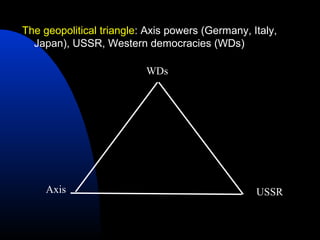
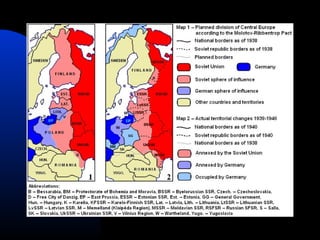
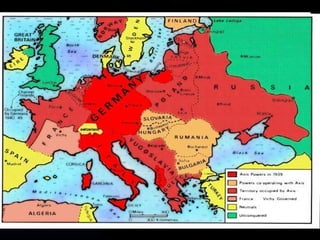
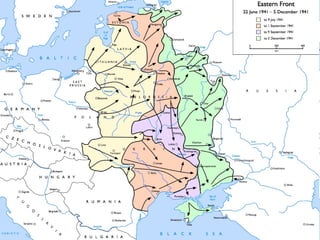
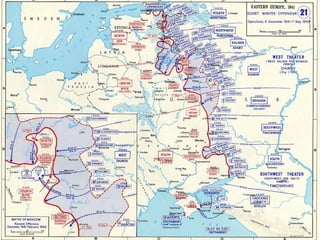
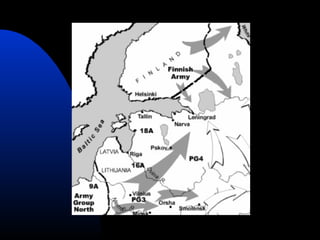
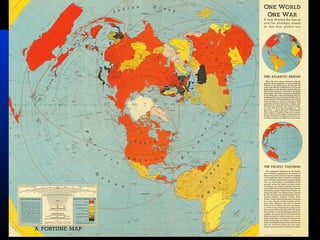
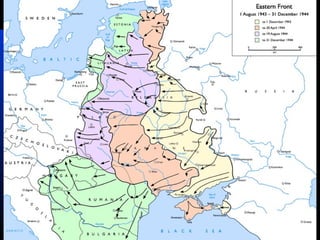
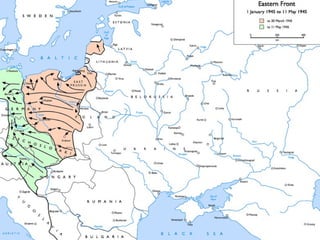
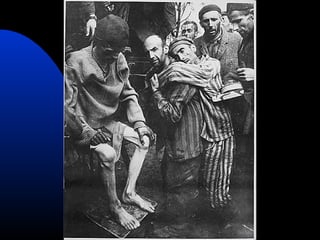
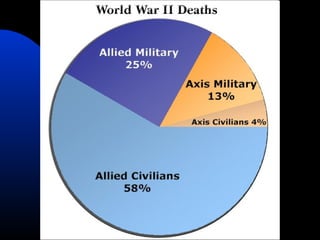
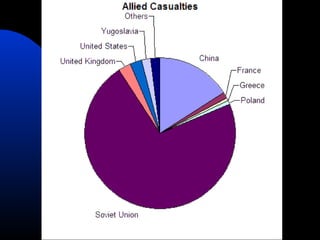
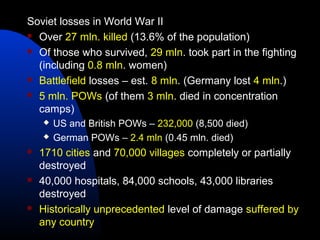
The document discusses the USSR's transformation and military preparedness leading up to and during World War II, focusing on Stalin's strategies and the geopolitical dynamics involving the Axis powers and Western democracies. It highlights key battles, such as the Siege of Leningrad and the Battle of Stalingrad, and presents the immense human and material costs suffered by the USSR. Ultimately, it reflects on the global implications of the conflict and the USSR's role in shaping the outcome of the war.