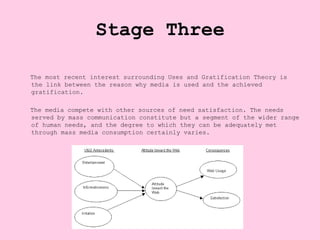
The Uses and Gratification Theory proposes that people actively seek out media to fulfill certain needs, and over time researchers have identified common reasons or gratifications that influence media selection, such as diversion, social interaction, and learning. The theory developed in three stages from 1944 to the present, with early work identifying gratifications for listening to soap operas and developing a formula for media selection, to later research grouping common uses of media and studying motivations for consuming different types of content.