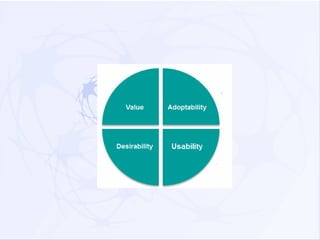
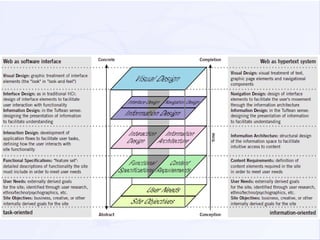
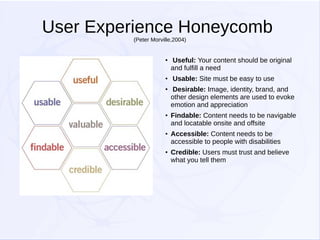
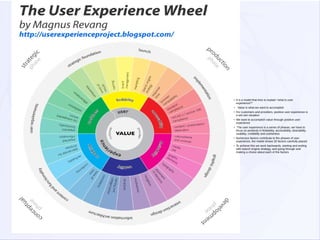
This document discusses various aspects of user experience (UX) design. It begins with definitions of UX, noting that UX refers to the quality of a person's experience interacting with a design. Models for understanding UX are presented, including the UX honeycomb model which describes six factors (useful, usable, desirable, findable, accessible, credible). Evaluation methods for UX are also listed, with over 60 techniques presented. The document aims to define terms and clarify relationships among elements of UX.