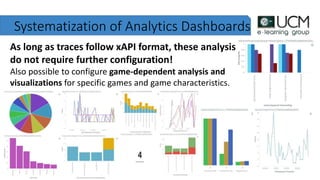
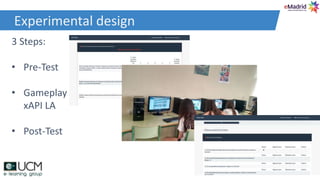
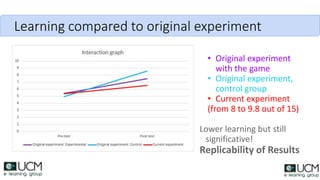
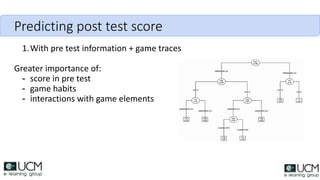
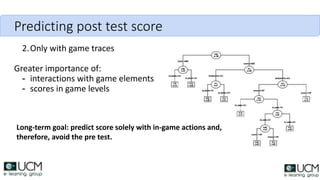
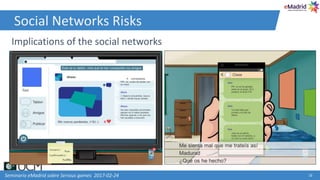
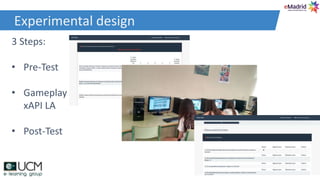
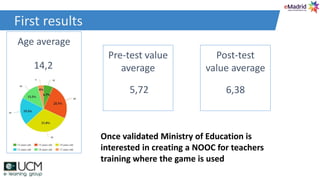
This document discusses how learning analytics can help take a more scientific approach to evaluating serious games. It presents three examples: 1) Using the xAPI standard to track all in-game interactions, 2) Applying game learning analytics to collect, analyze, and visualize learner data from a first aid game pilot study, and 3) Conducting a case study using analytics from a game for teaching subway navigation to people with Down syndrome. The document argues that learning analytics can help create better games and formally validate their impact on learning.