The document outlines a basic obstetric ultrasound training program aimed at educating healthcare professionals in rural areas to enhance patient care and reduce maternal mortality rates. It covers ultrasound principles, terminology, pregnancy assessments, and practical scanning techniques for effective decision-making in obstetric care. Key topics include early pregnancy scanning, including gestational sac and fetal measurements, as well as conditions like oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios.



![WHAT IS ULTRASOUND?
1. High frequency sound[pressure]waves
2. >20,000HZ[2kHz] upper limit of
human hearing.
3. 2MHZ-10MHZ medical diagnostic
frequency range.
4. Ultrasound waves are created by a
vibrating crystal within a ceramic probe.
5. “Piezoelectric” principle- electric
current causes crystals to vibrate,
returning waves create electric current.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingslides-180823124416/85/BASIC-OBSTETRIC-ULTRASOUND-TRAINING-4-320.jpg)
![HISTORY OF ULTRASOUND
- First introduced to medical world
in 1950s.
- However, has its beginnings in the
1880s when Pierre Curie introduced
simple echo sounding methods.
- This led to the discovery of
SONAR- [Sound navigating and
ranging]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingslides-180823124416/85/BASIC-OBSTETRIC-ULTRASOUND-TRAINING-5-320.jpg)
![IN ULTRASOUND THE FOLLOWING EVENTS
HAPPEN:
-The ultrasound machine transmits high frequency [1-12
mhz] sound pulses into the body using the probe.
- The sound waves travel into the body and hit a
boundary between tissues [e.g between fluid and soft
tissue or between soft tissue and bone].
- Some of the sound waves reflect back to the probe
while some travel on further until they reach another
boundary and reflect back to the probe.
- The reflected waves are detected by the probe and
relayed to the machine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingslides-180823124416/85/BASIC-OBSTETRIC-ULTRASOUND-TRAINING-6-320.jpg)

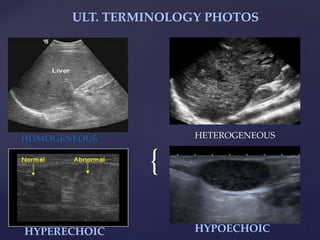
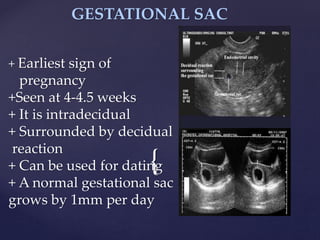
![{
ULT. TERMINOLOGY CONT’D
ECHOGENICITY: Capacity of a structure in the path of an
ultrasound beam to reflect back sound waves.
HYPERCHOGENIC: Refers to materials that produces
echoes that are stronger than normal or surrounding tissues
ANECHOIC: Free from echoes or reverberations
COMPLEX: Lesions composed of anechoic[cystic] and
echogenic[ solid] components.
ECHOES: The reflection of an ultrasound wave back to the
transducer from a structure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingslides-180823124416/85/BASIC-OBSTETRIC-ULTRASOUND-TRAINING-8-320.jpg)



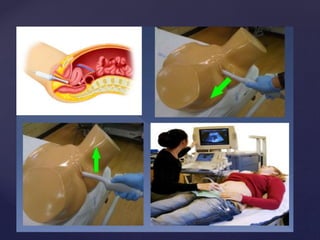

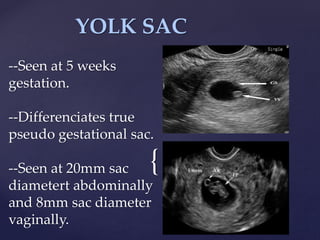




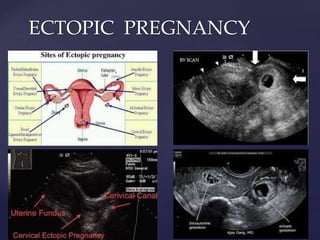
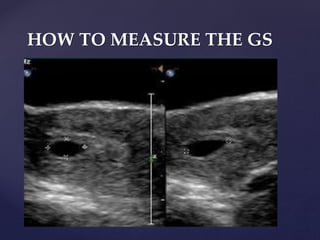
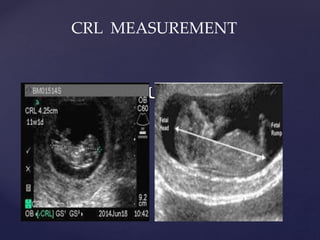

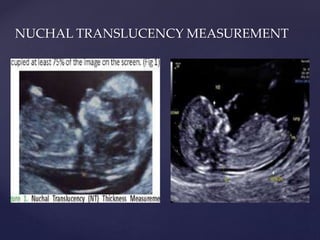
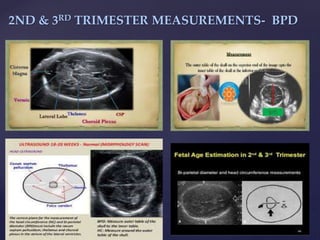

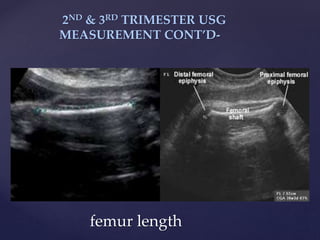
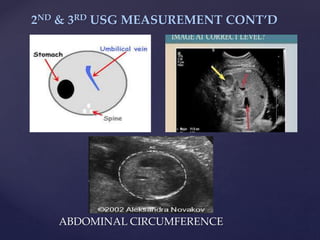
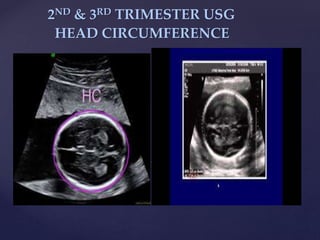
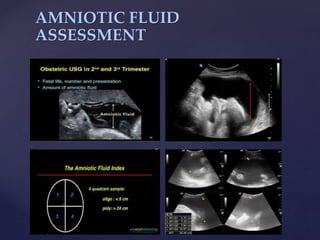
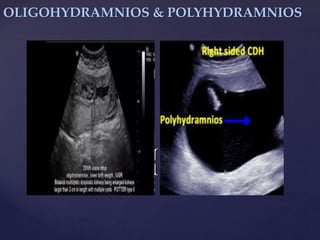
![{
OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS
-Defn: Considerate deficiency of amniotic
fluid volume <200mls, 0.5-5.5percent of all
pregnancies
-Reasons: Fetal diseases,[ malformations,
hypotrophia, acardiacus]: maternal diseases[
Diabetes with microangiopathy, gestosis],
PROM, bad hydration, post-term pregnancy.
-Symptoms: Decreased fluid, fetal
movements, circumference of the abdomen,
easy to feel fetus parts and hard to move
presenting parts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingslides-180823124416/85/BASIC-OBSTETRIC-ULTRASOUND-TRAINING-34-320.jpg)
![{
POLYHYDRAMNIOS
Defn: Excess amniotic
fluid [the largest
single pocket
measuring 11cm
approximately]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingslides-180823124416/85/BASIC-OBSTETRIC-ULTRASOUND-TRAINING-35-320.jpg)