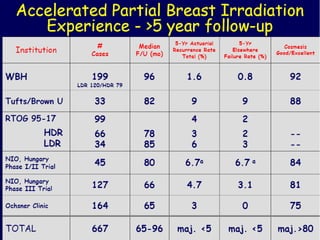
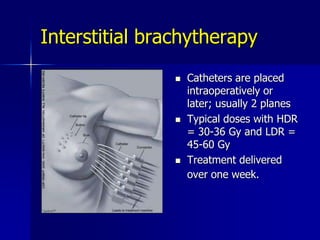
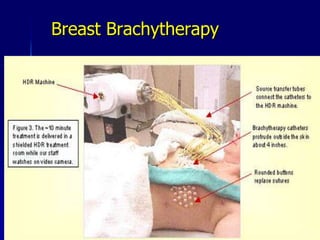
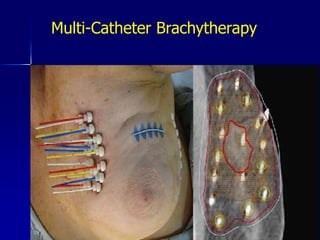
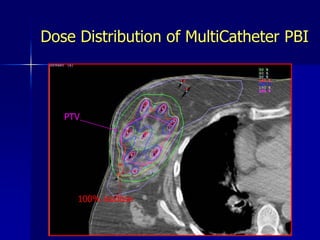
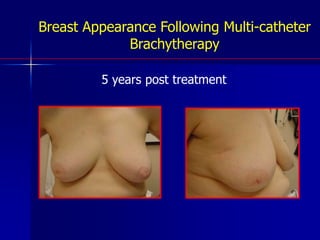
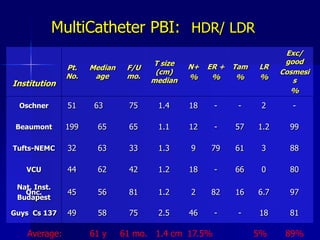
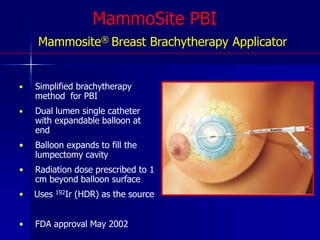
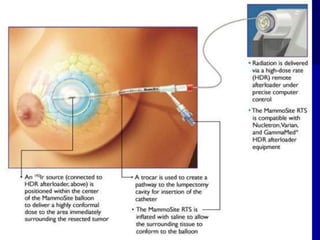
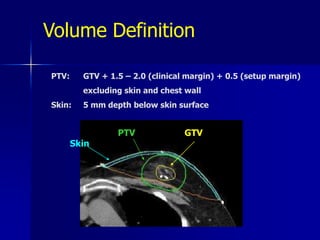
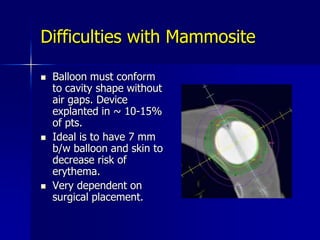
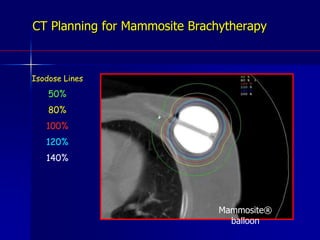
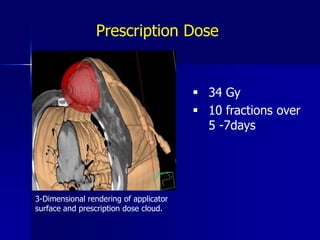
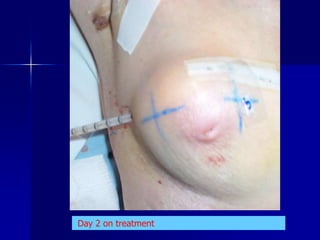
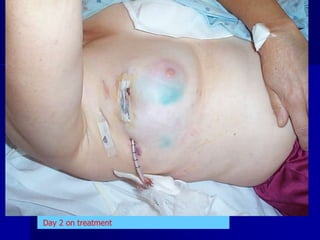
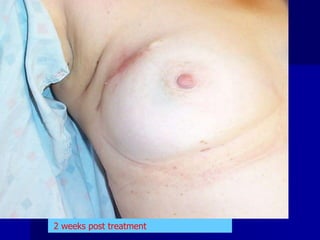
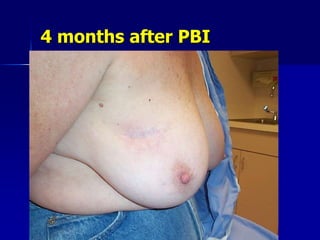
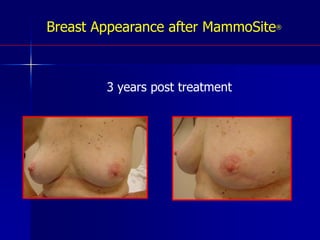
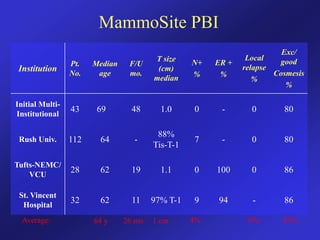
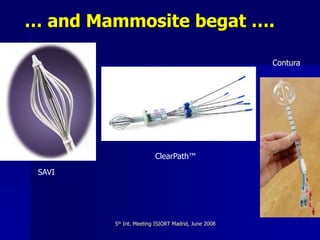
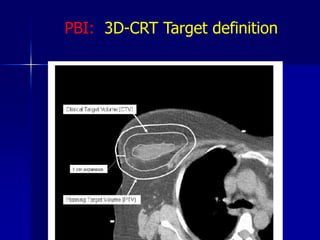
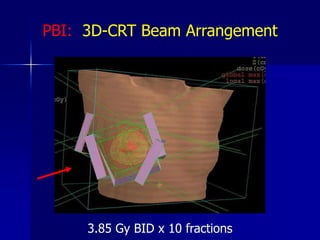
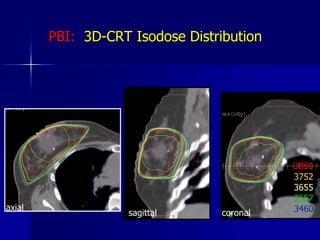
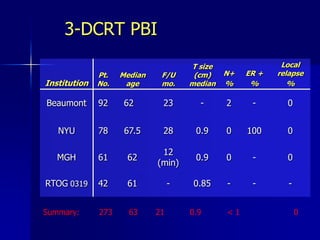
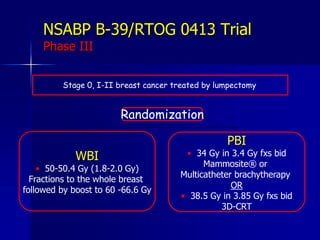
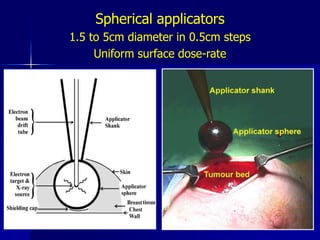
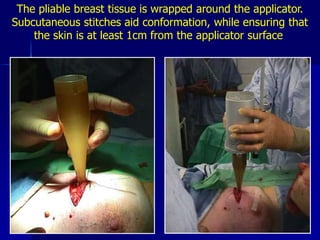
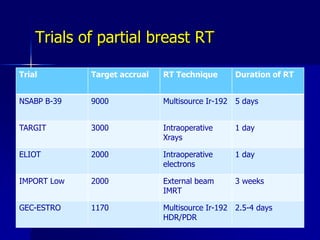
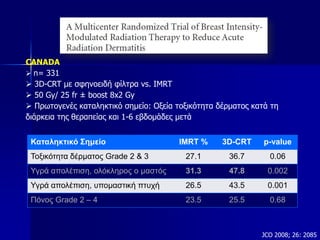
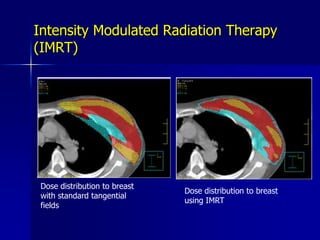
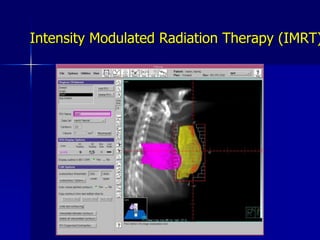
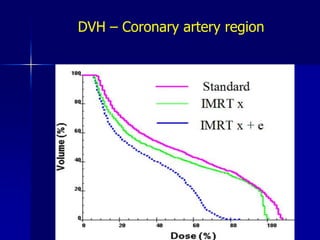
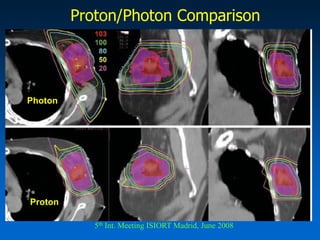
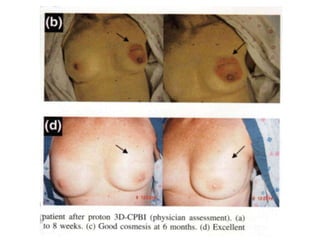
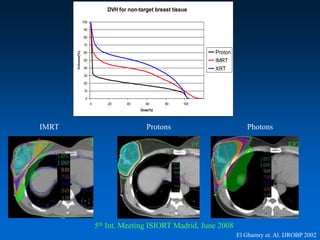
This document discusses therapeutic approaches to breast cancer treatment, focusing on radiotherapy techniques. It provides a historical overview of radiotherapy and highlights results from randomized trials demonstrating the benefits of radiotherapy after lumpectomy in reducing local recurrence rates and improving survival. Modern external beam radiotherapy techniques like 3D conformal radiation therapy and accelerated partial breast irradiation are described. Various techniques for partial breast irradiation including brachytherapy, MammoSite, and 3D-CRT are summarized along with their benefits, limitations, and results from studies. Ongoing trials evaluating partial breast irradiation are also mentioned.