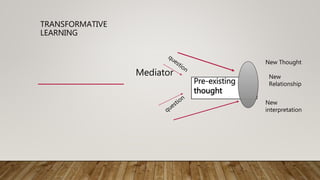
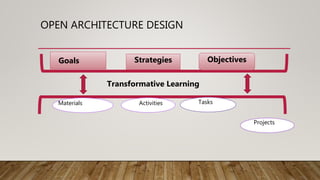
The document discusses the implementation of open architecture in educational settings to enhance transformative learning experiences for adult learners in language acquisition. It emphasizes the role of teachers as mediators, fostering critical self-reflection and critical thinking skills, while engaging learners in a collaborative exploration of cultural and contextual understandings. The adoption of an open architecture approach allows for greater flexibility in curriculum design, supporting the integration of transformative elements into traditional learning materials.