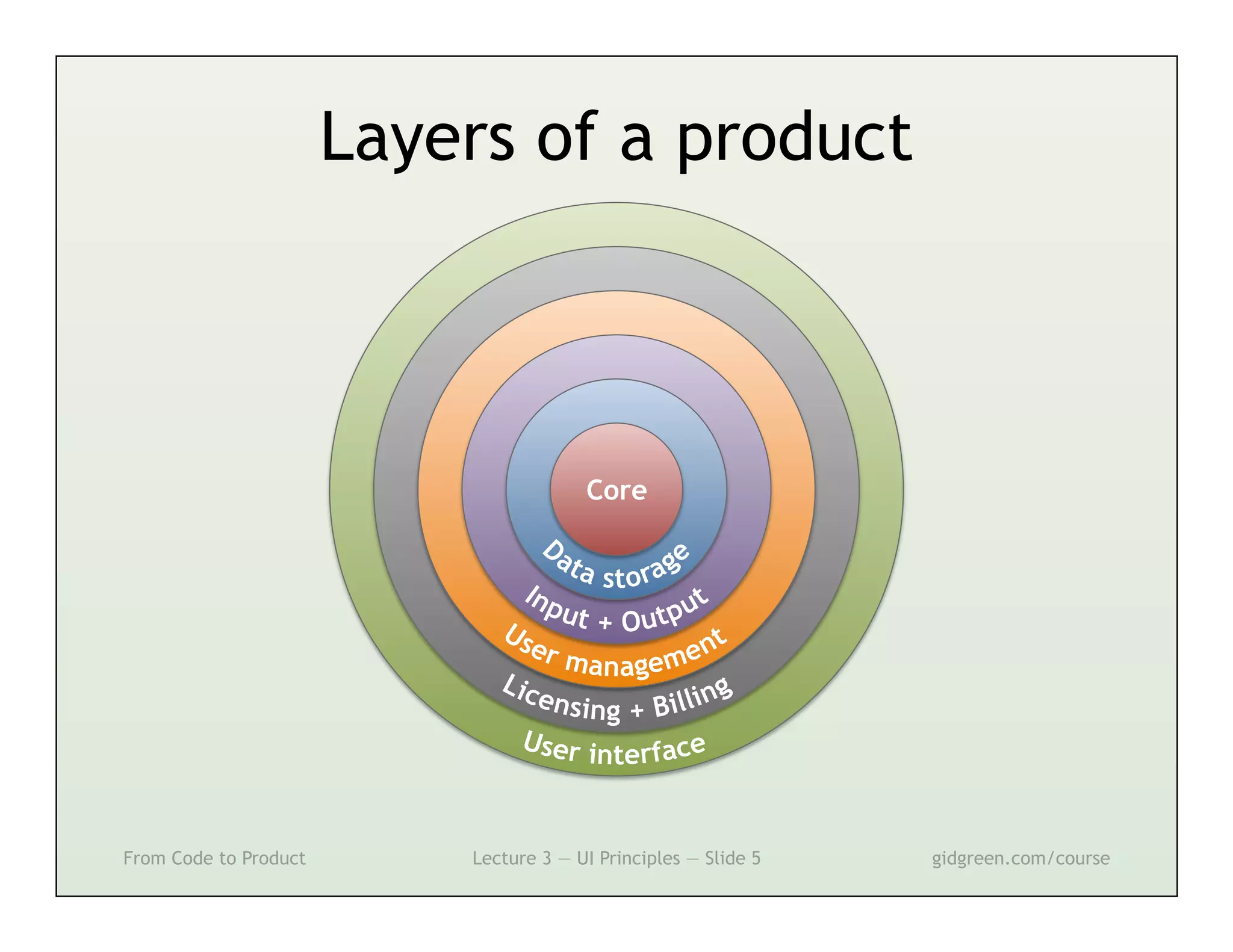
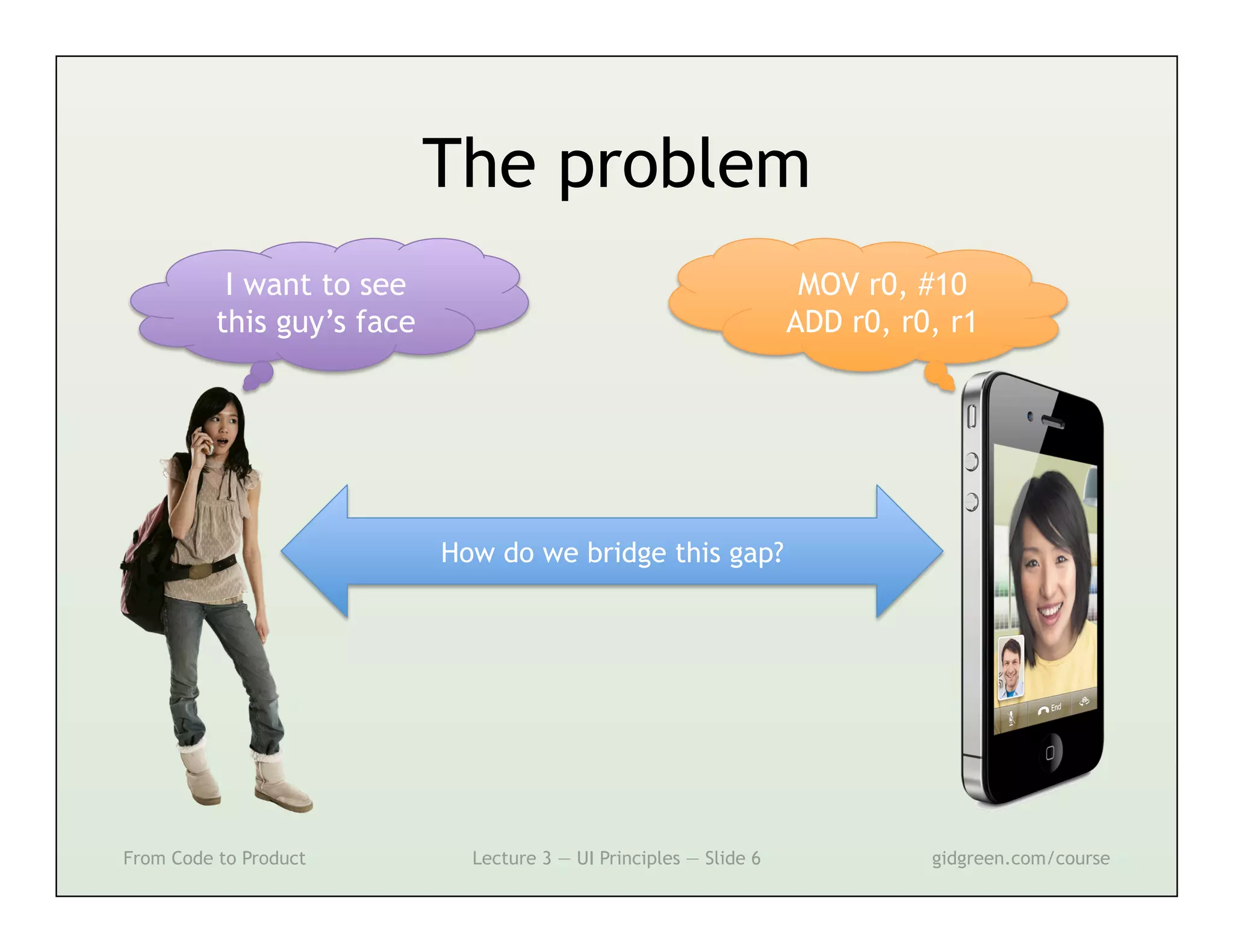
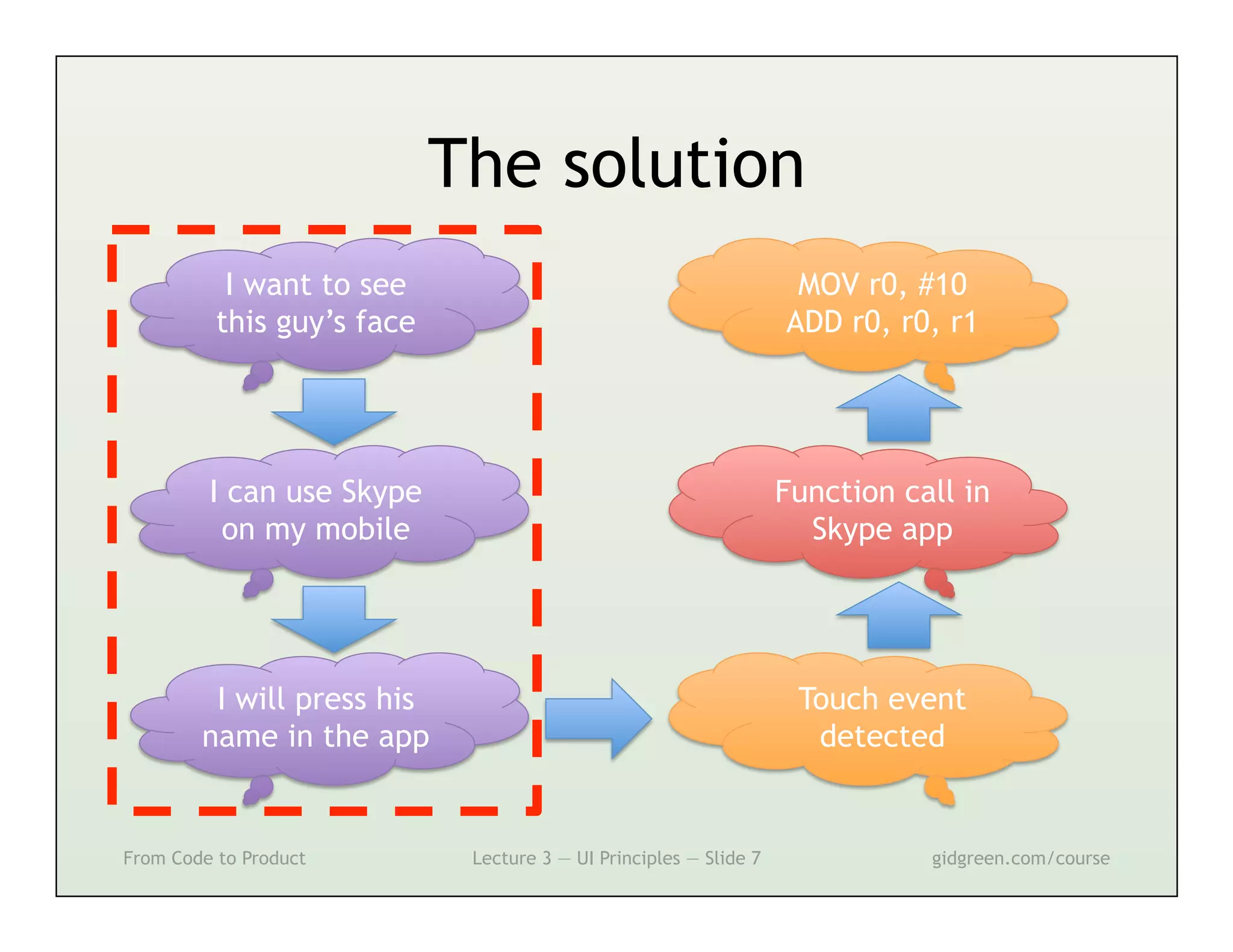
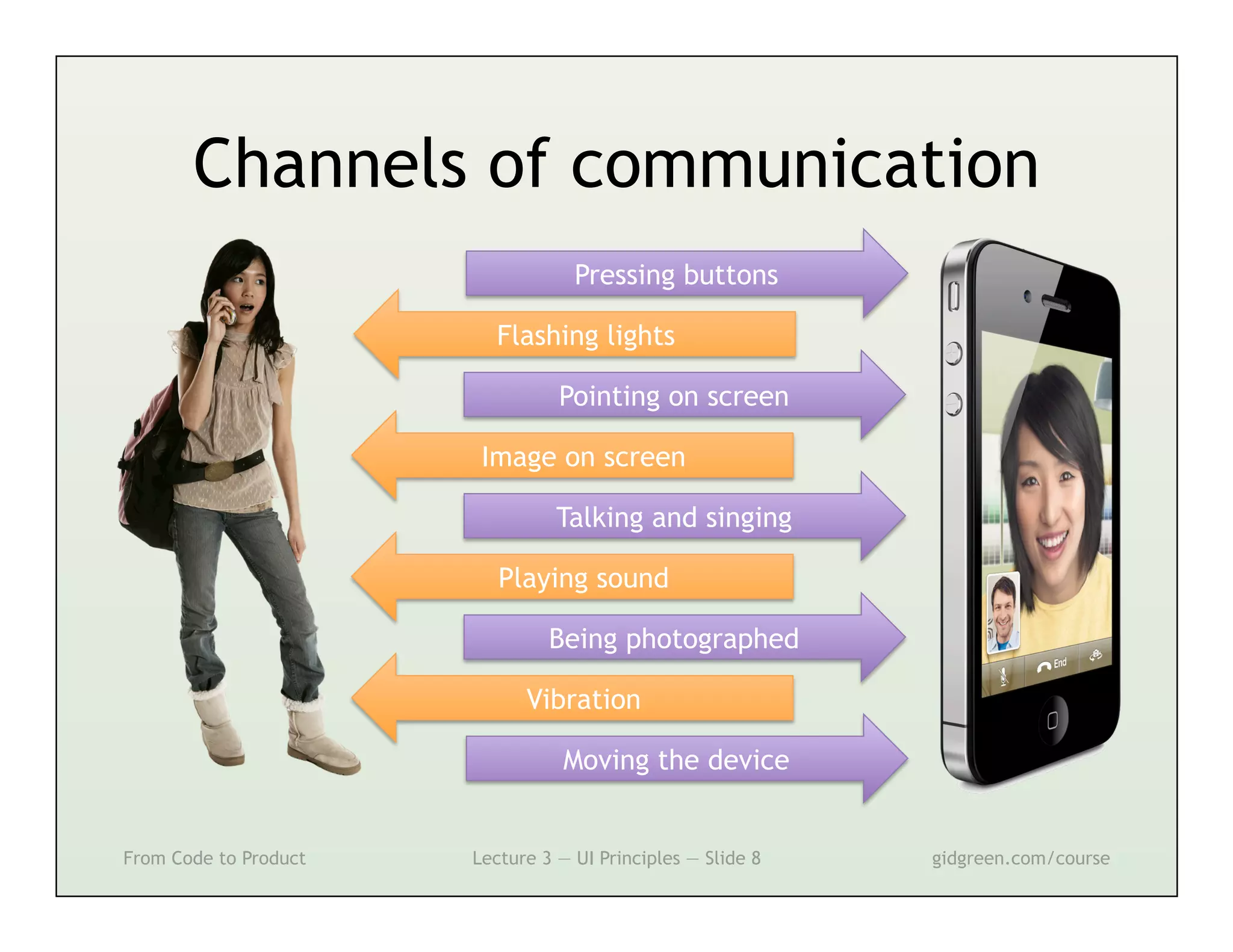
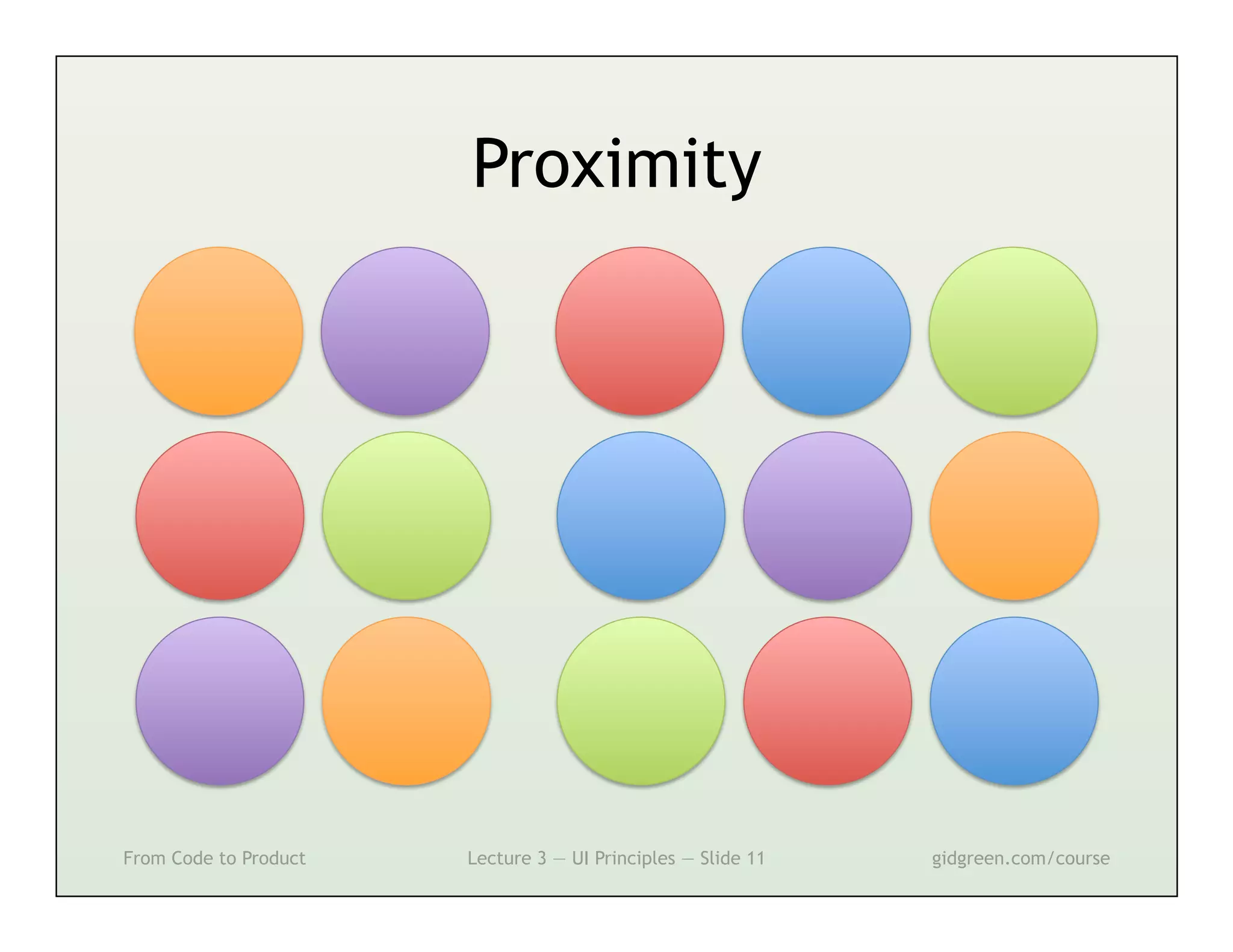
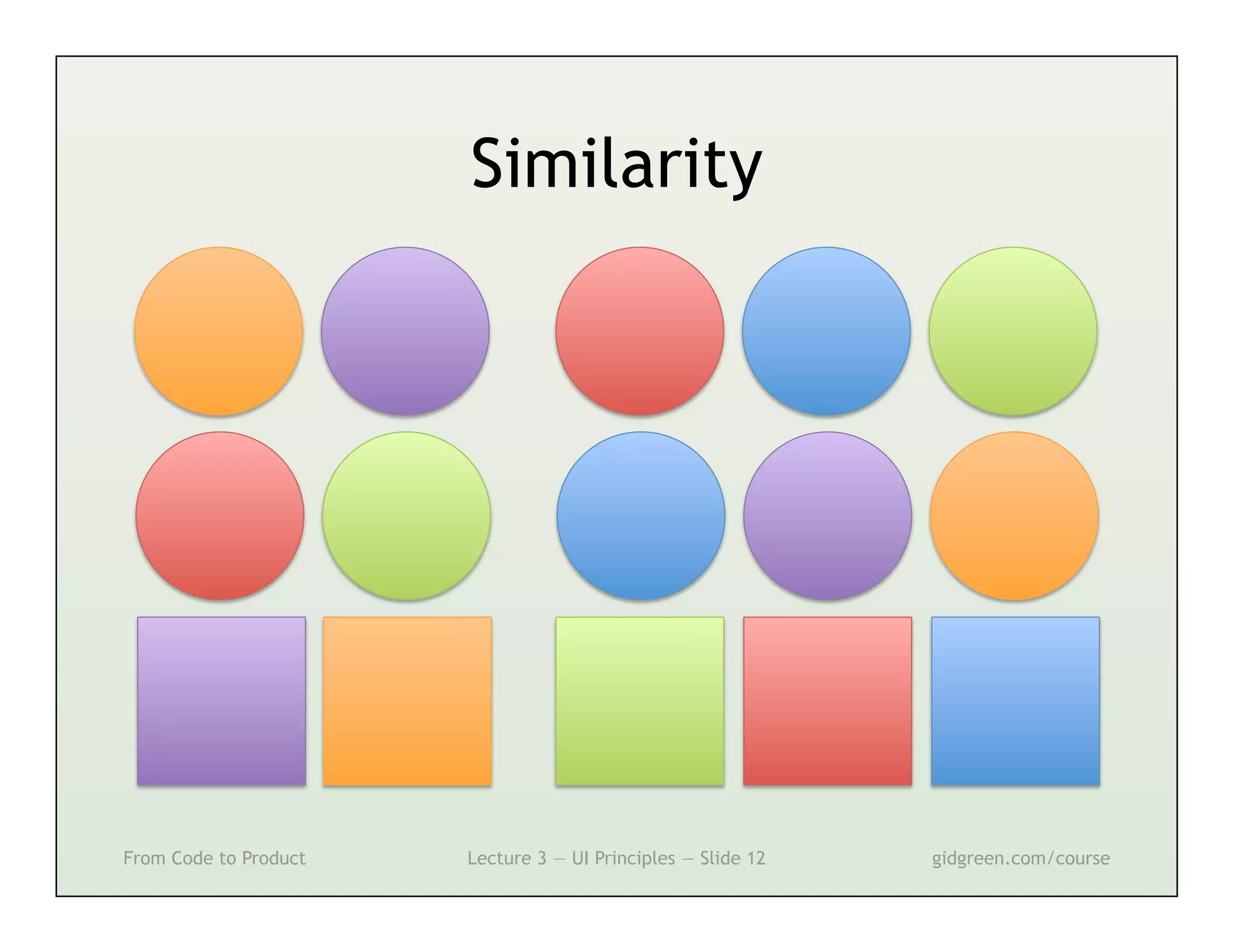
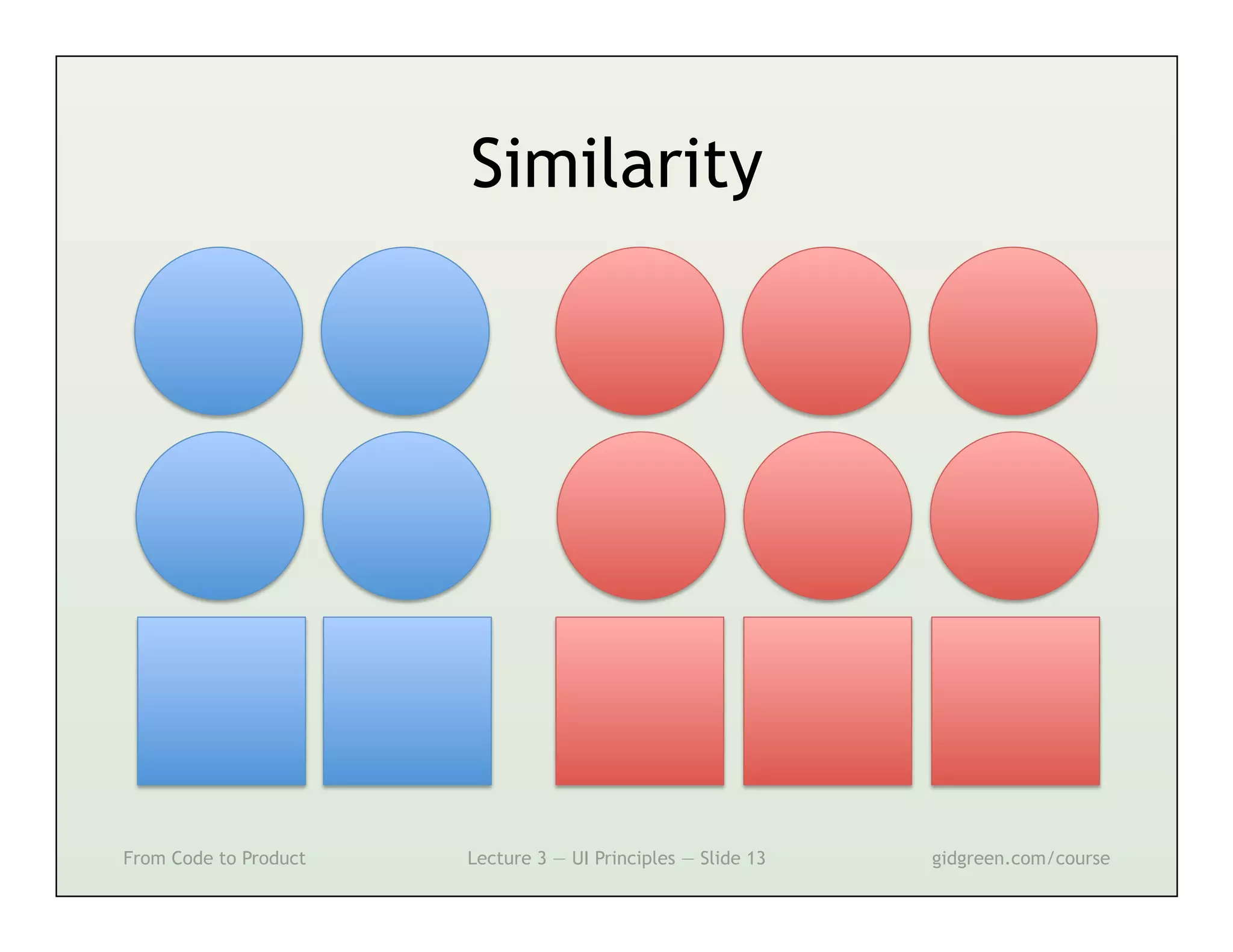
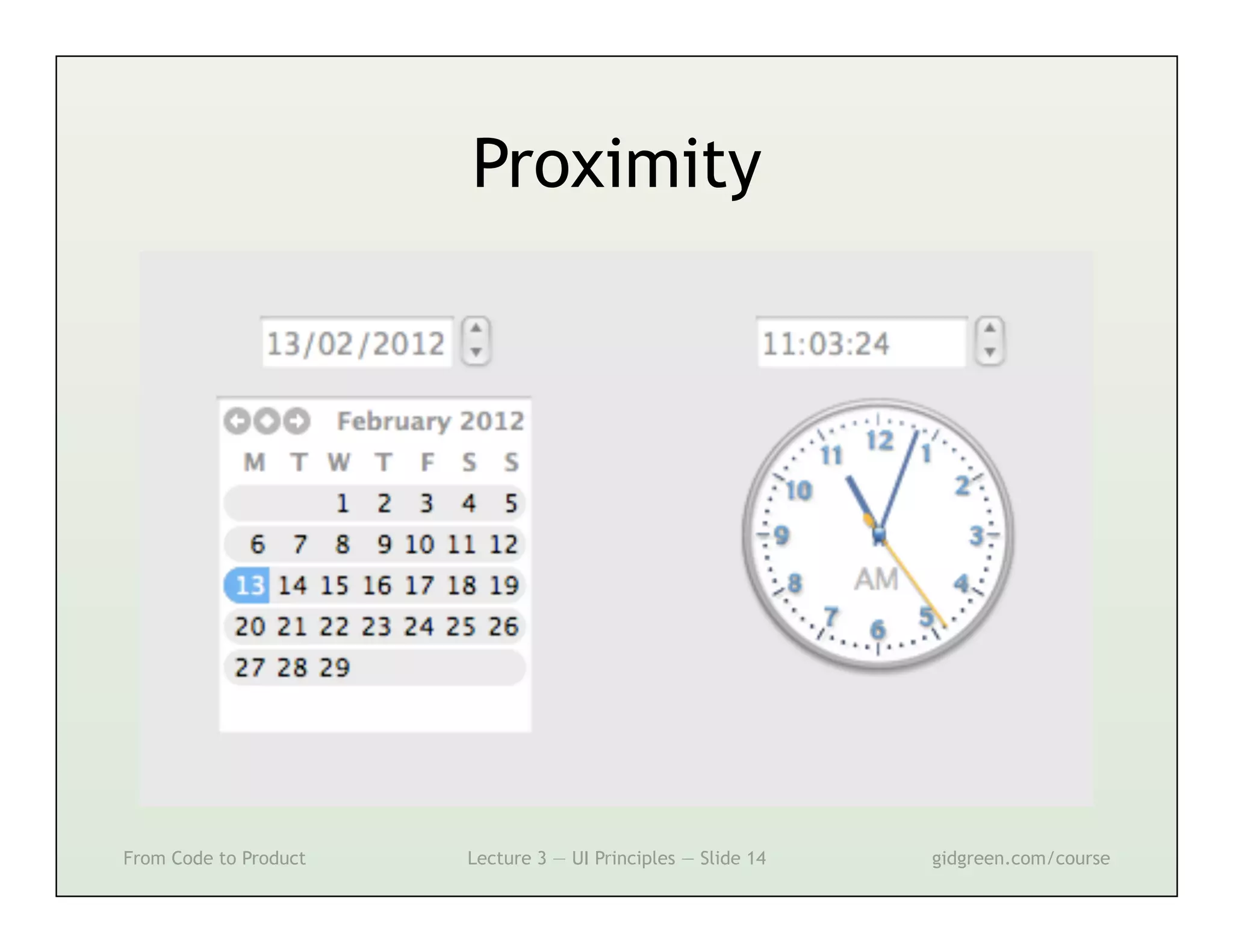
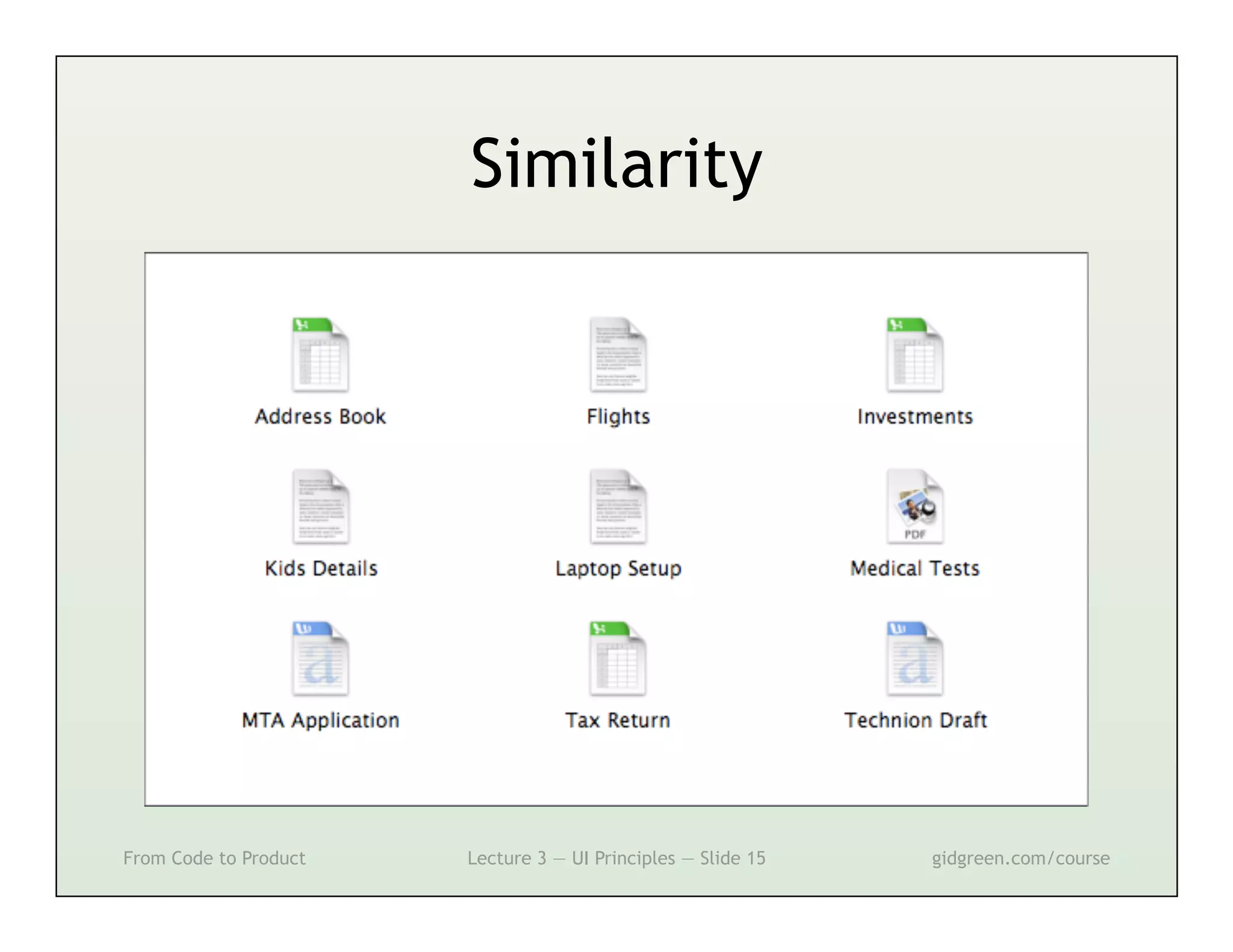
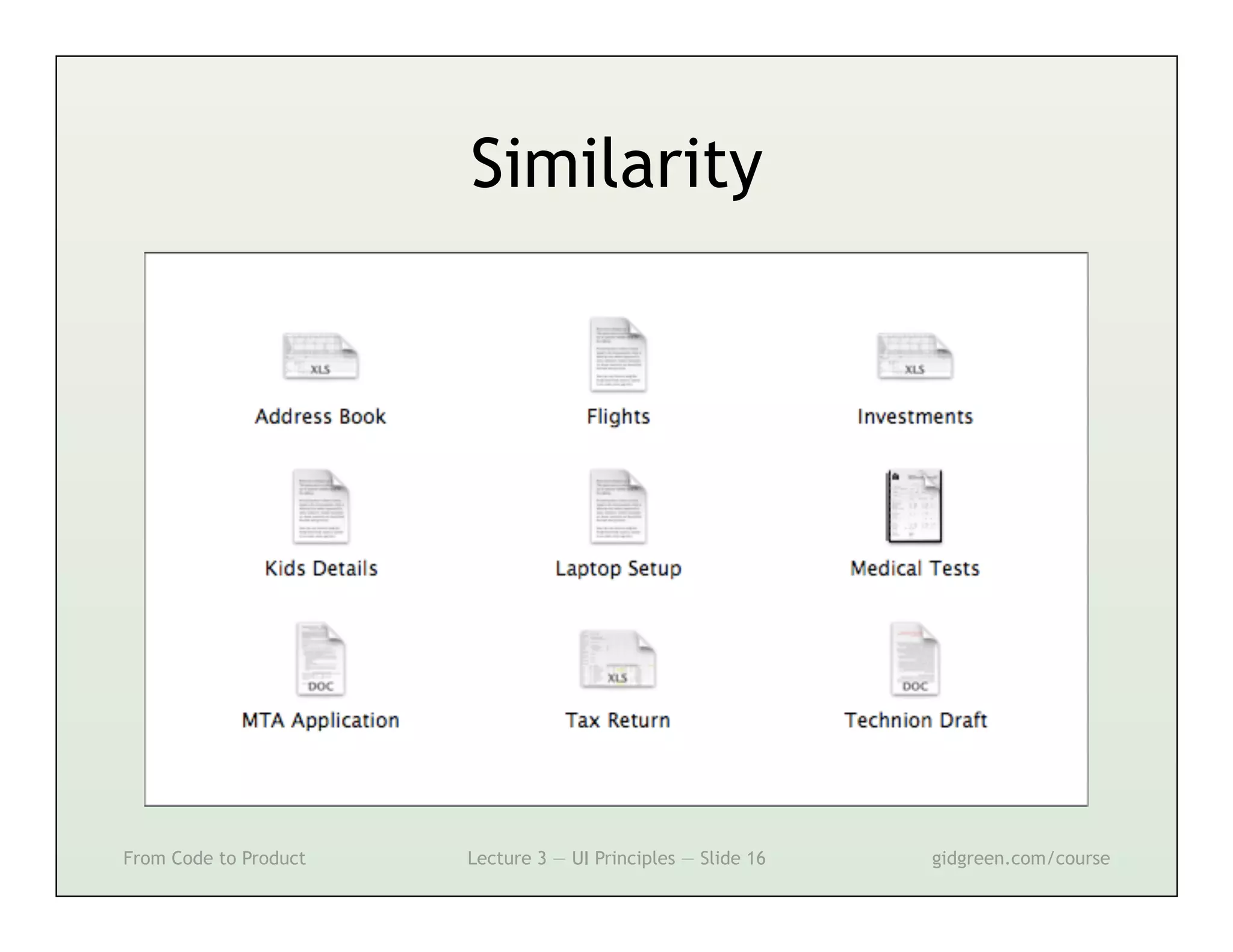
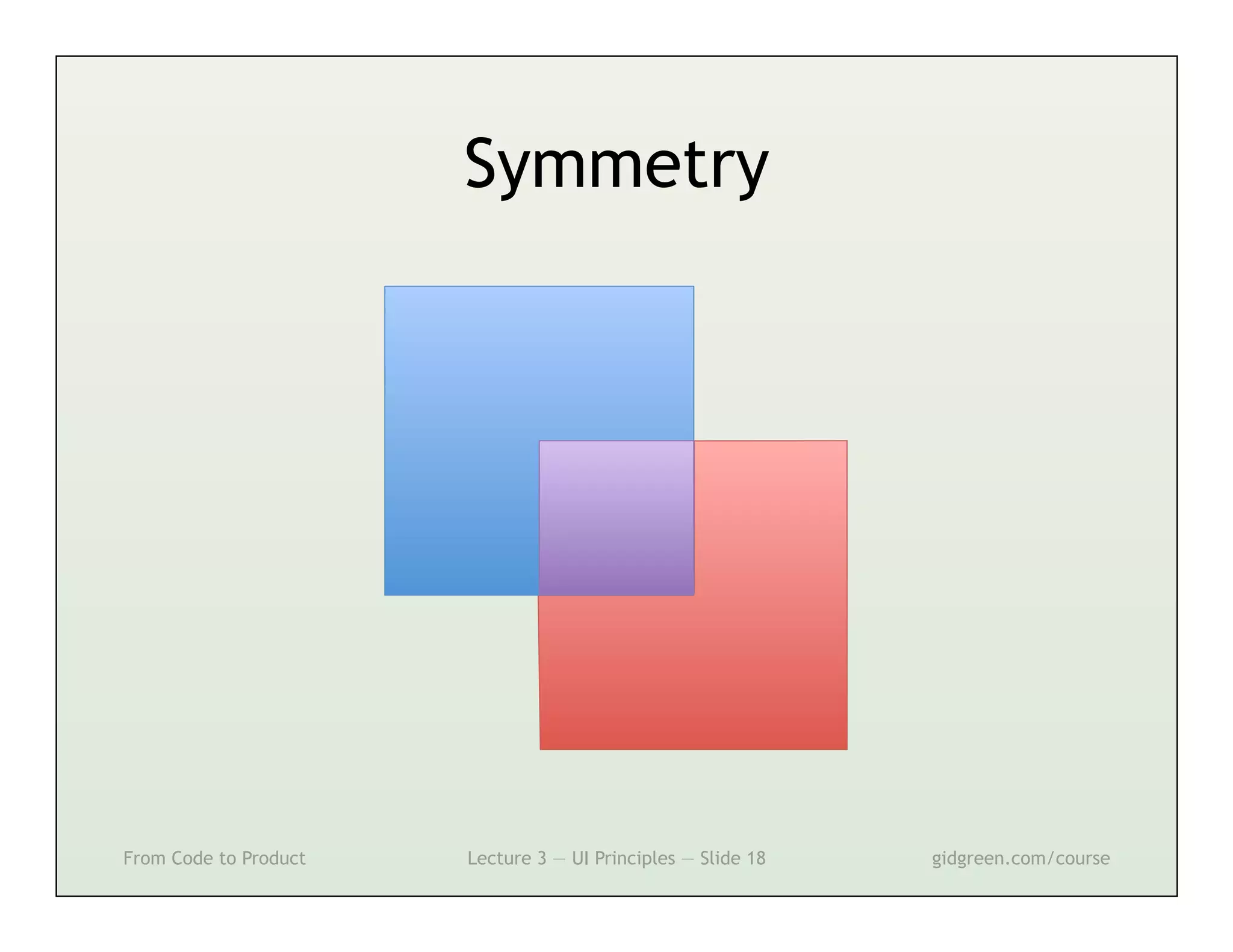
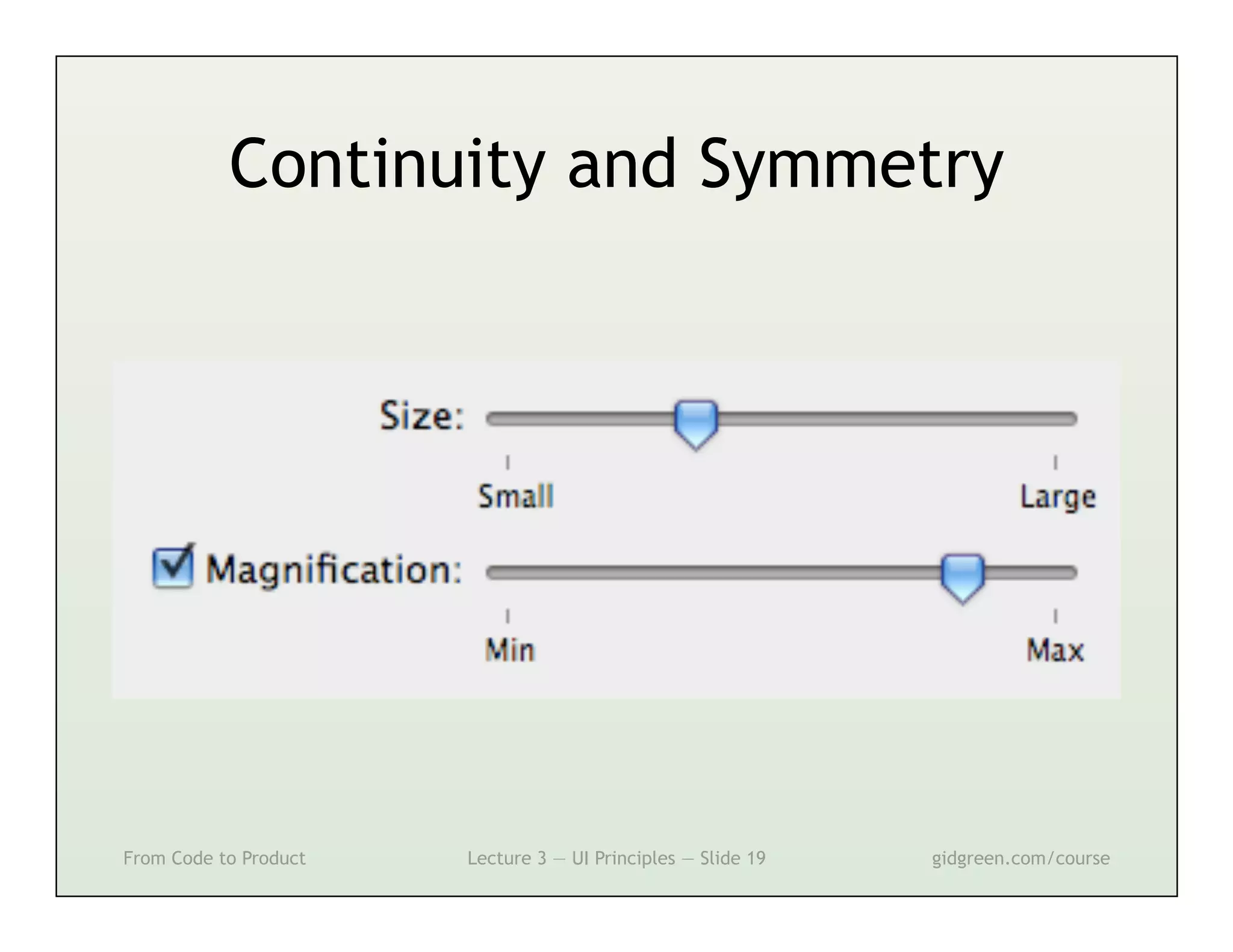
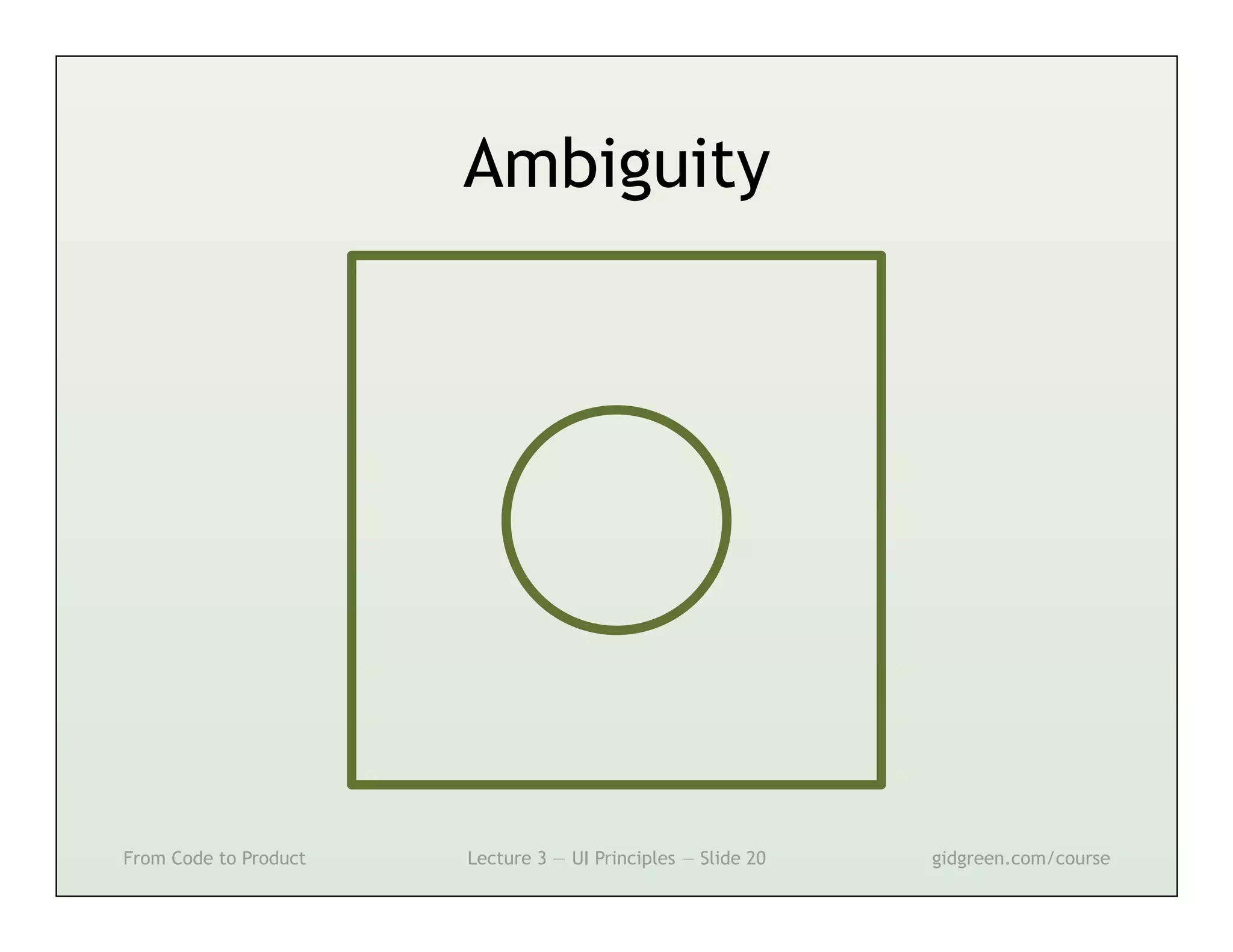
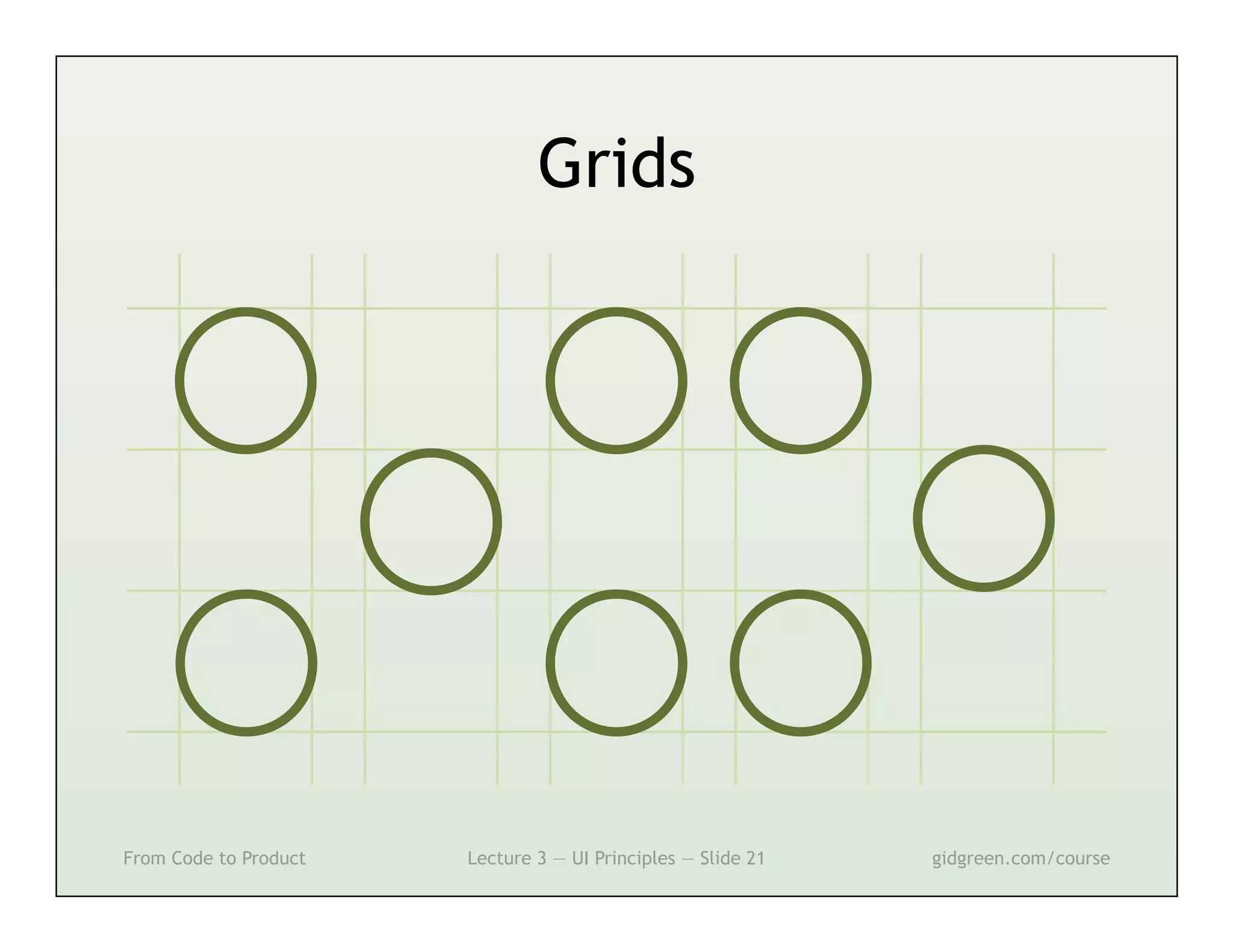
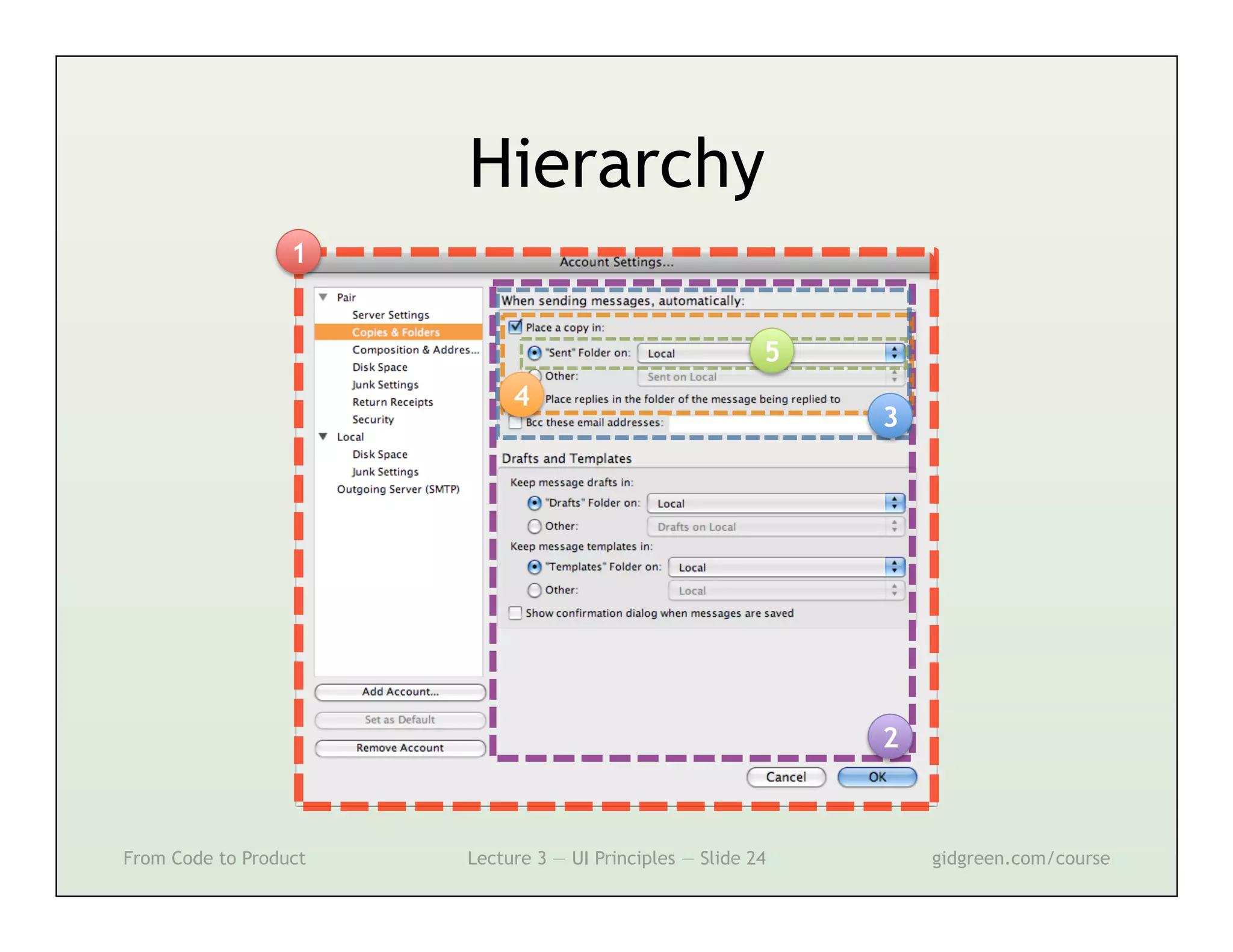
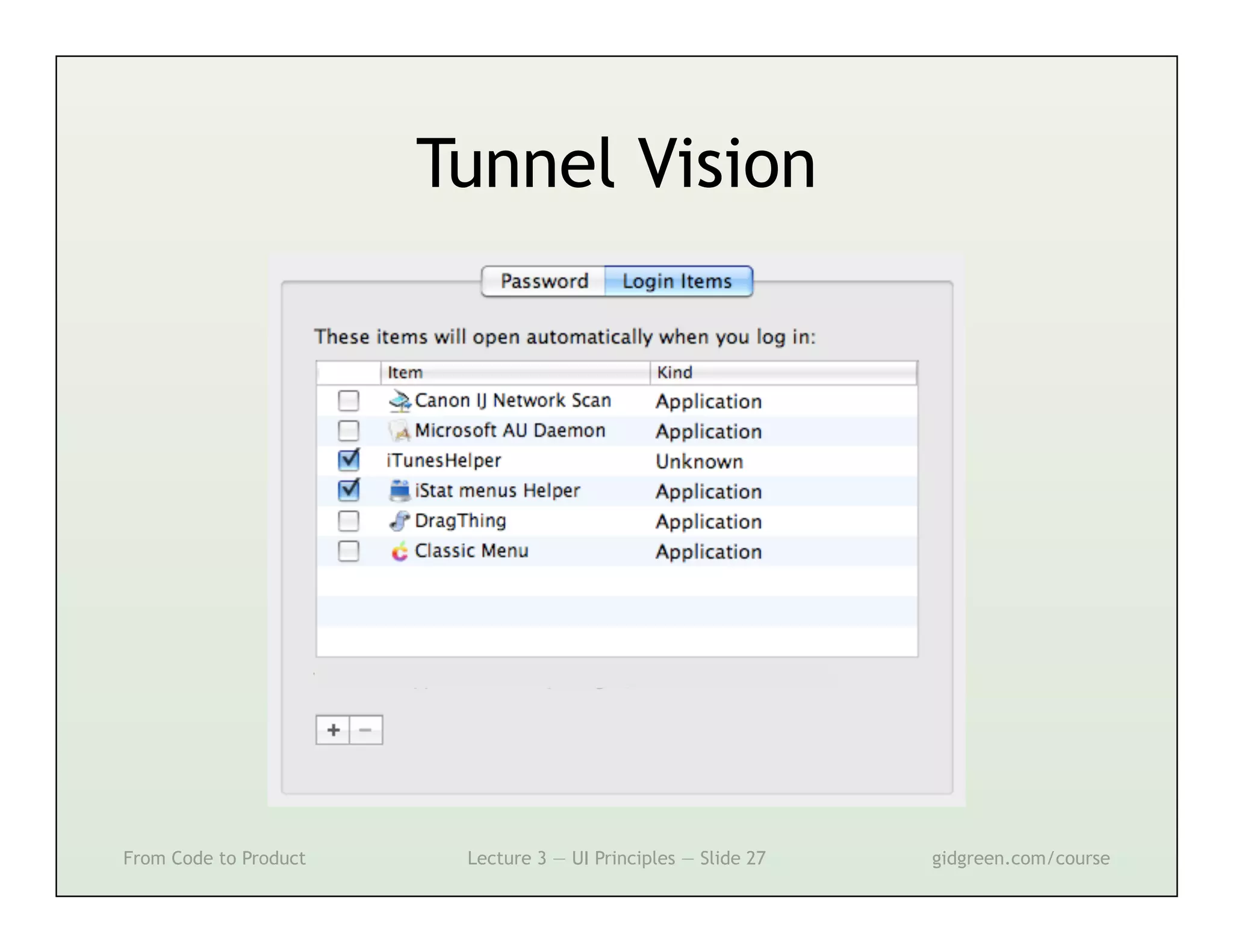
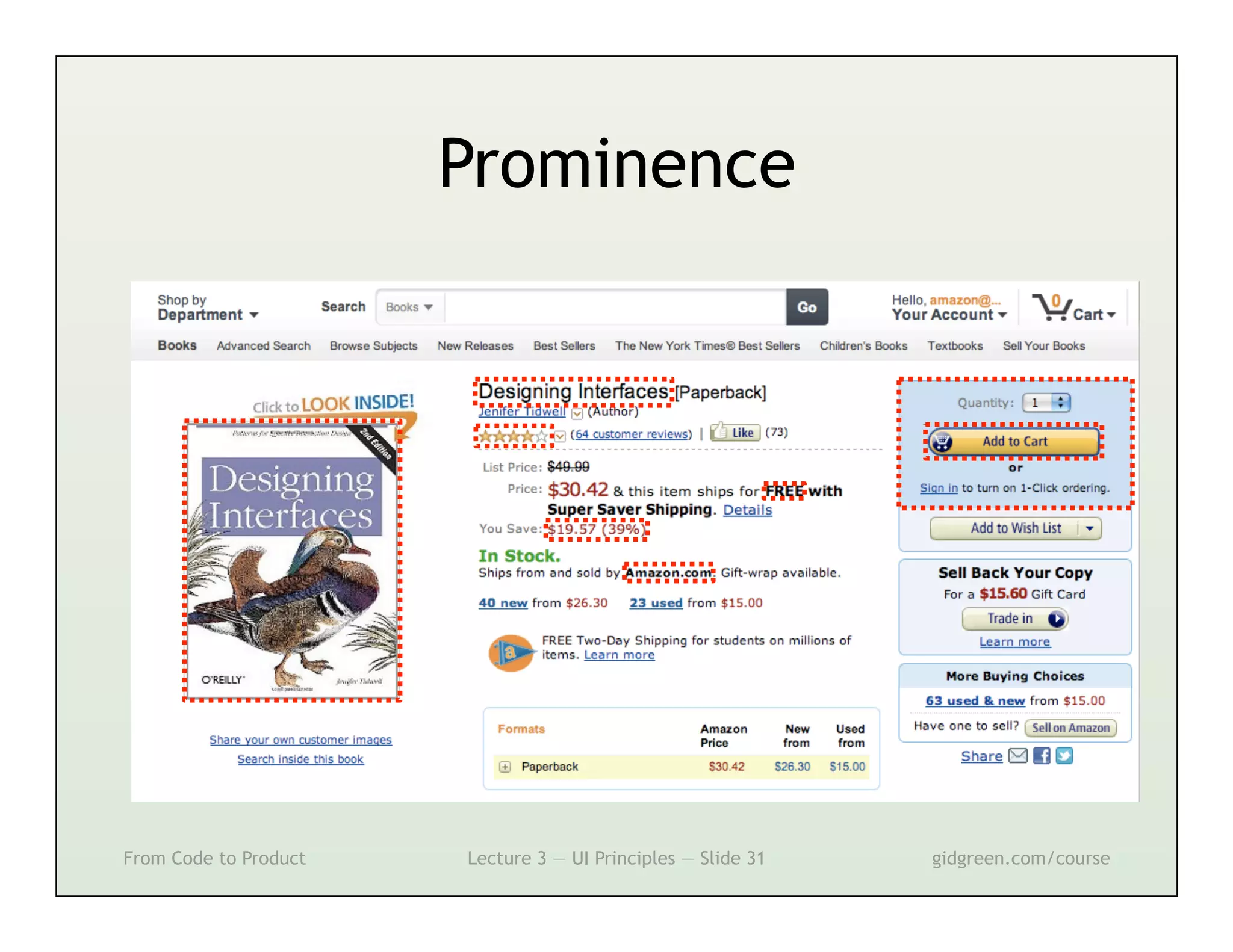
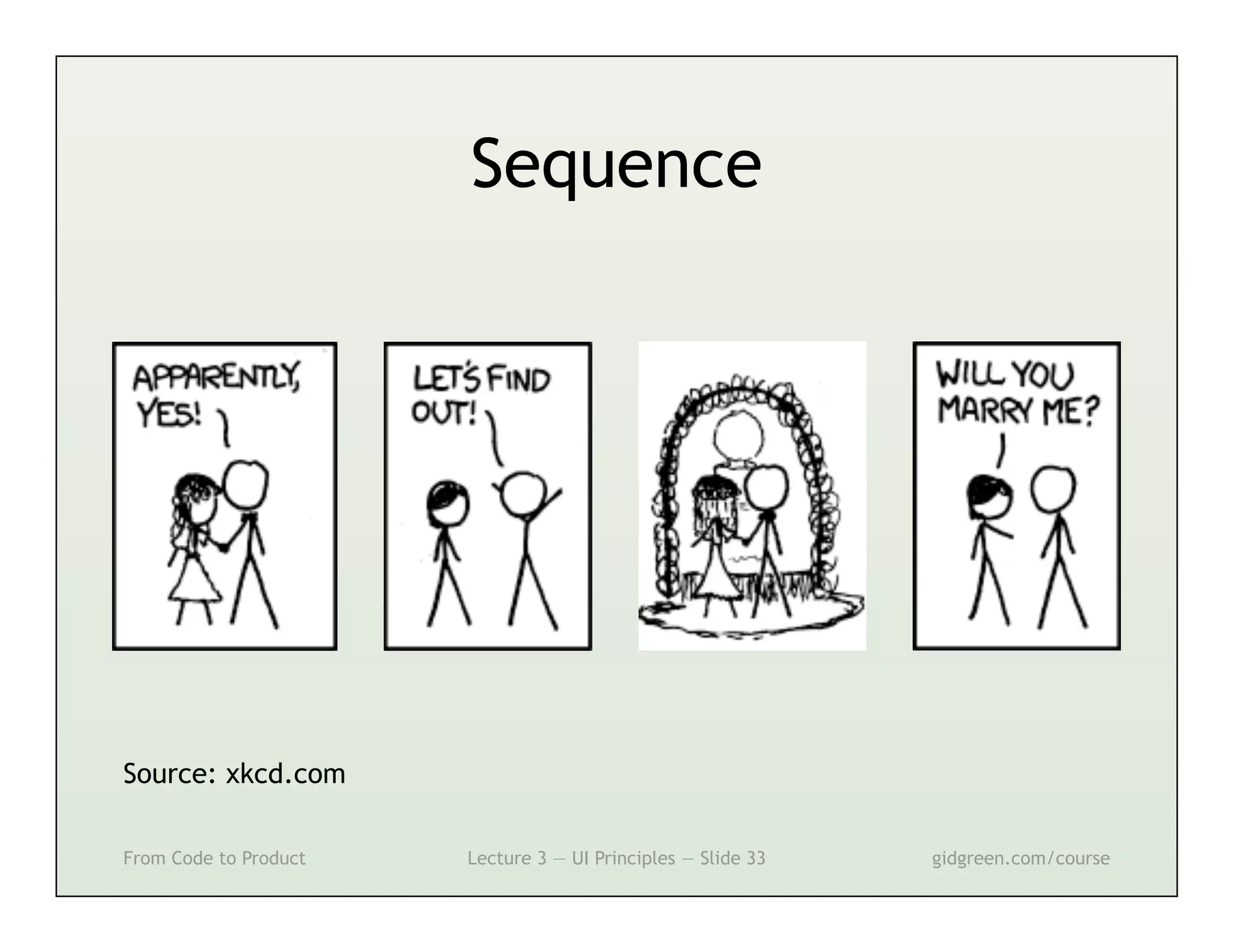
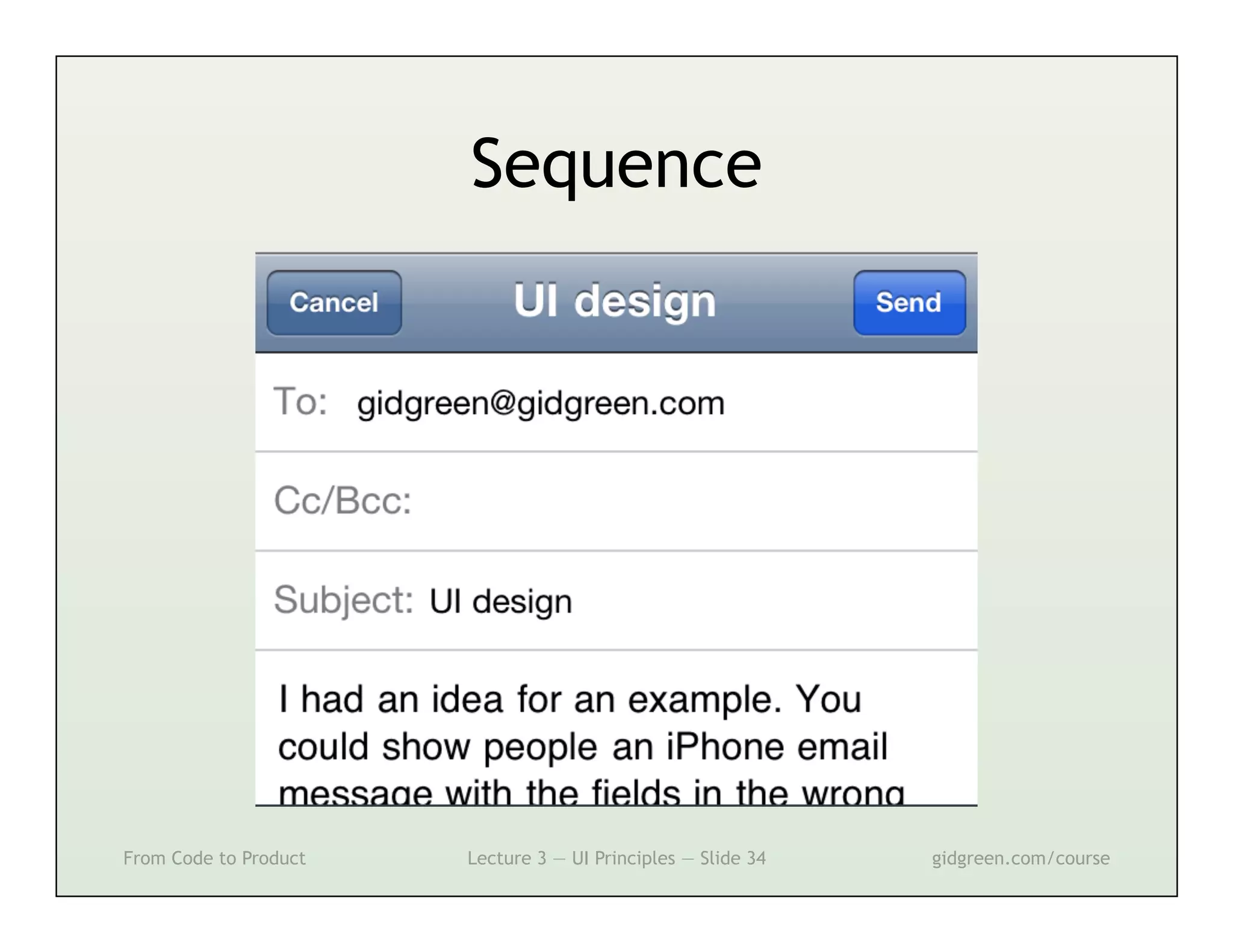
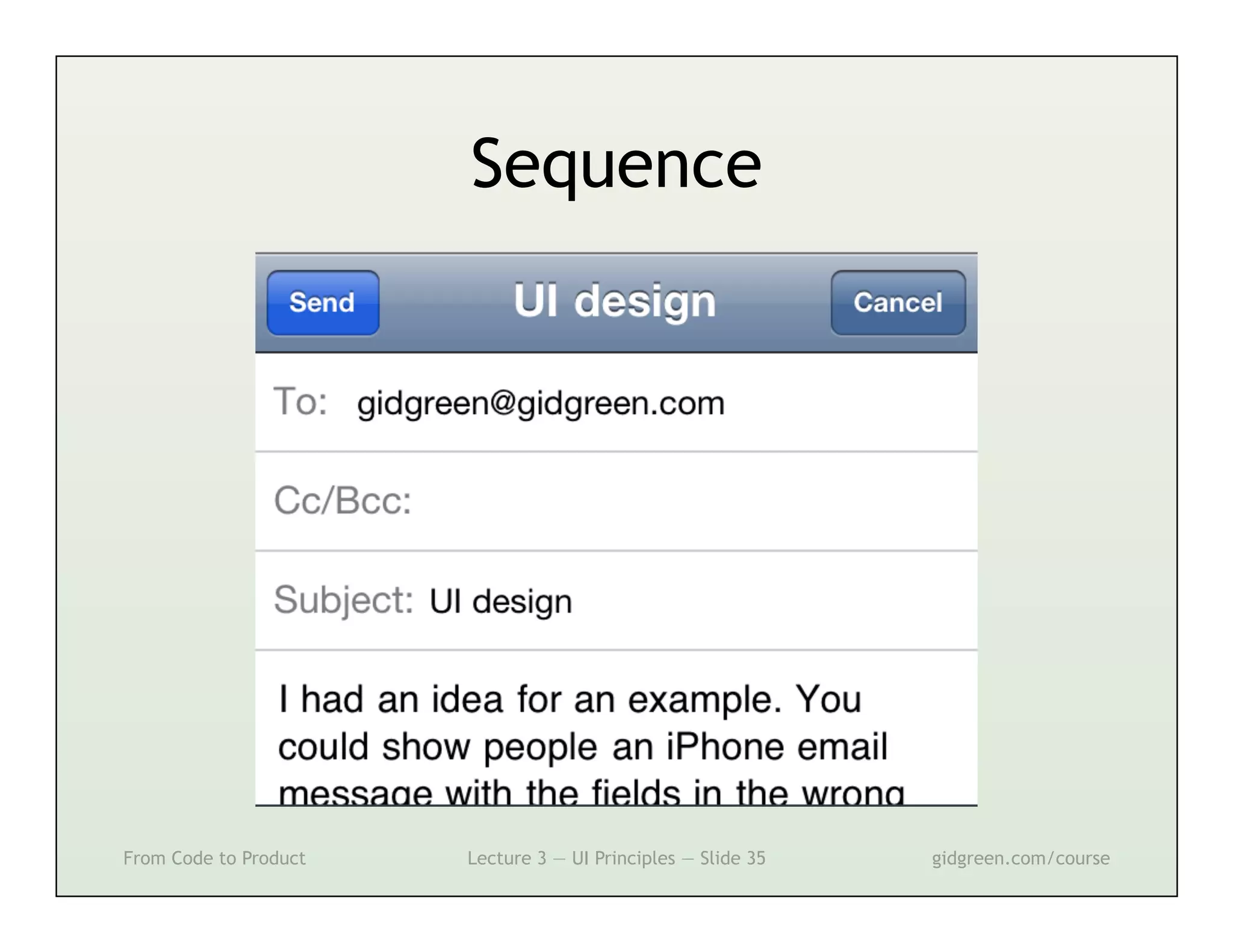
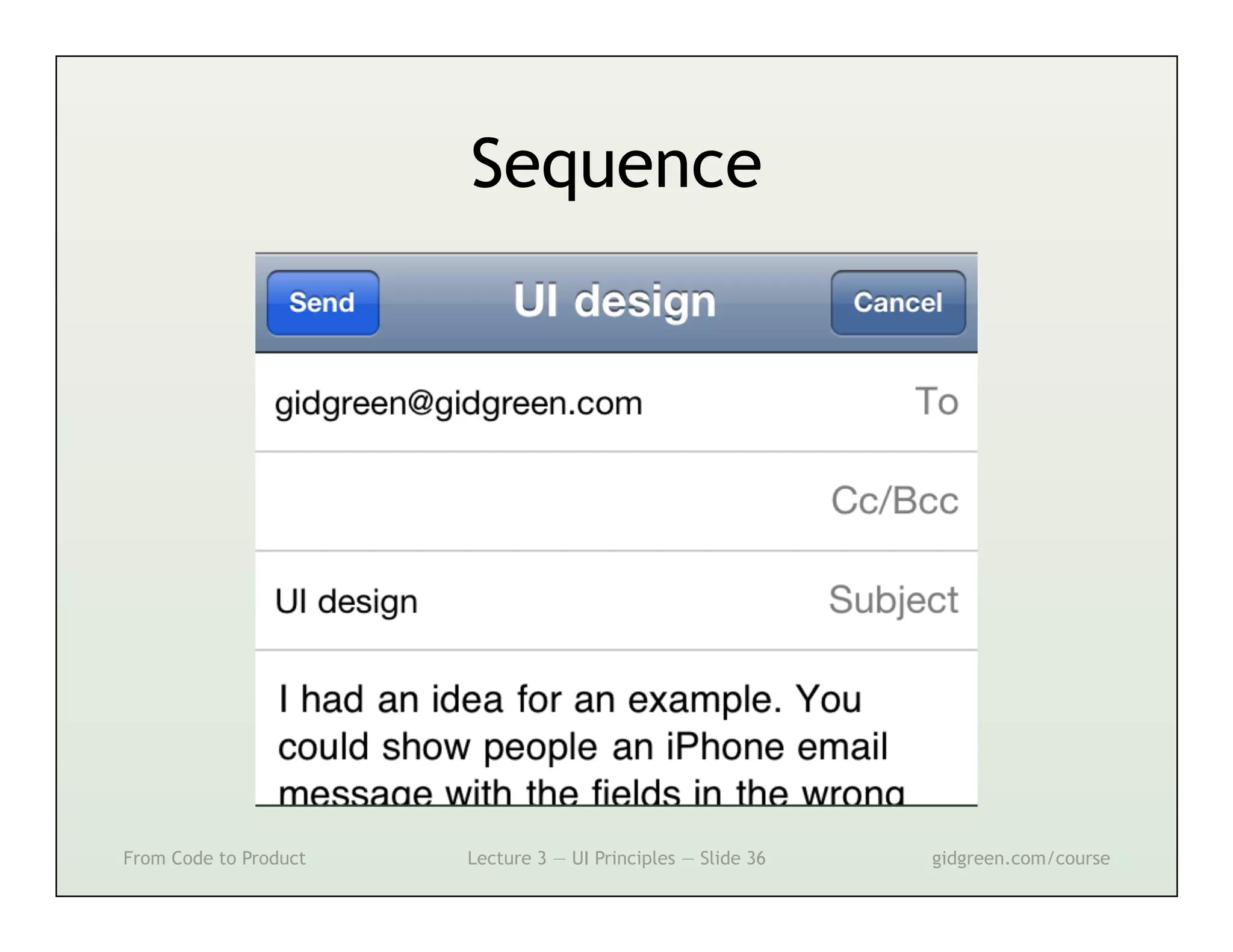
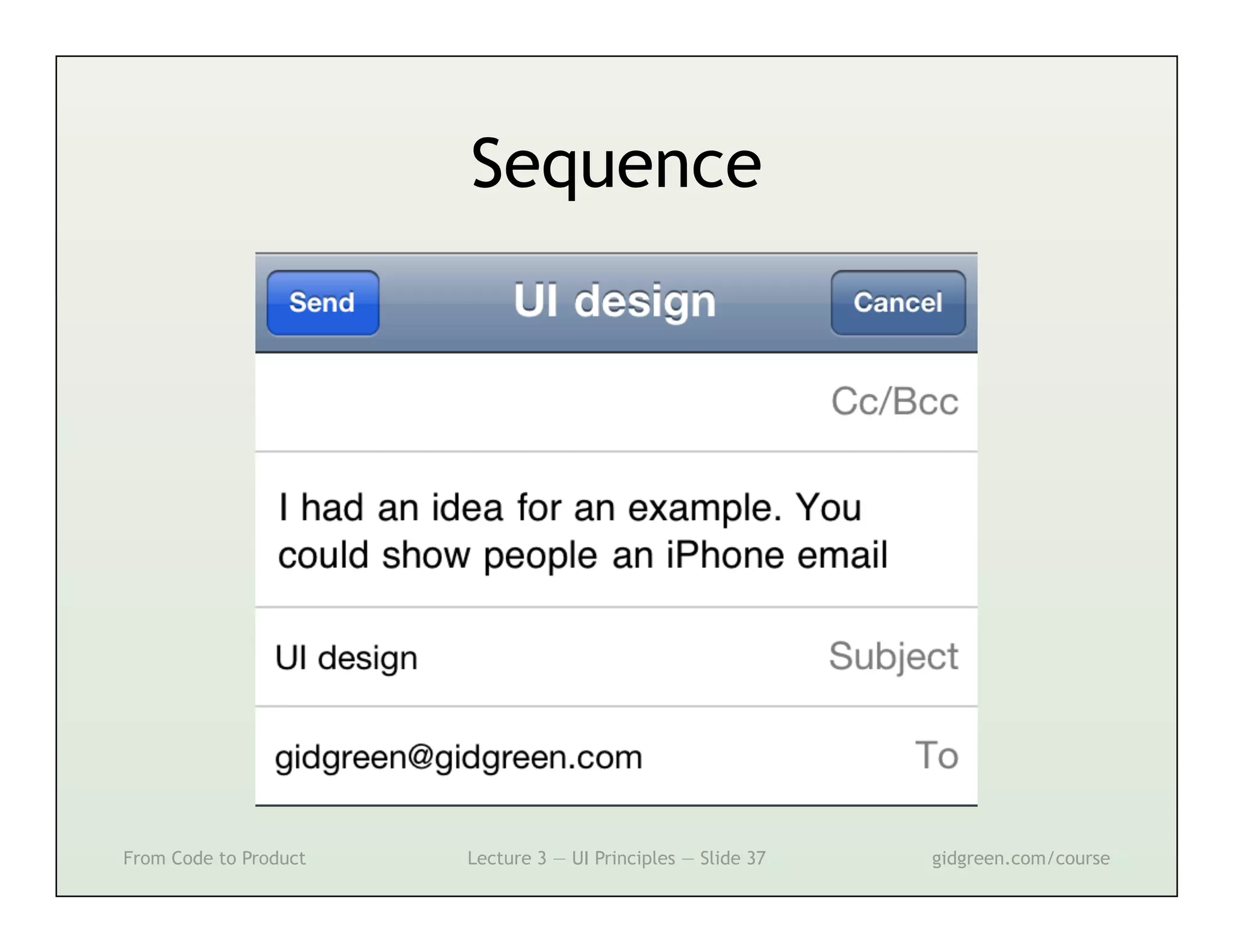
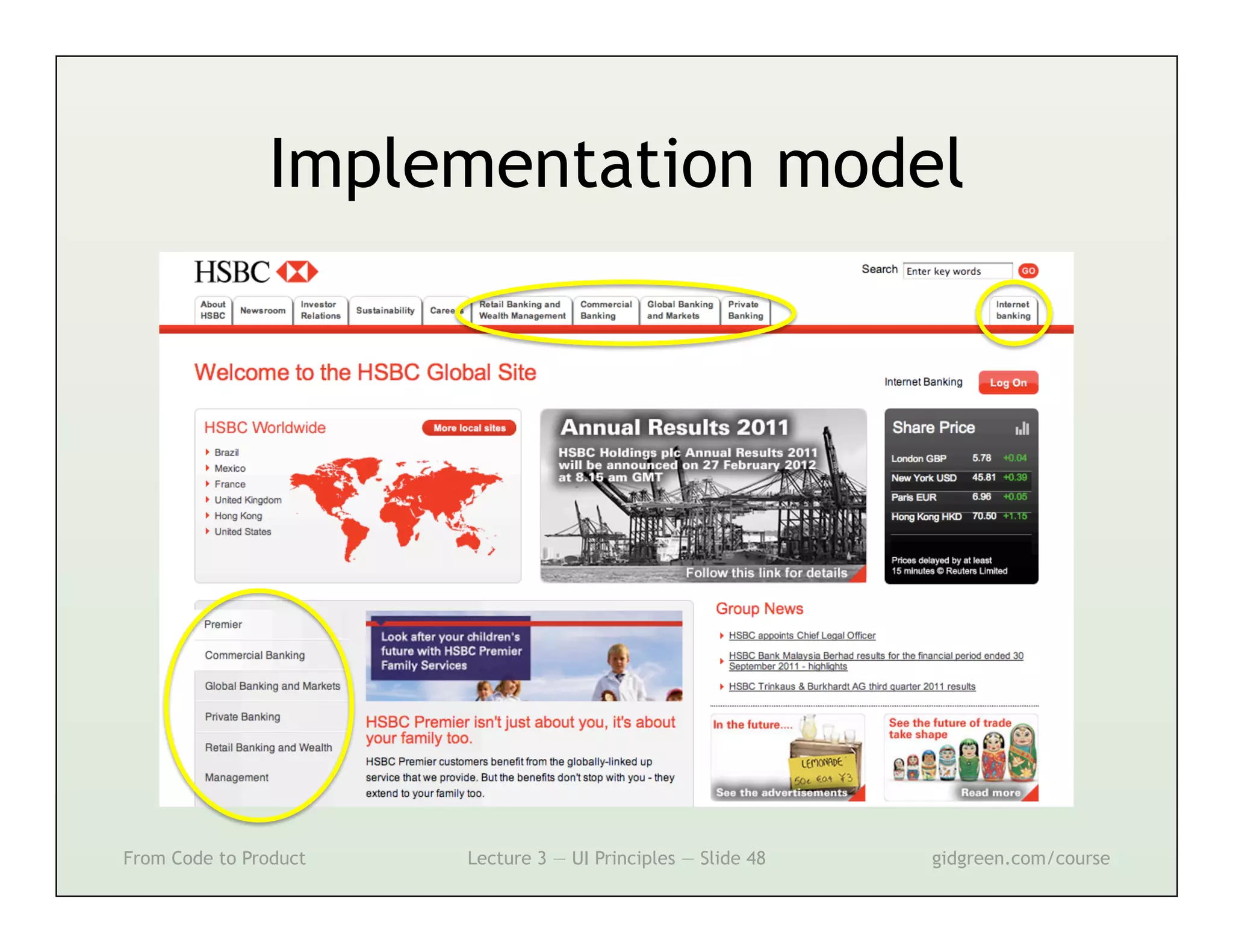
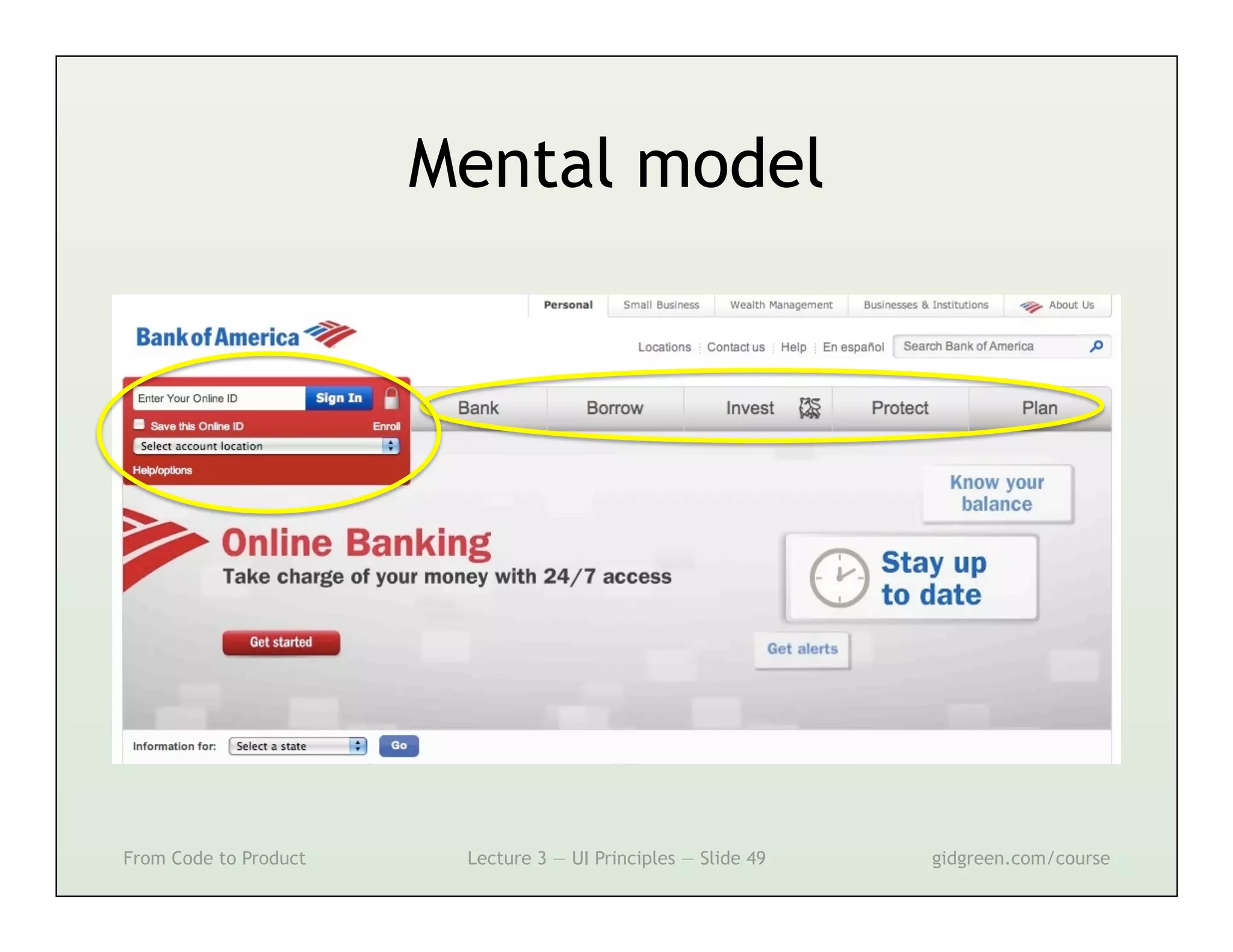
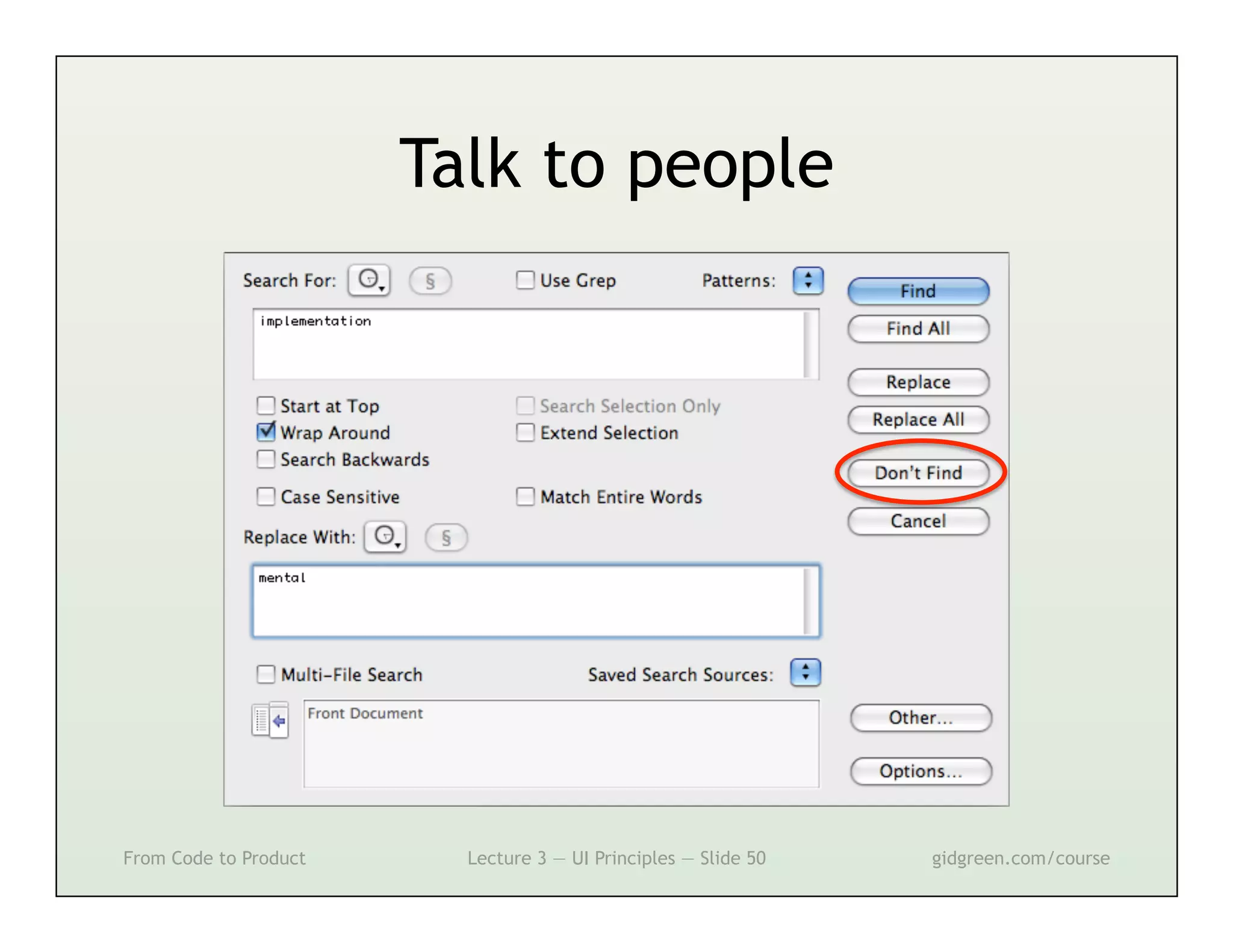
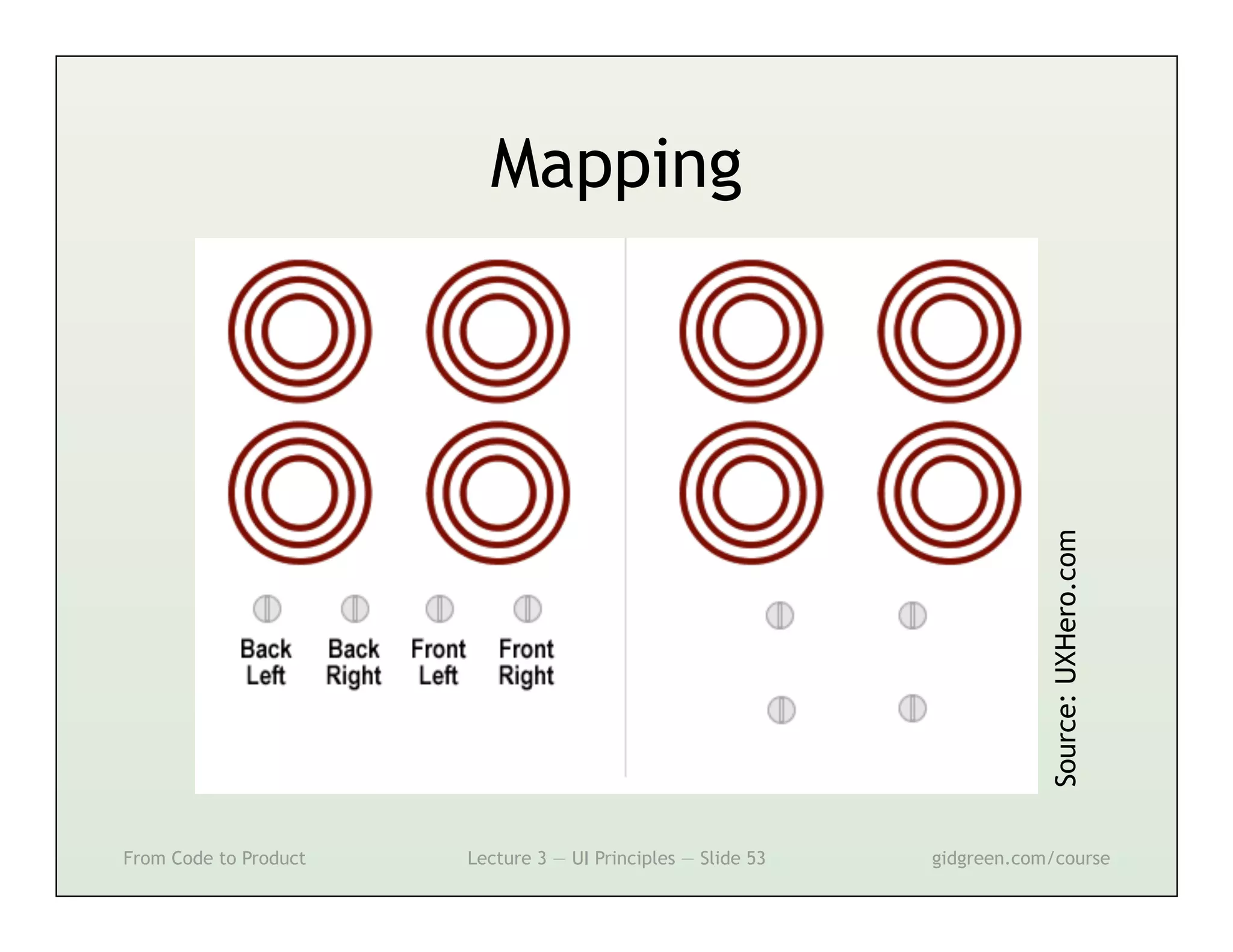
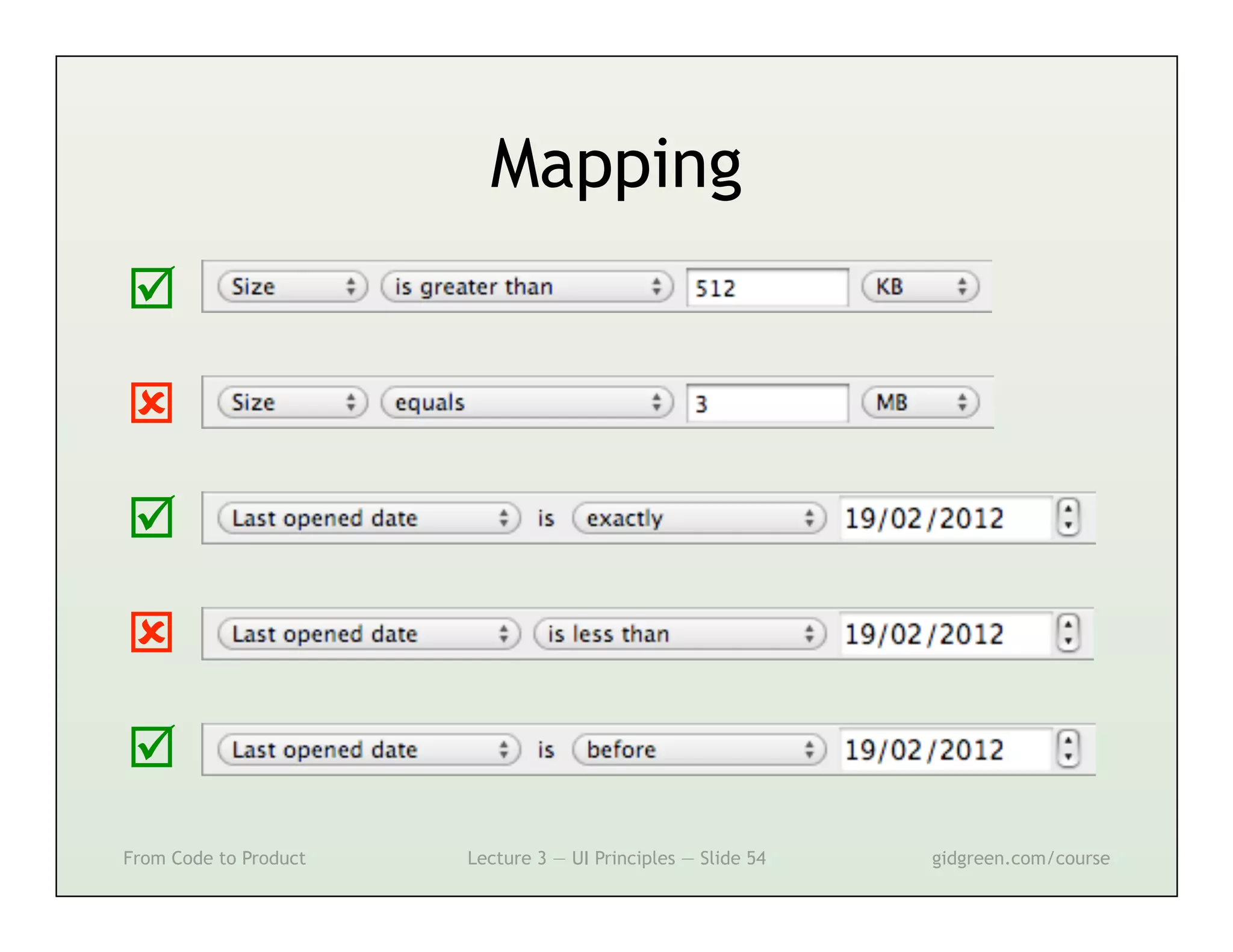
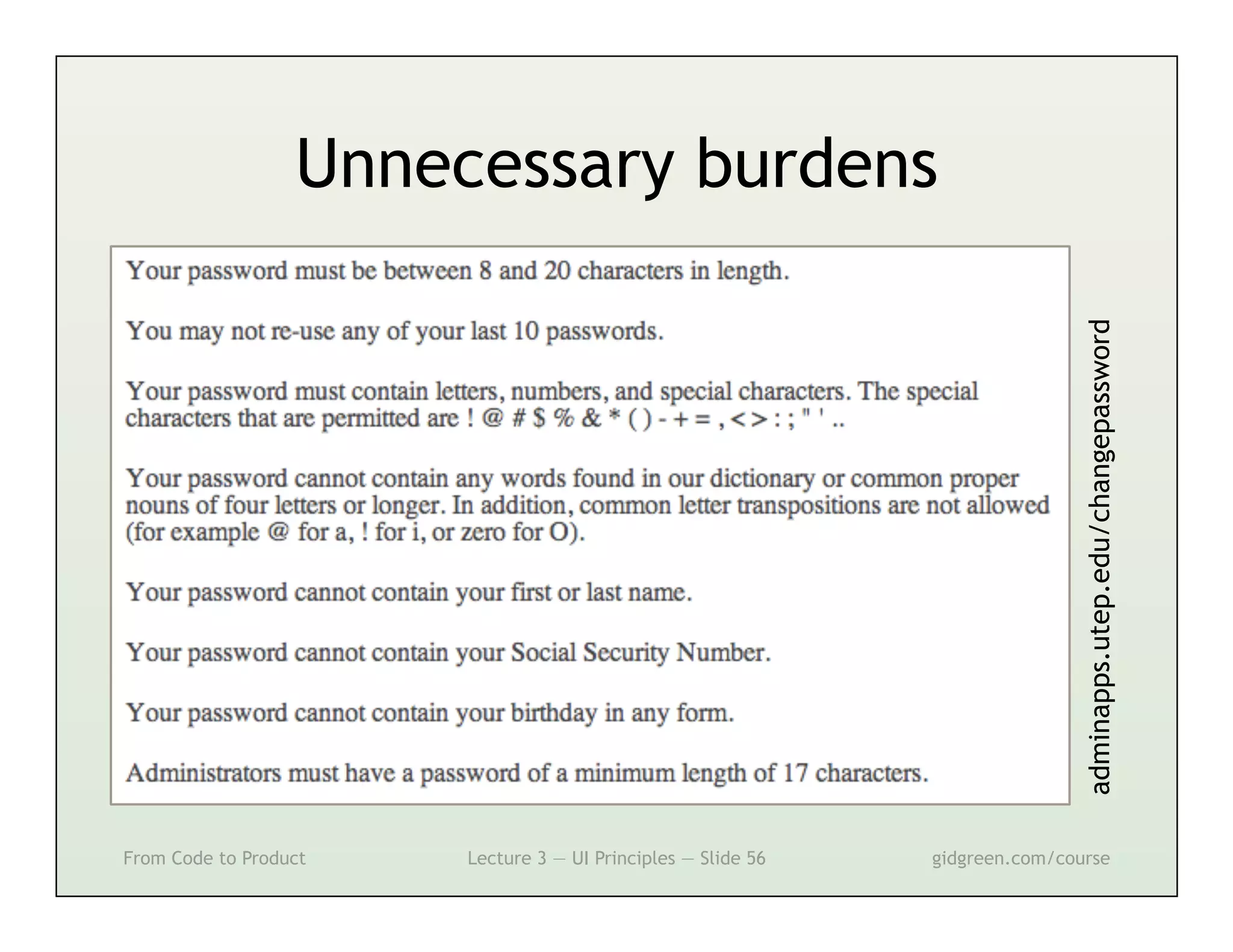
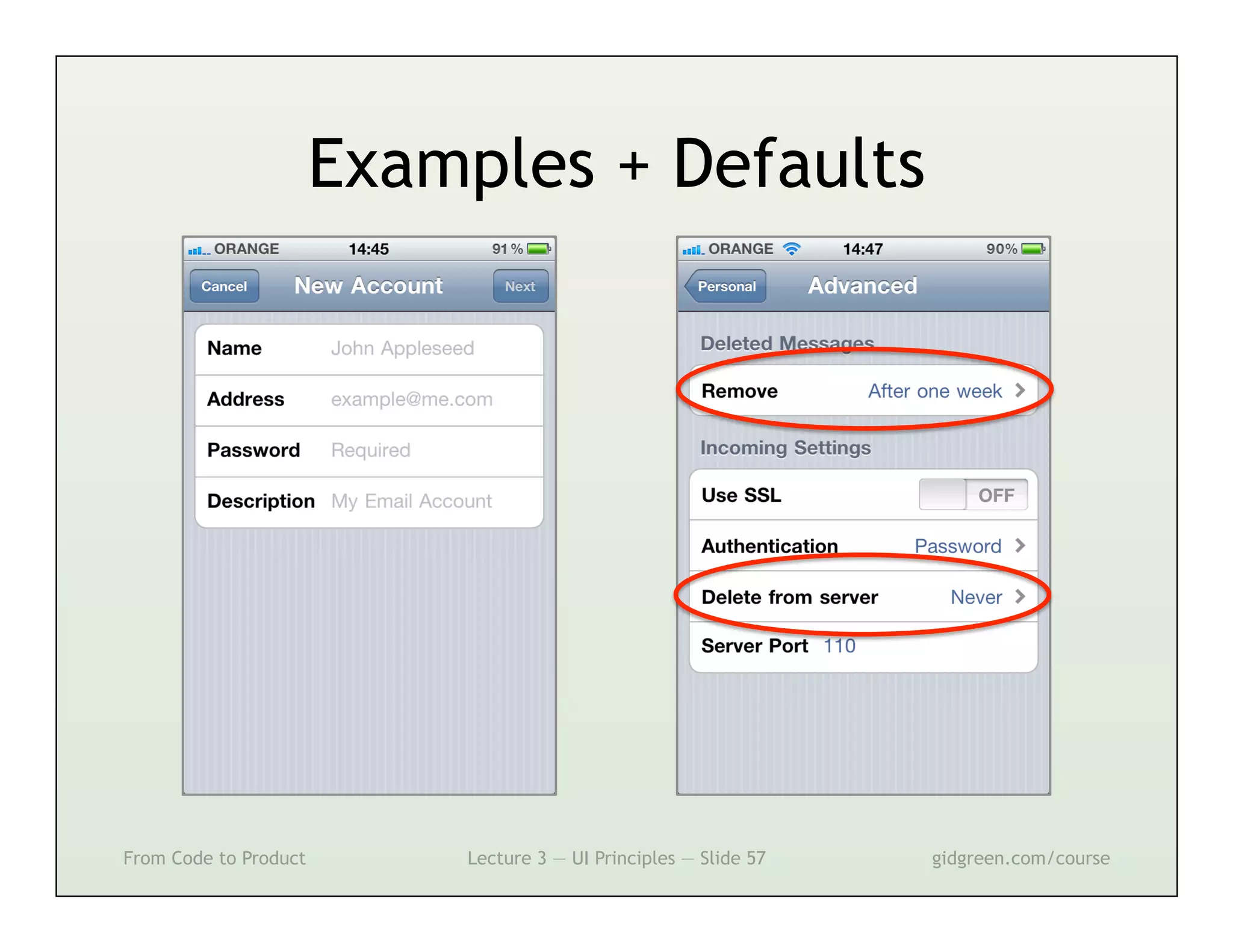
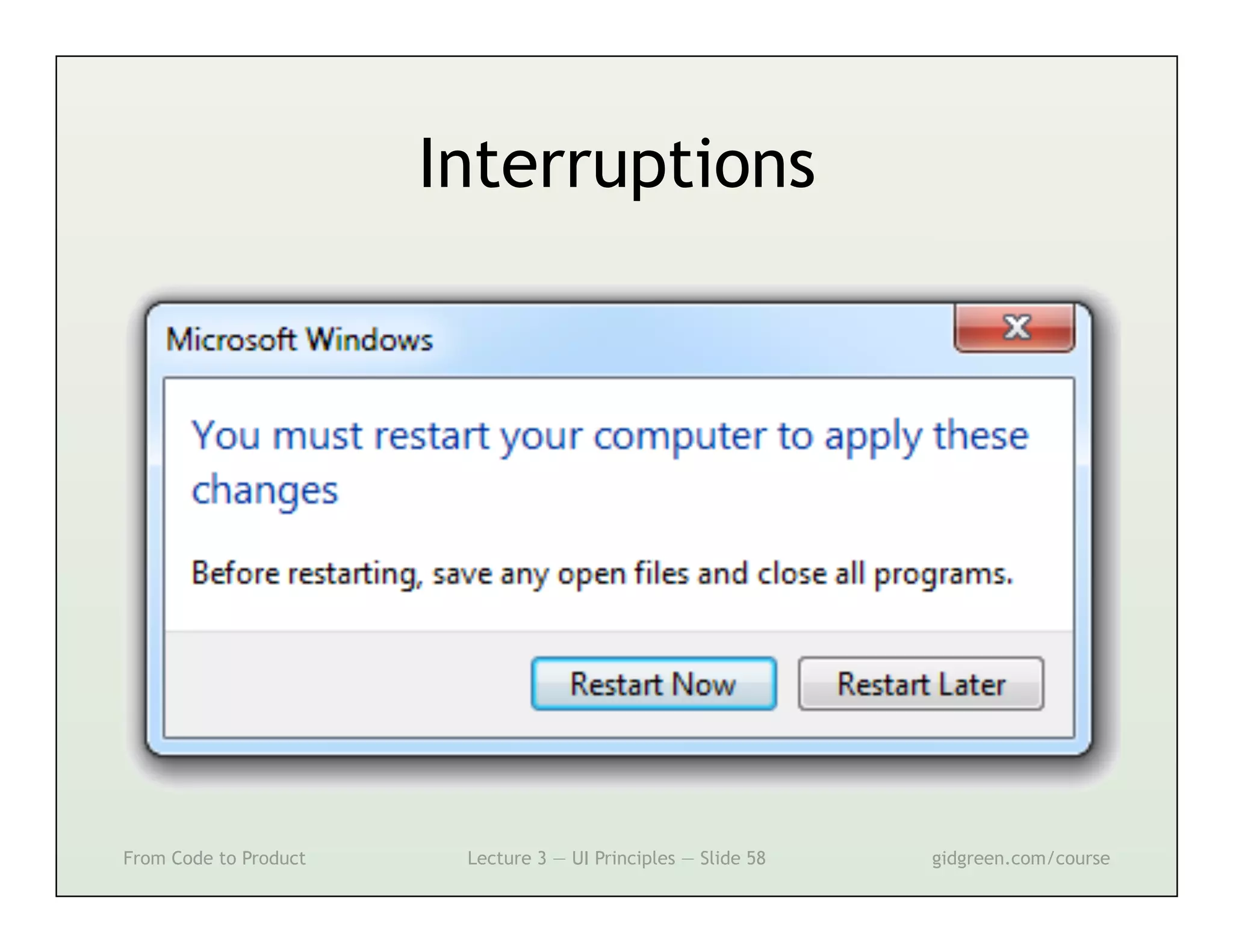
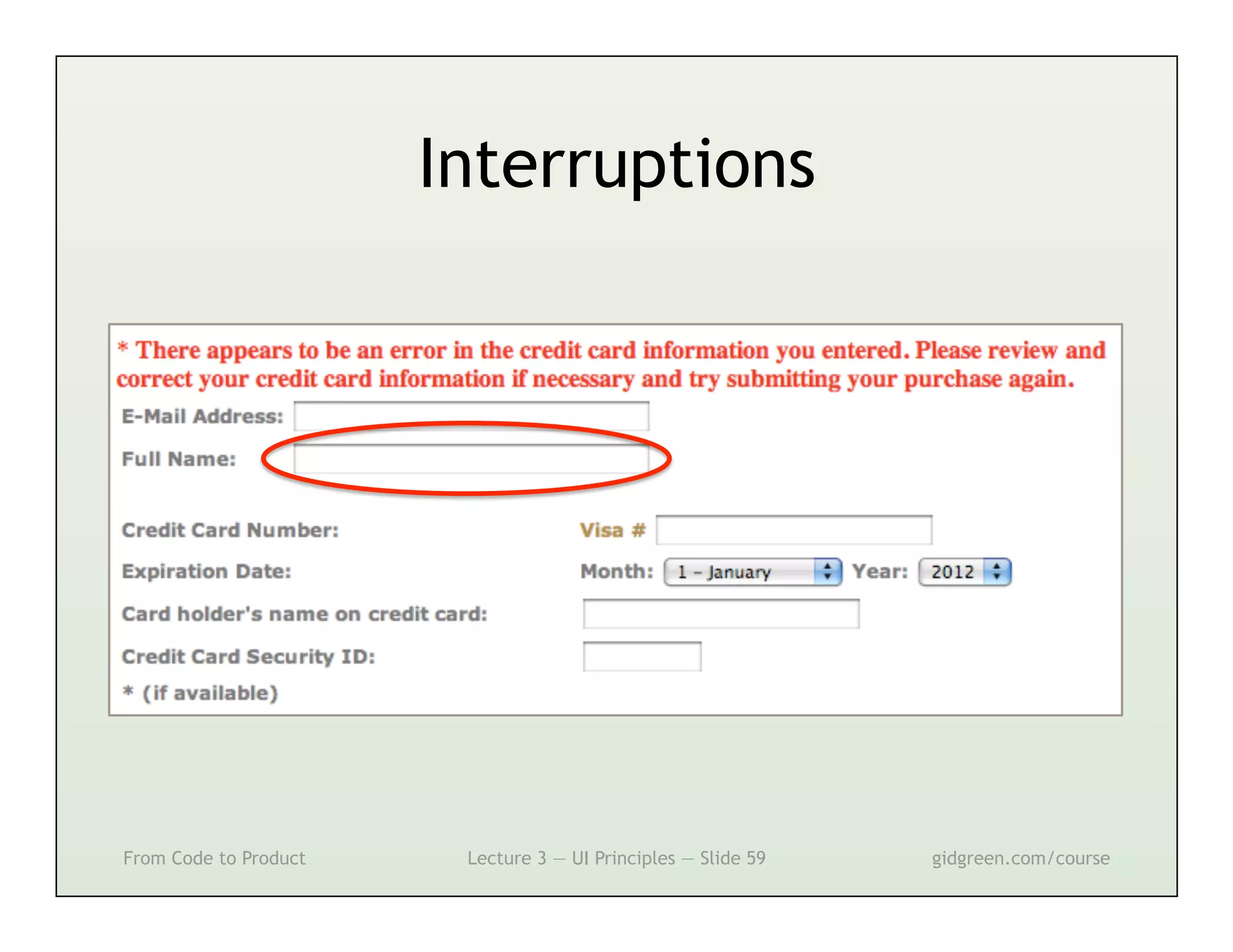
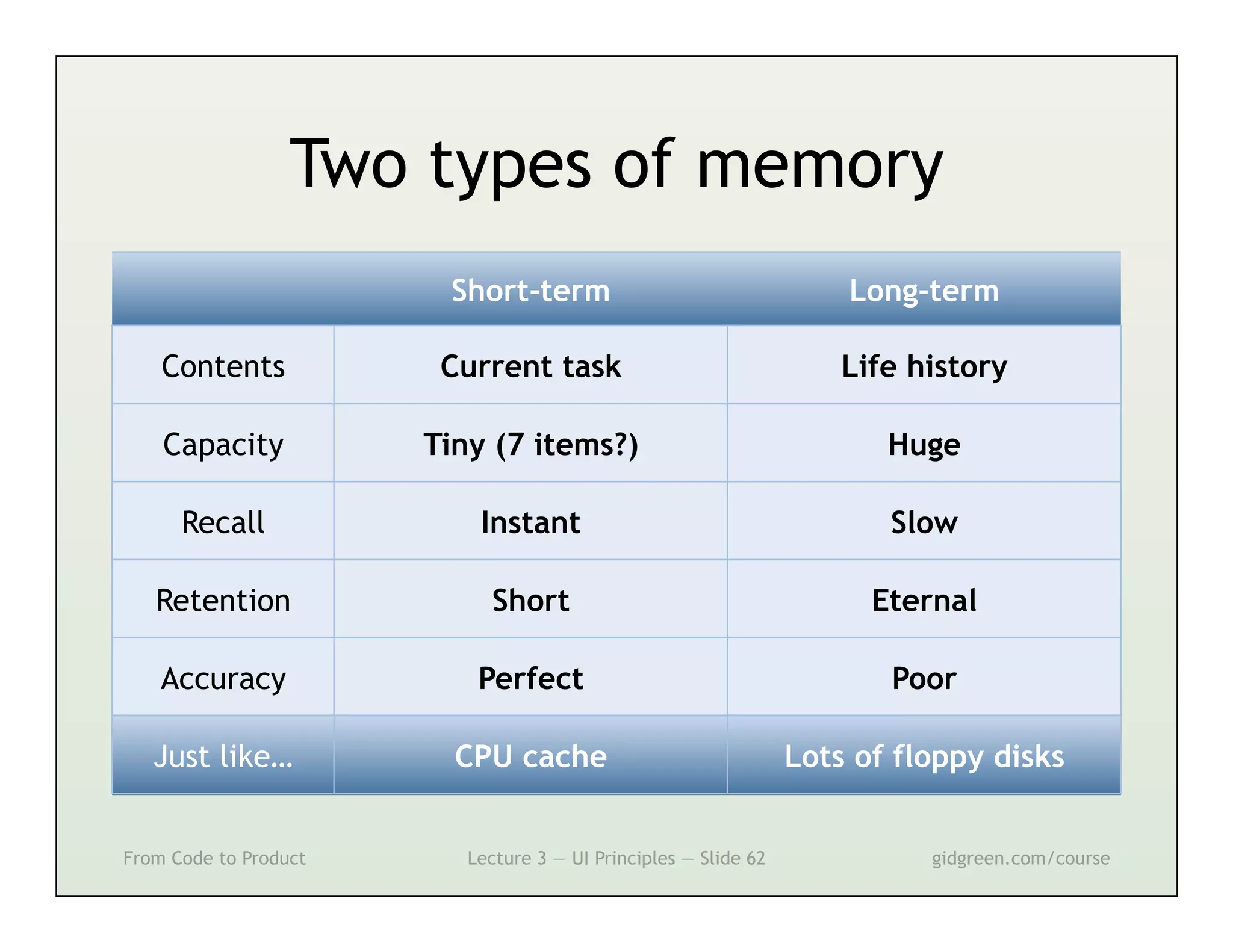
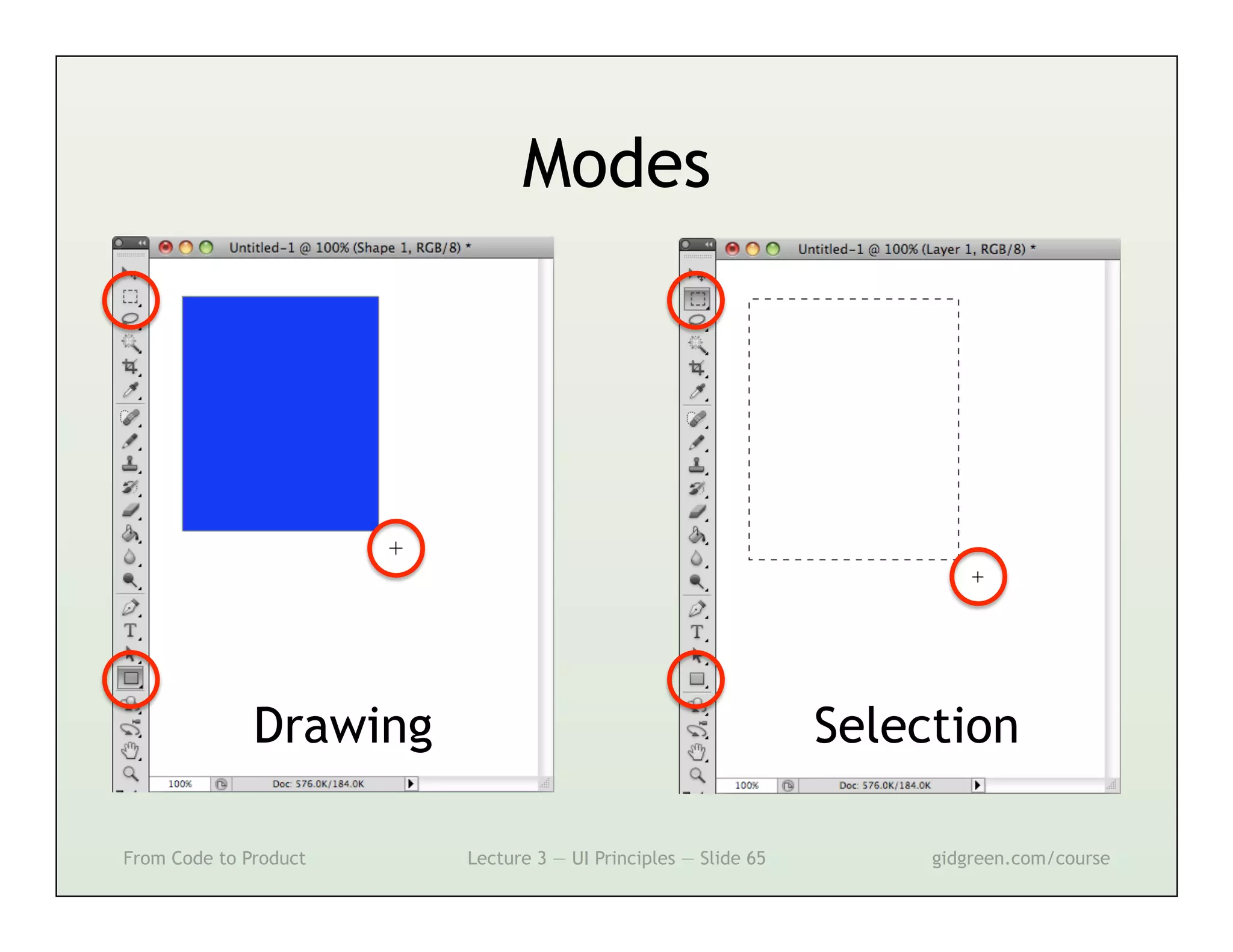
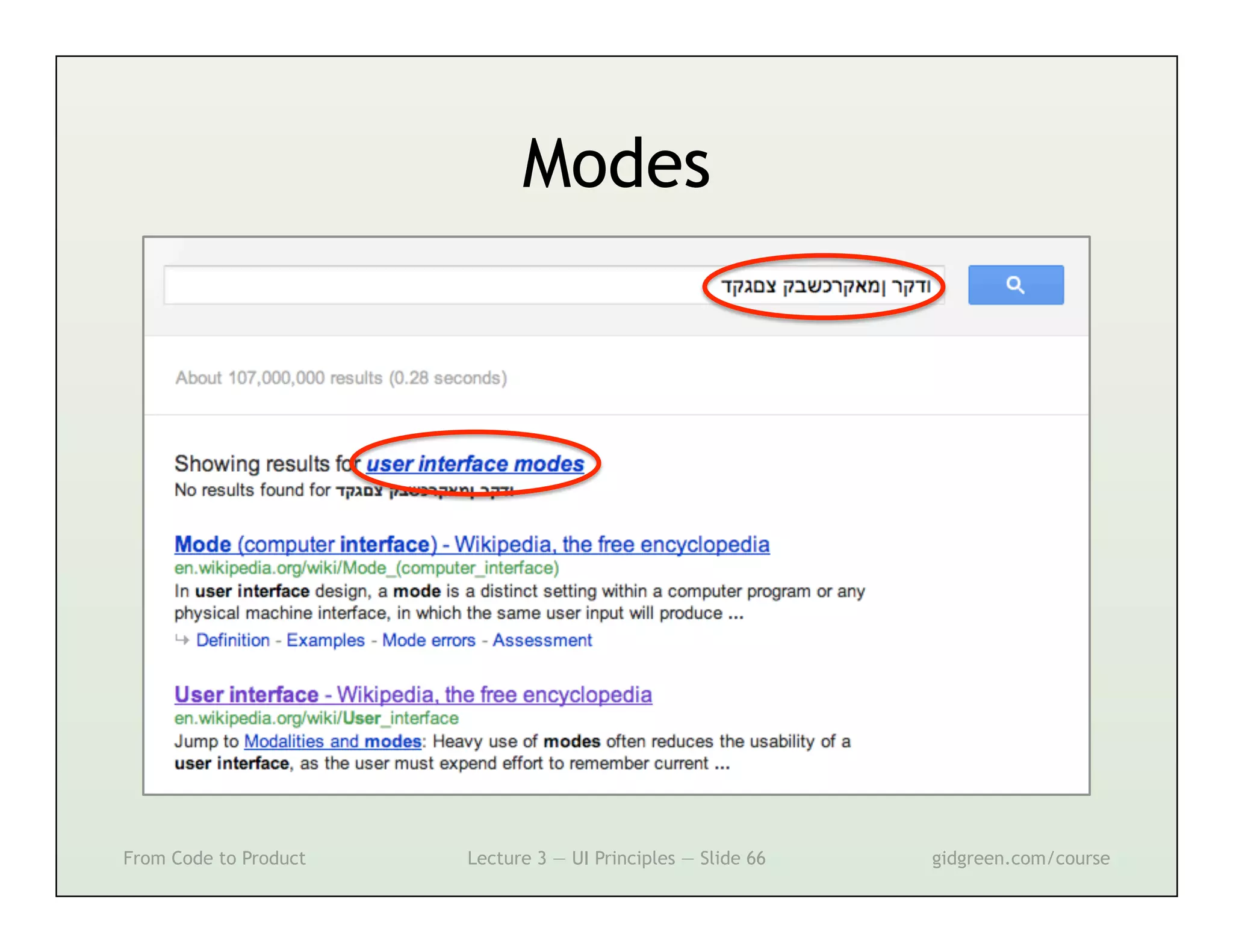
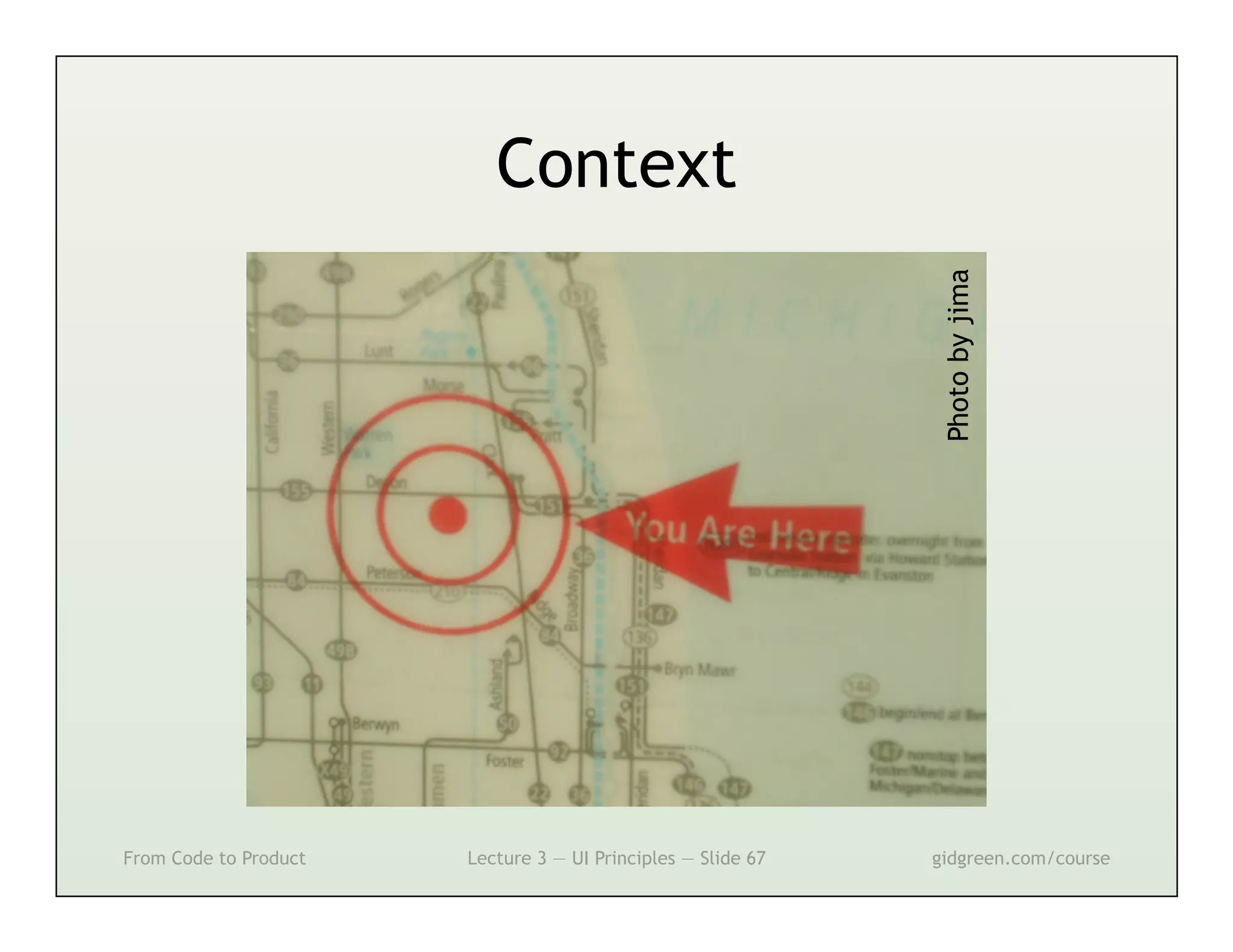
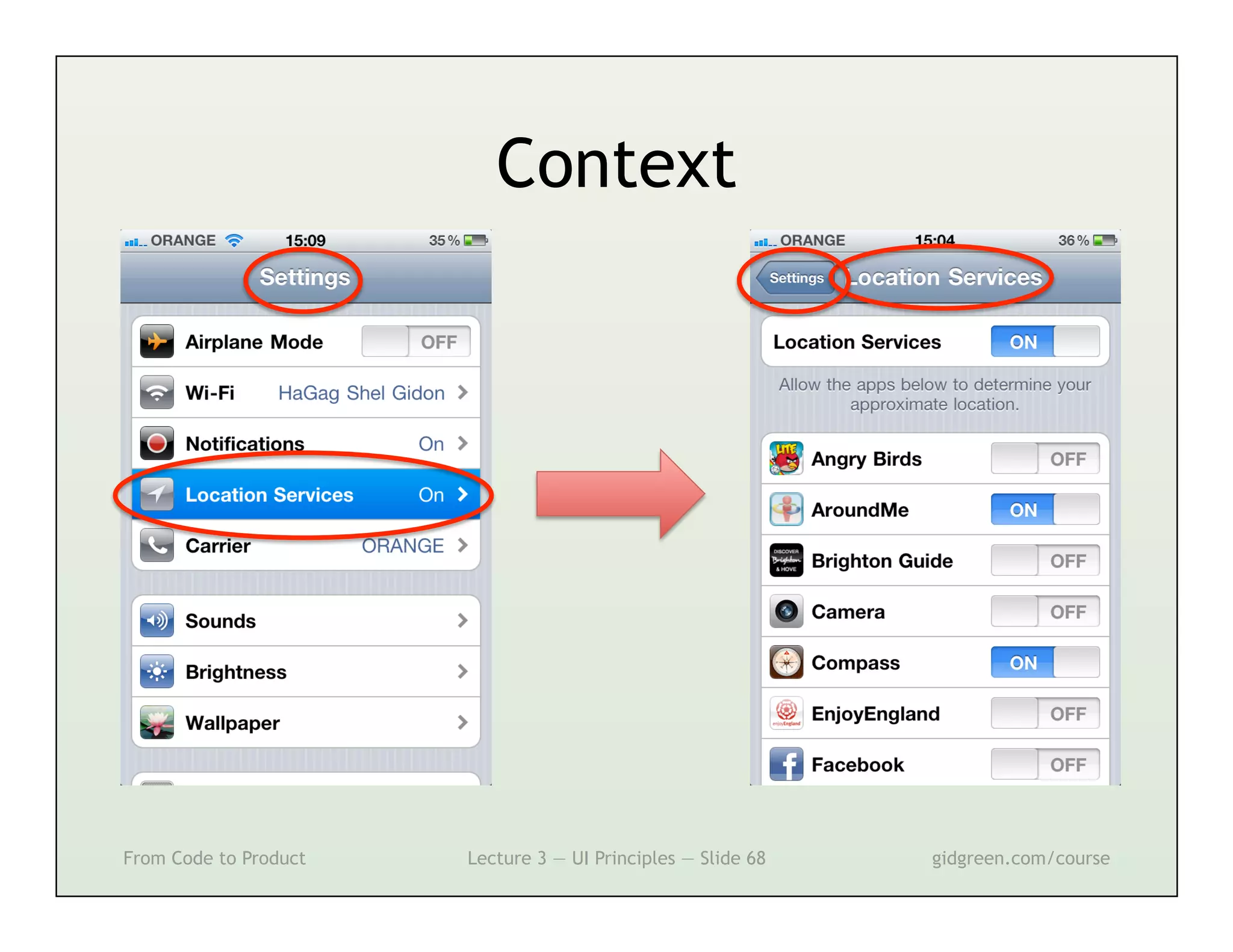
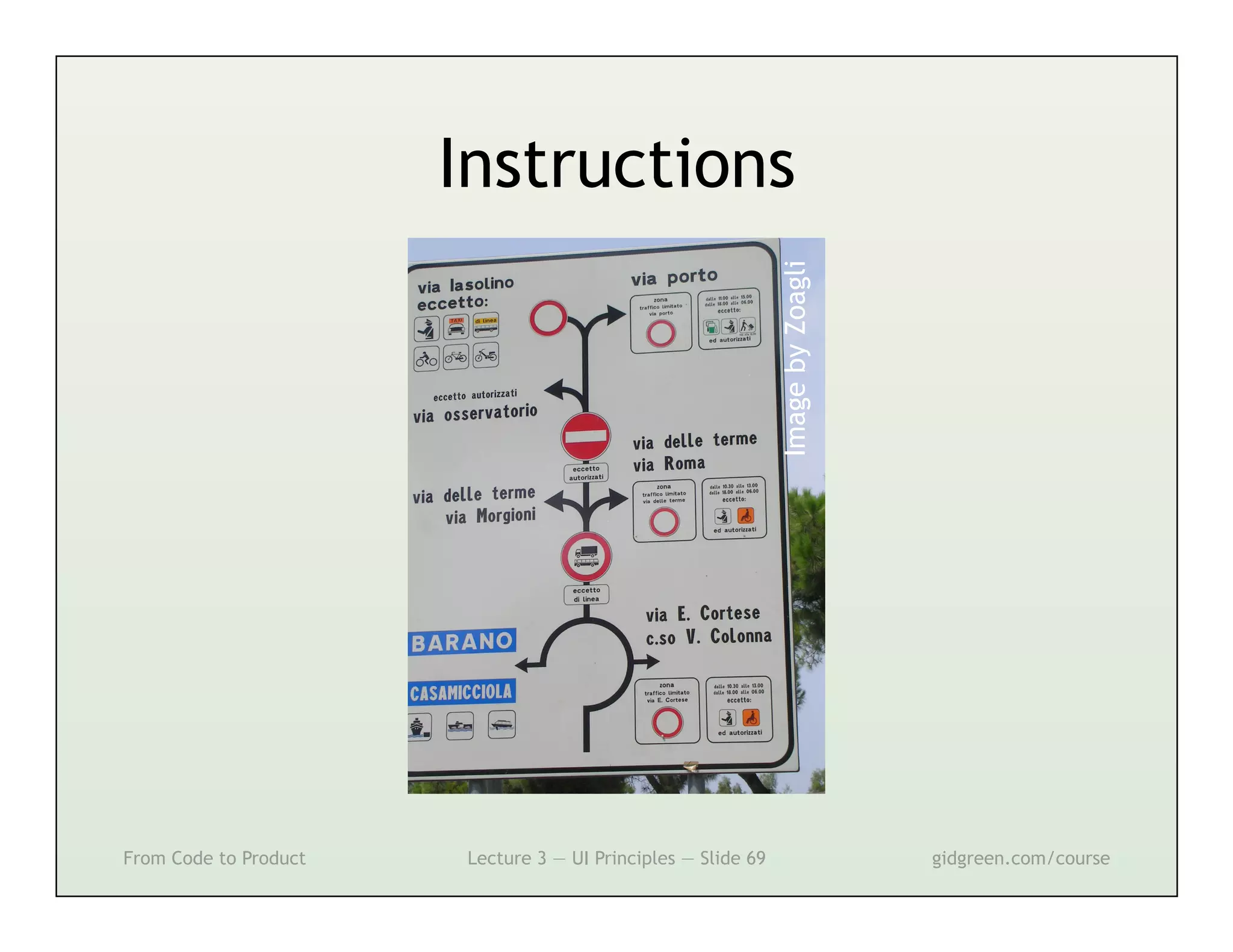
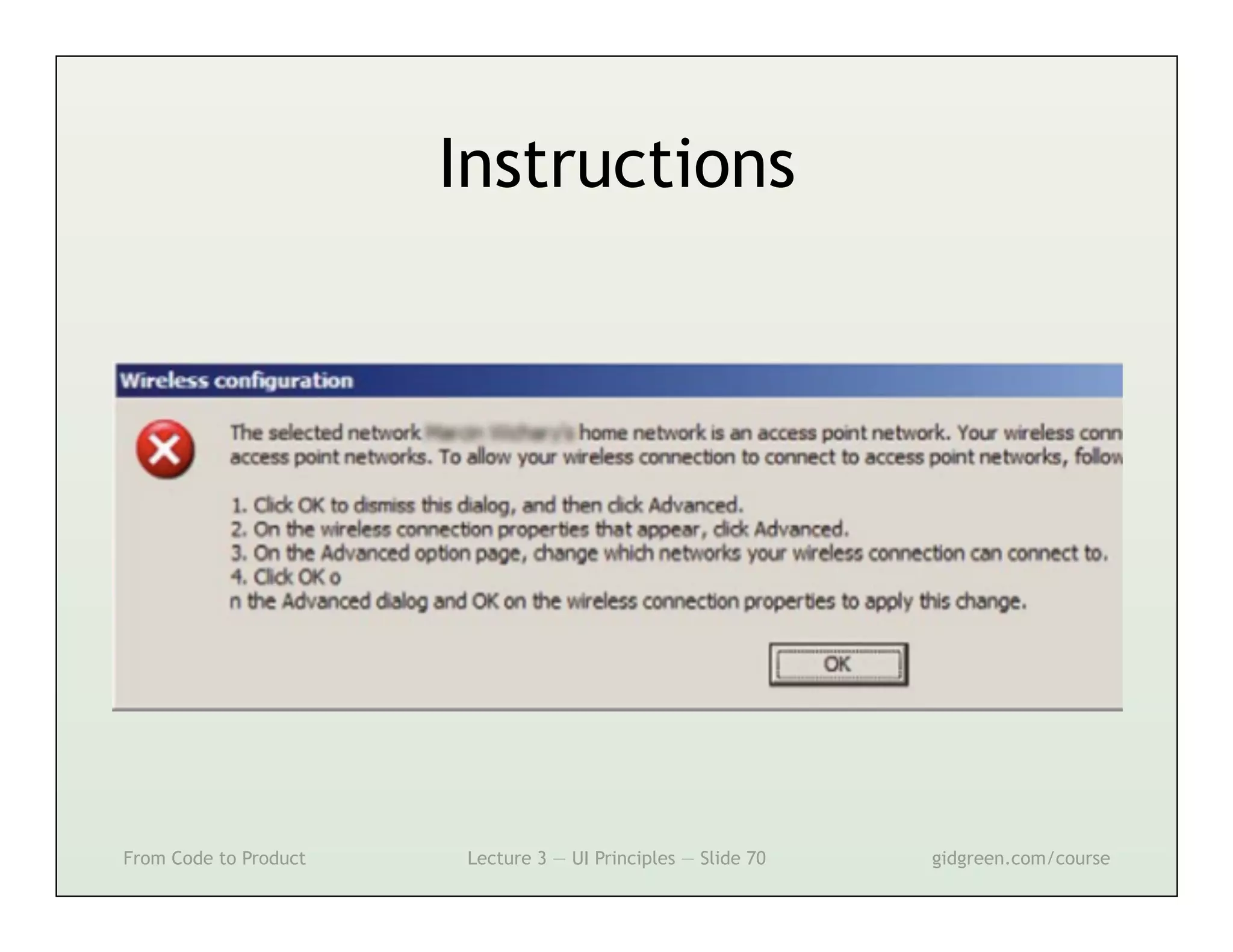
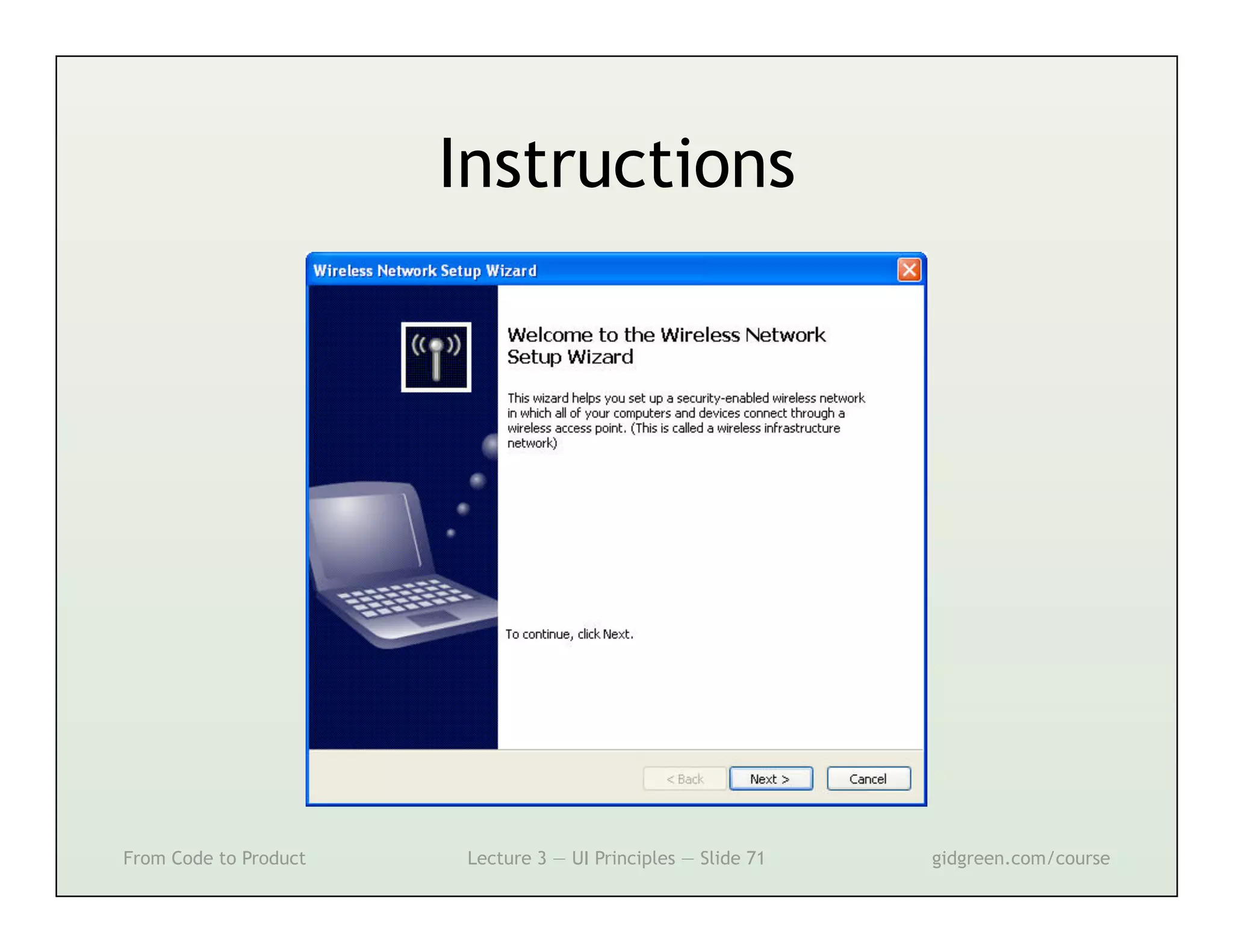
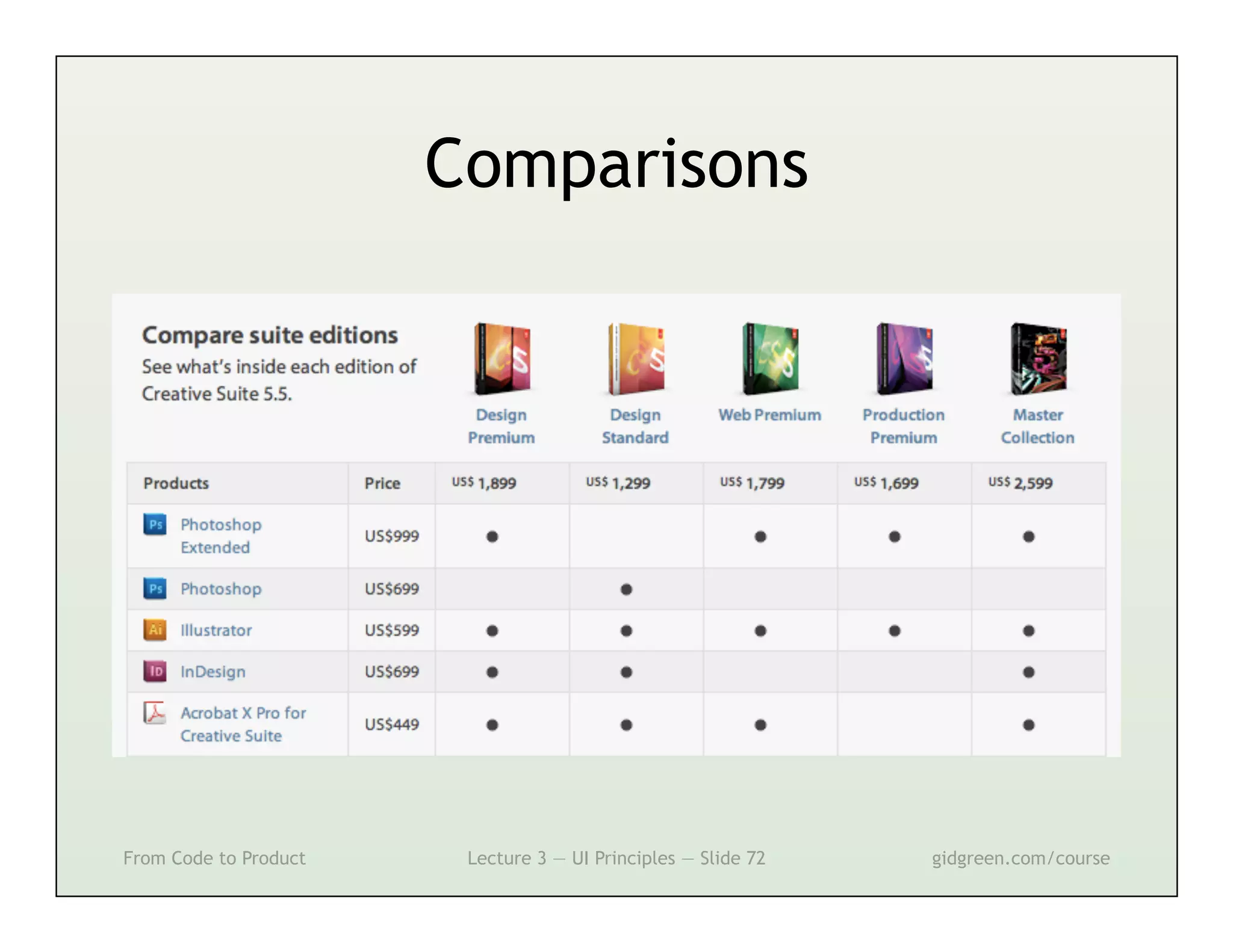
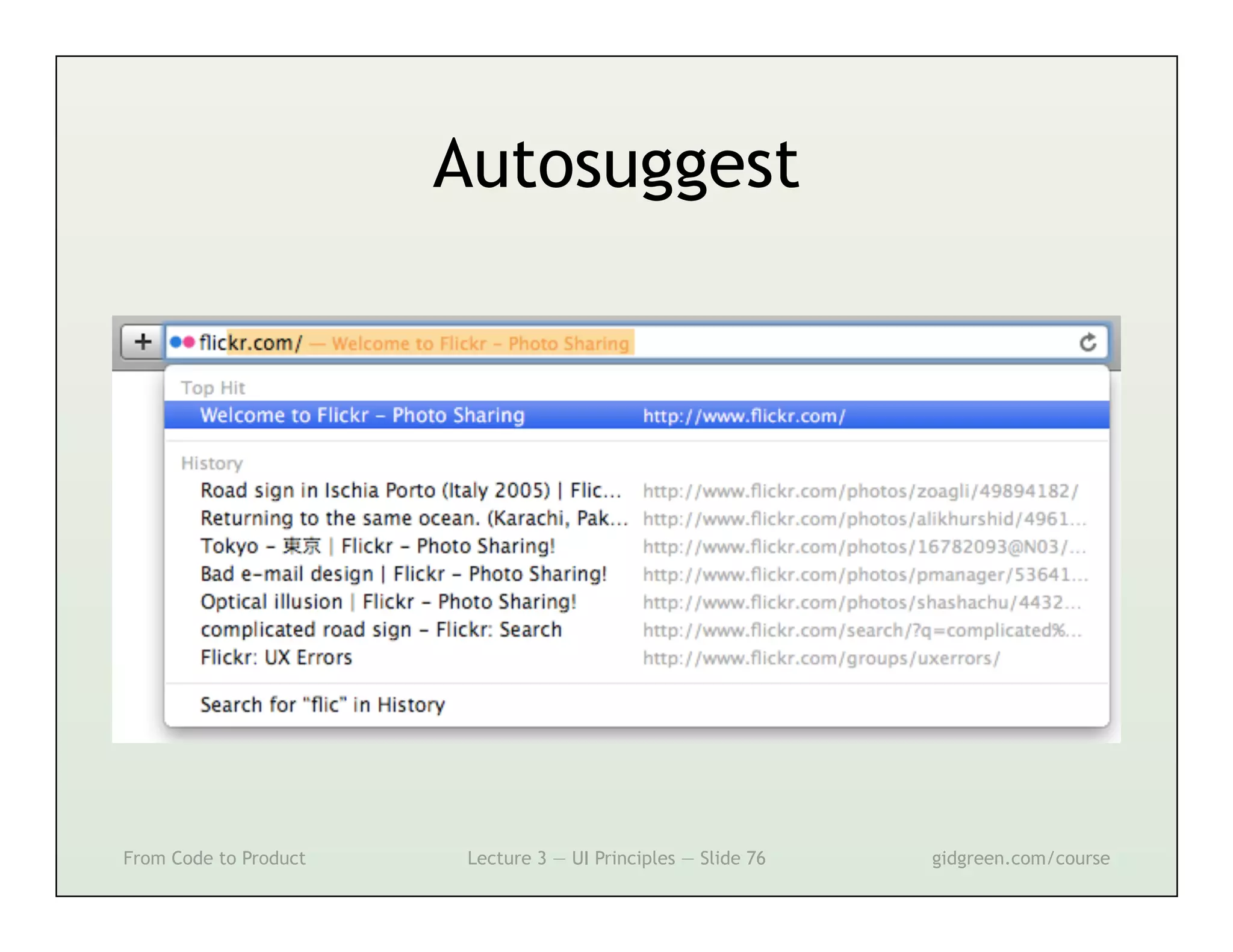
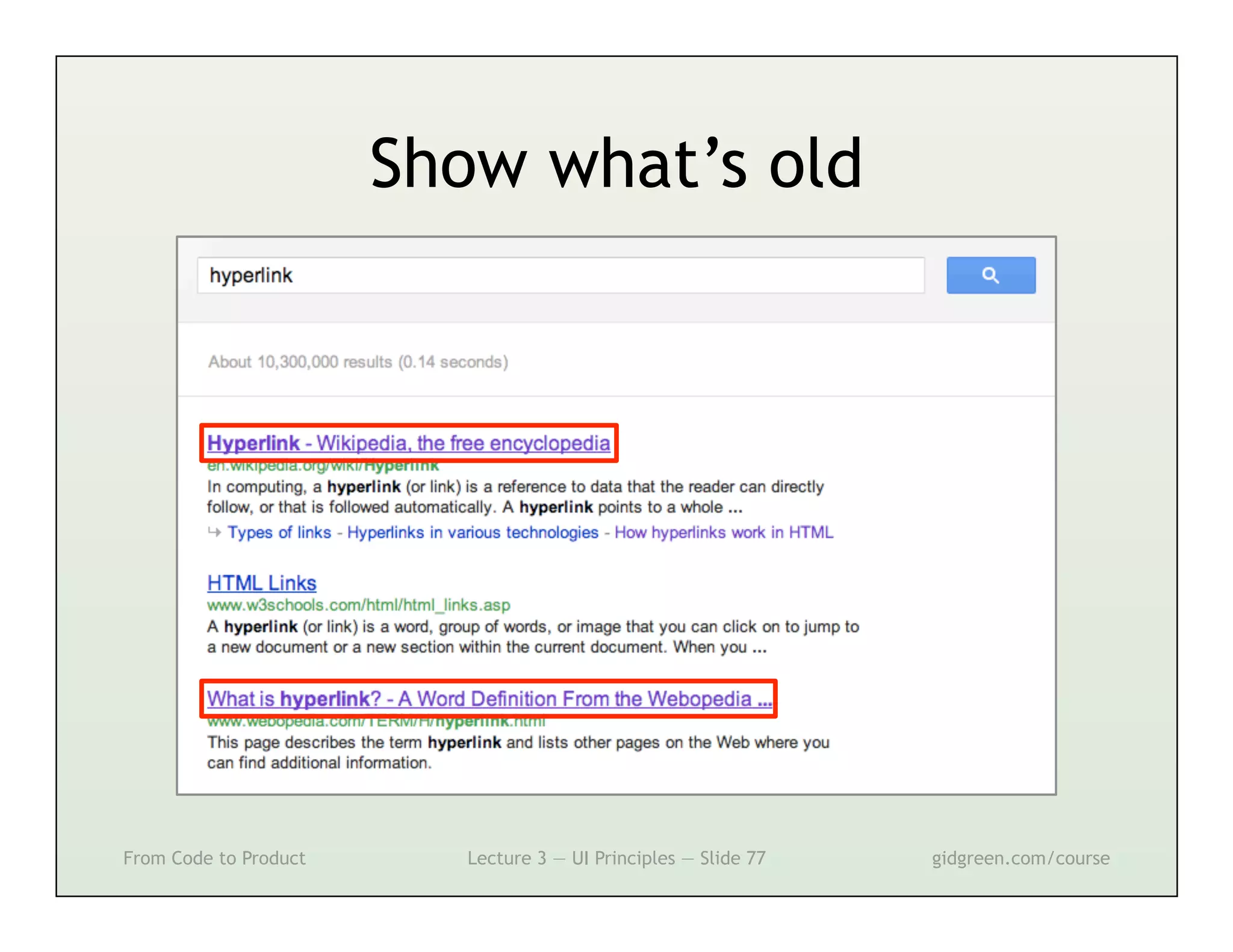
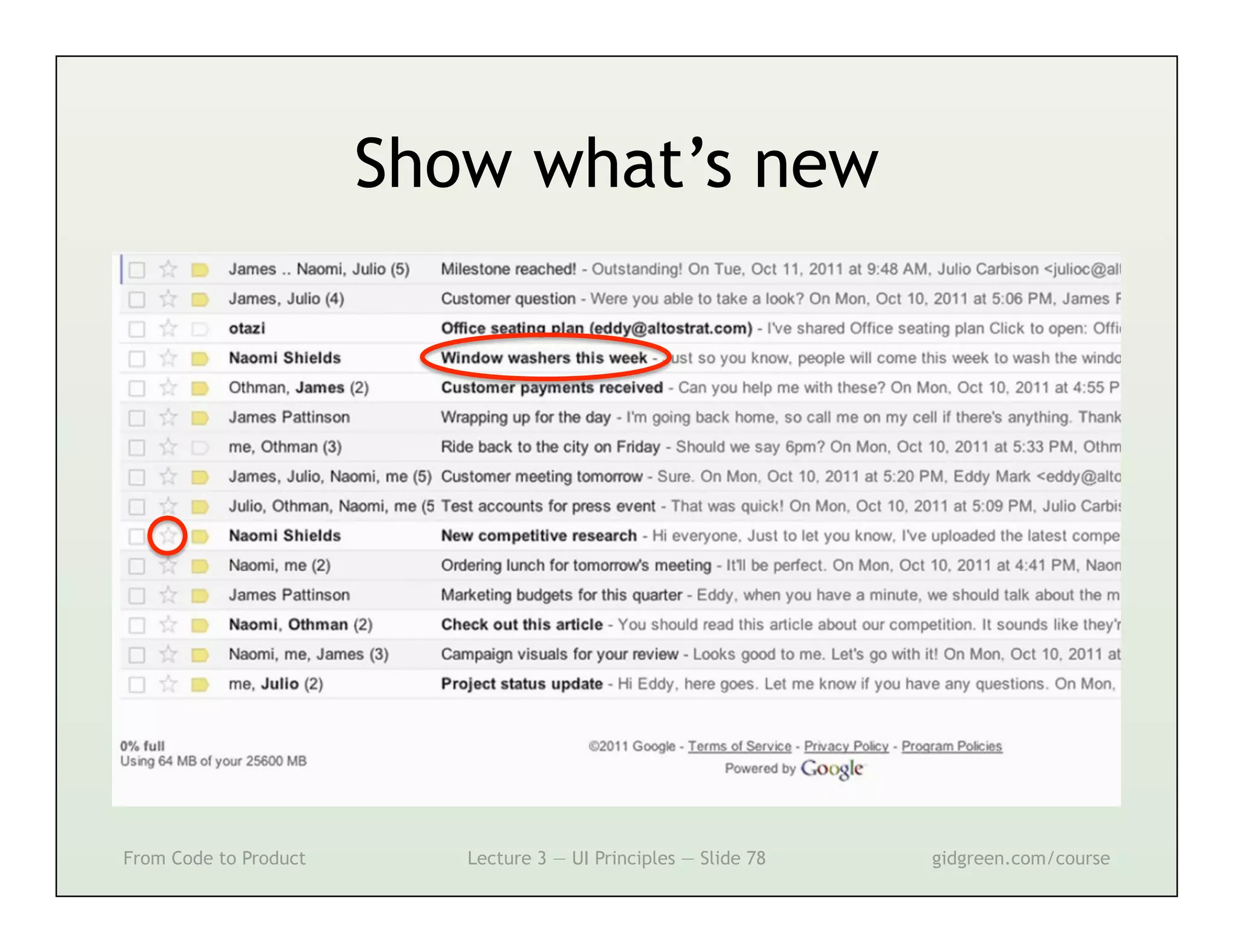
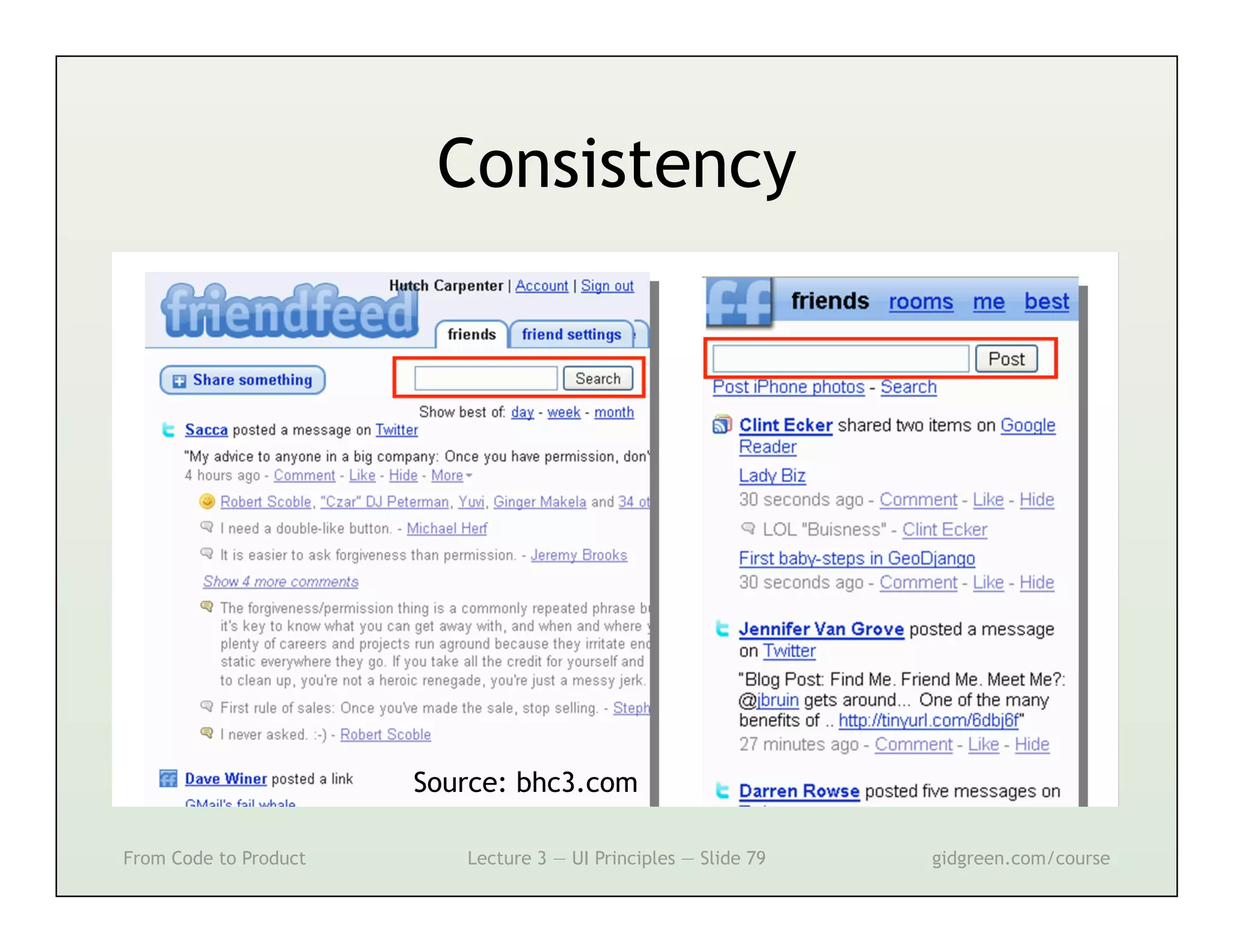
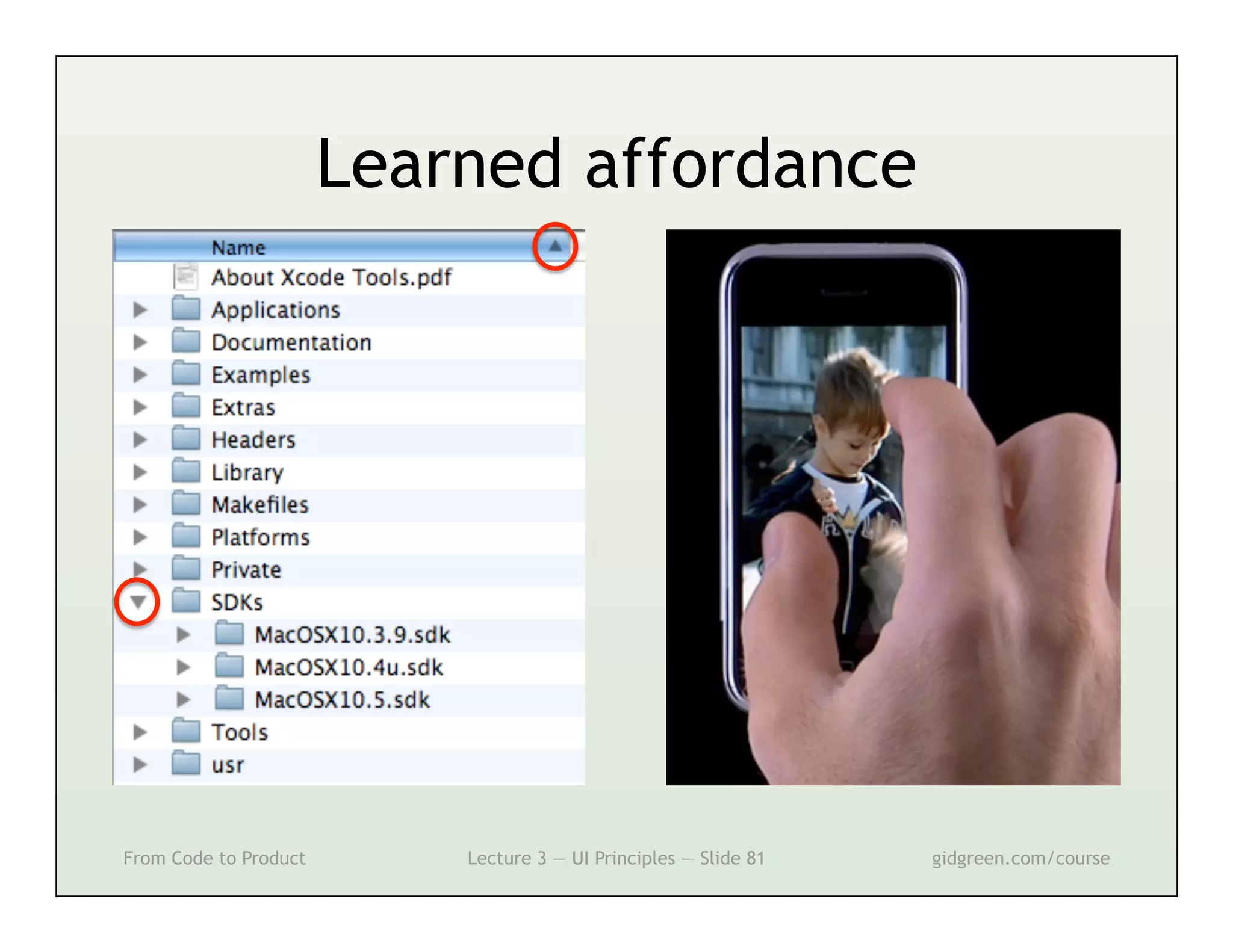
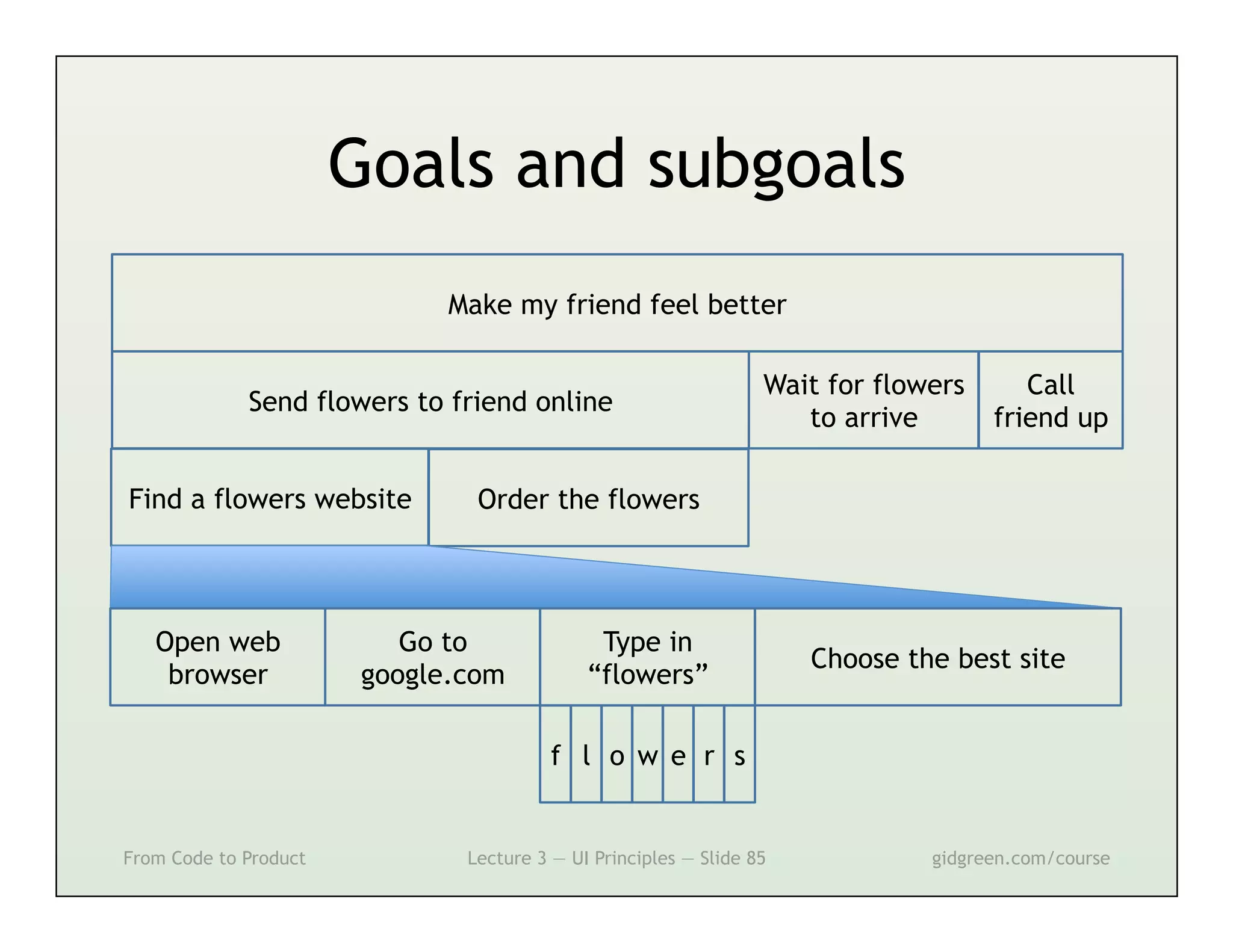
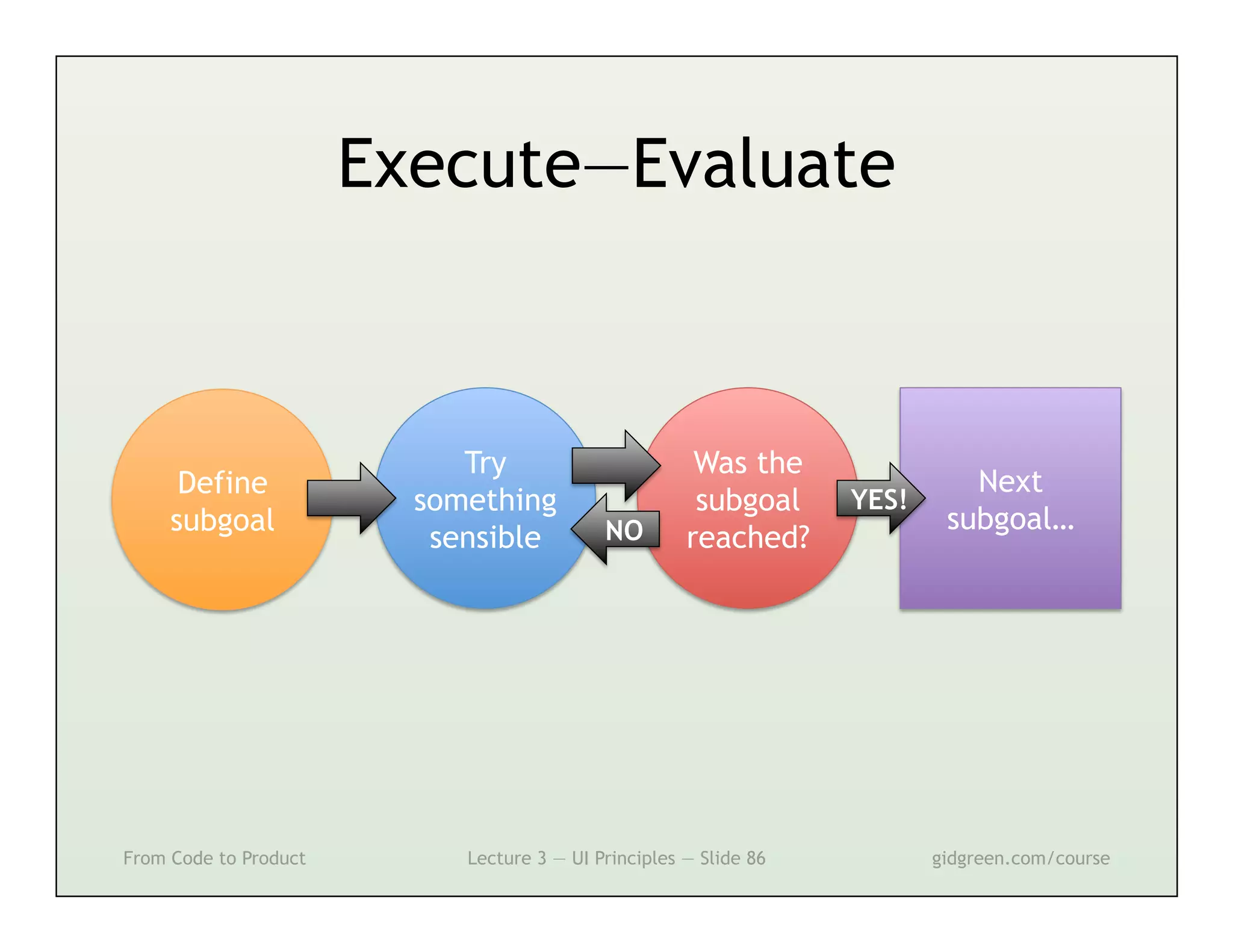
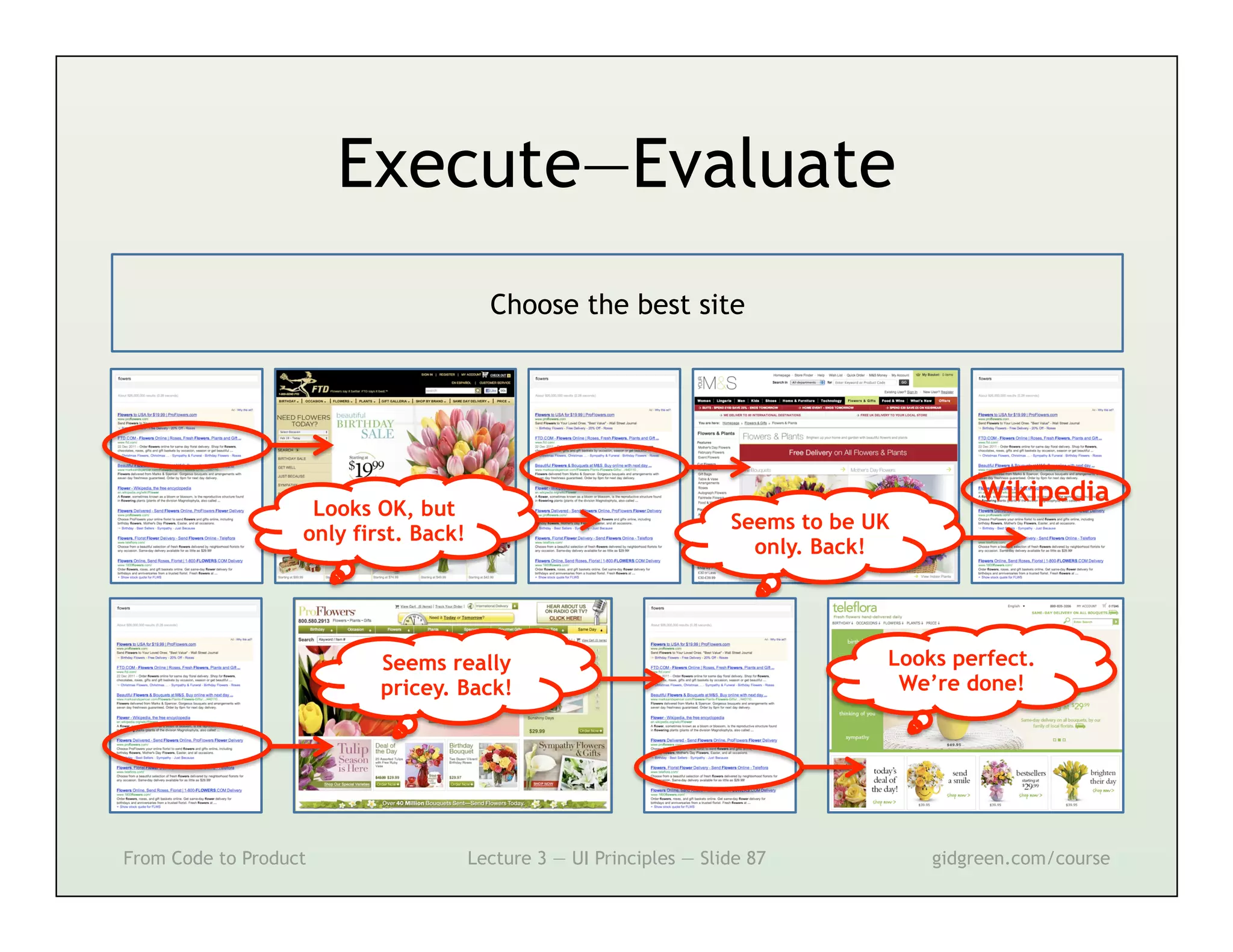
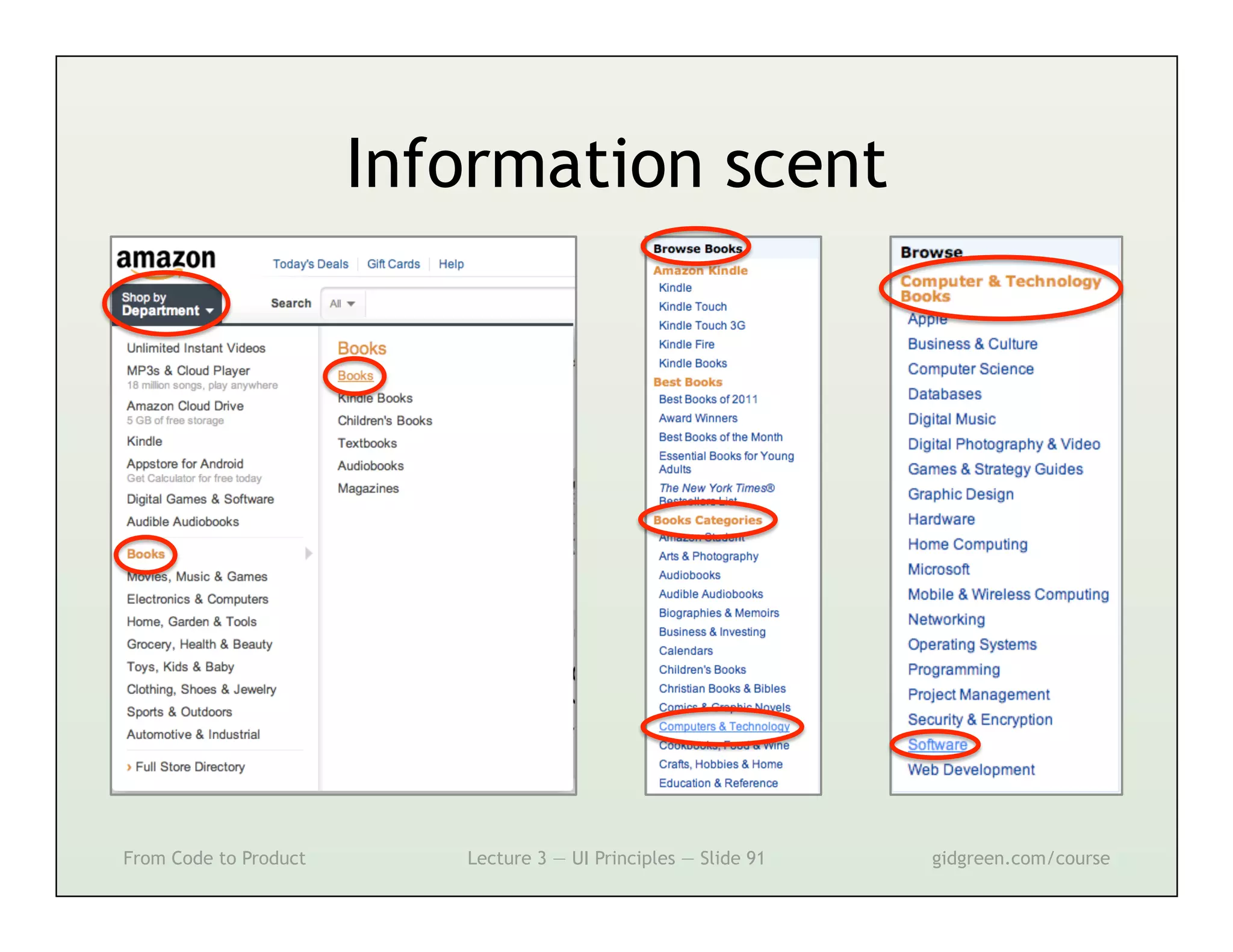
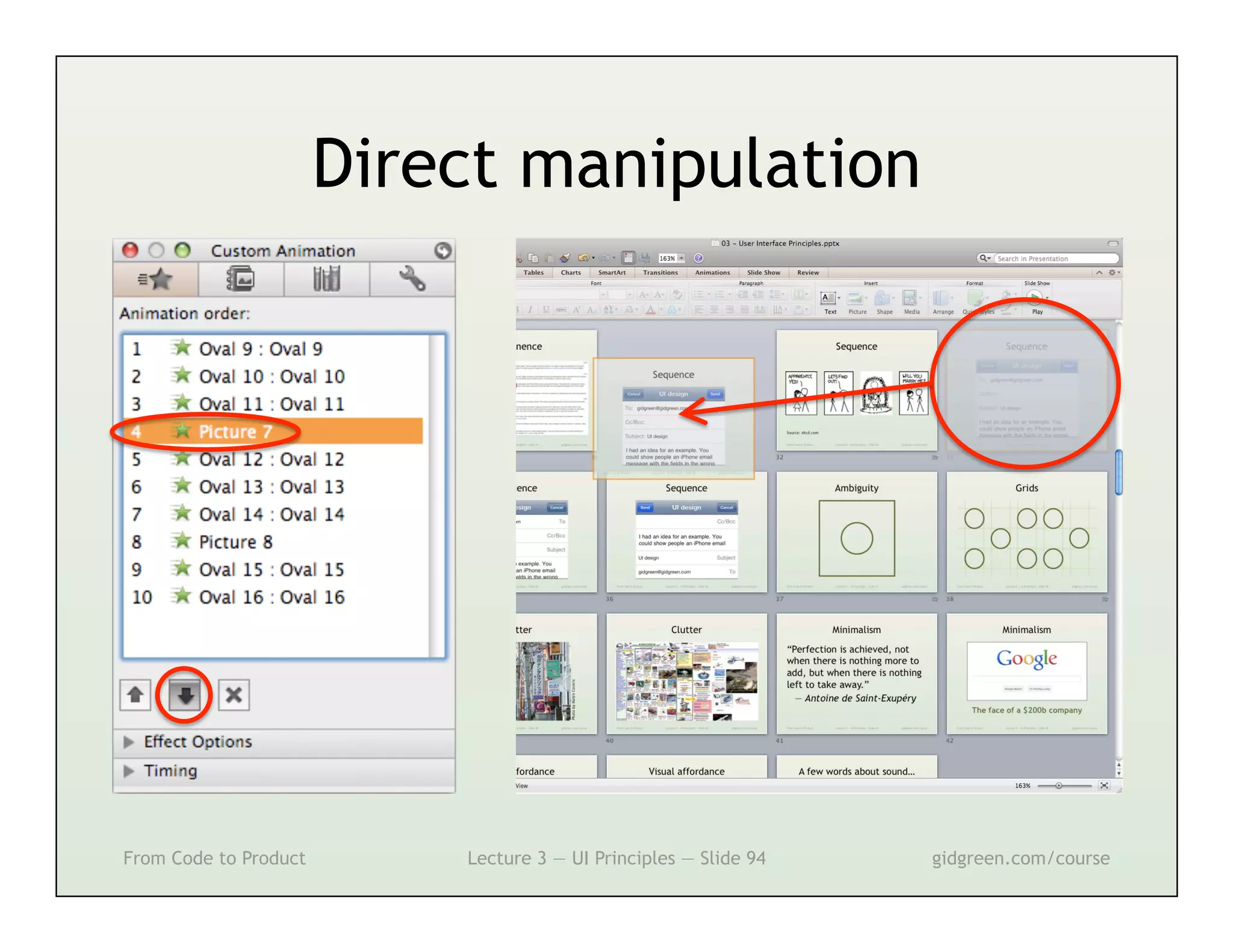
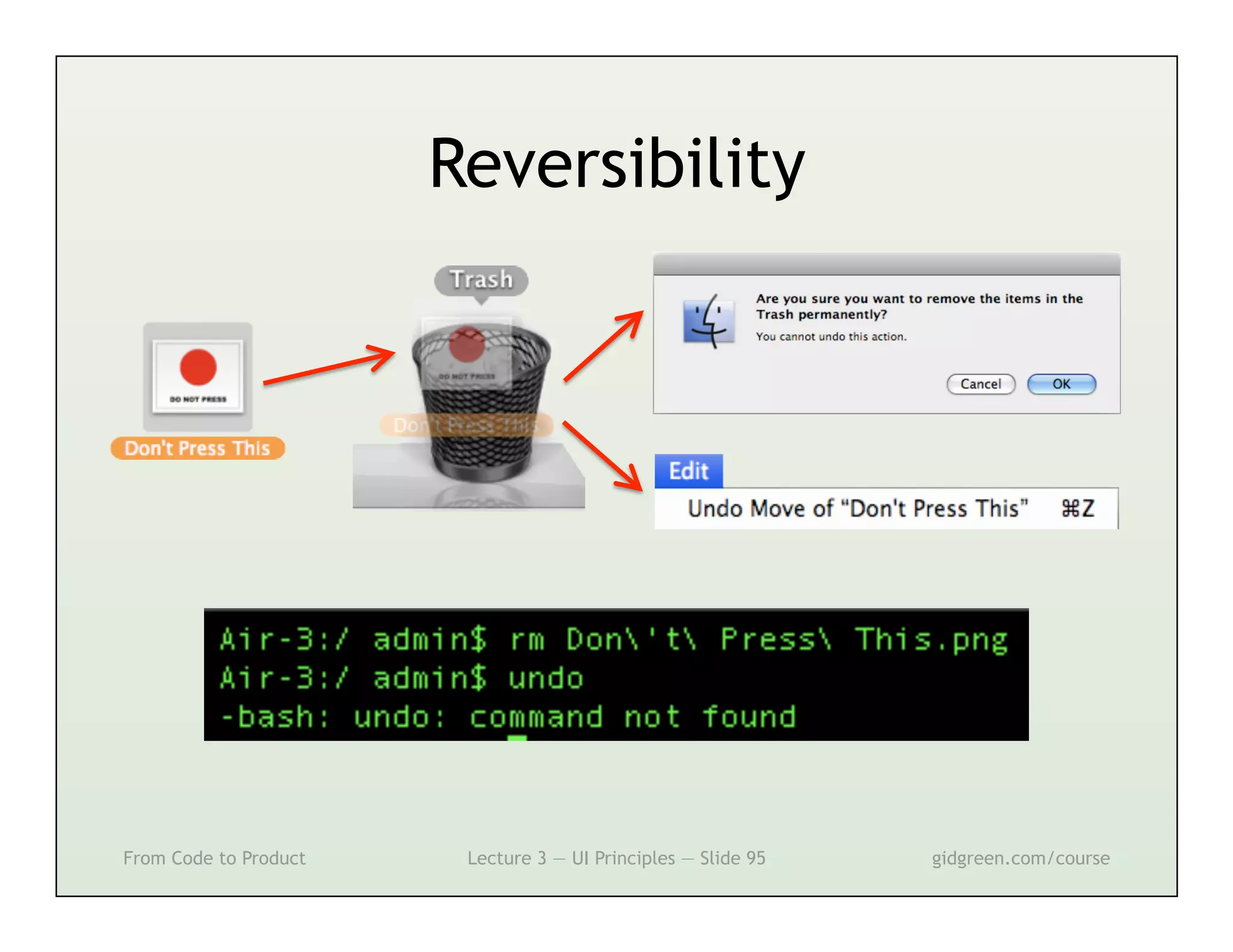
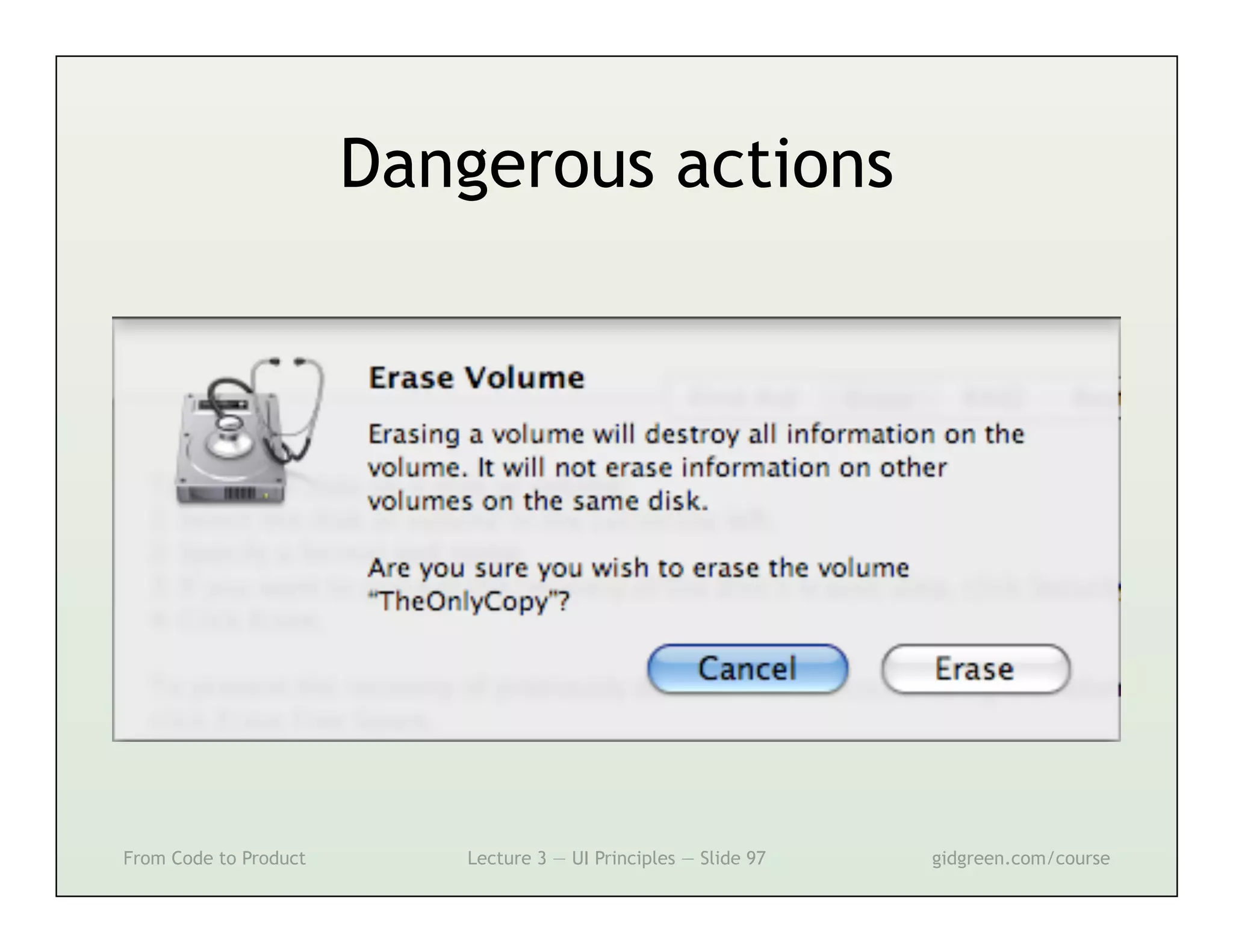
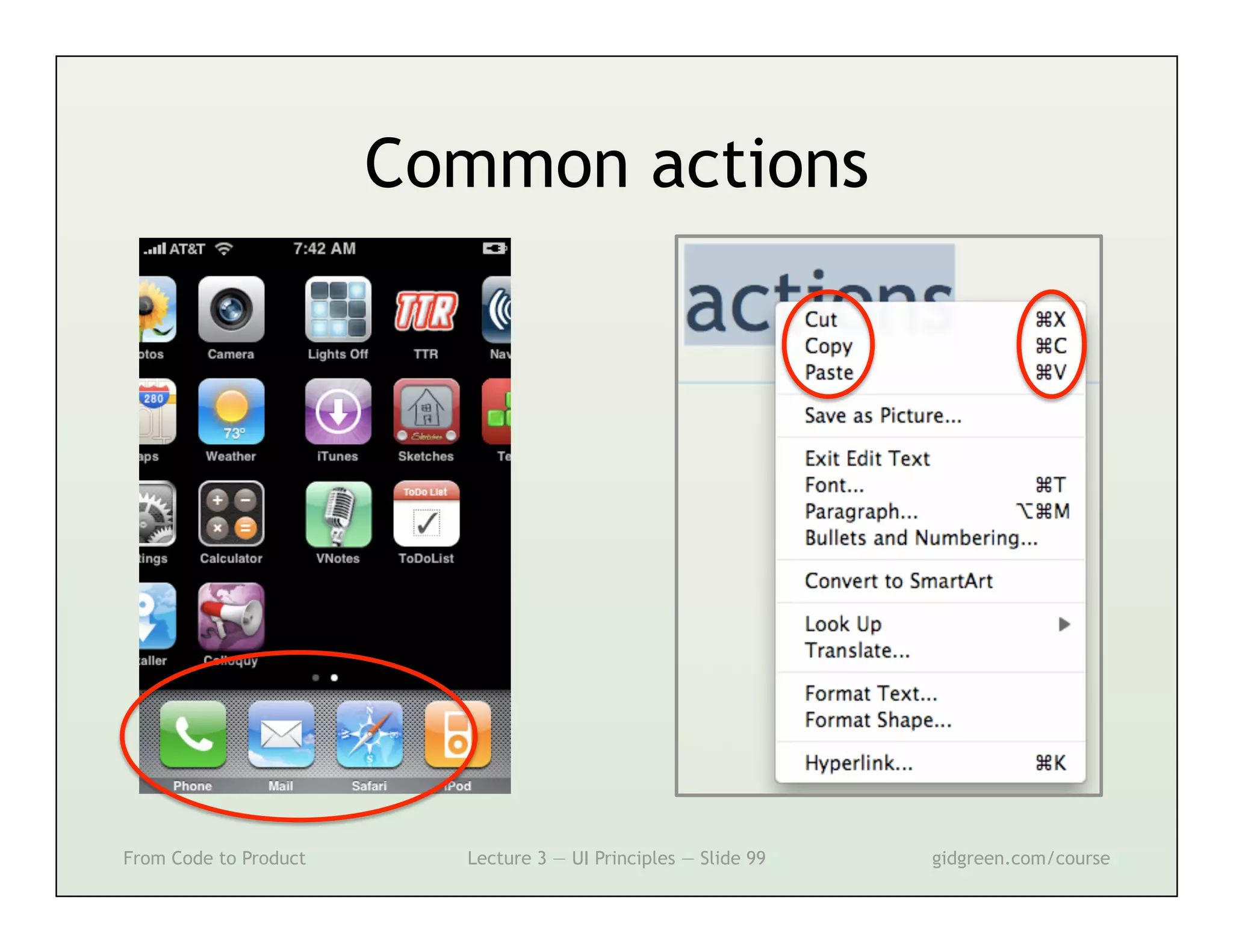
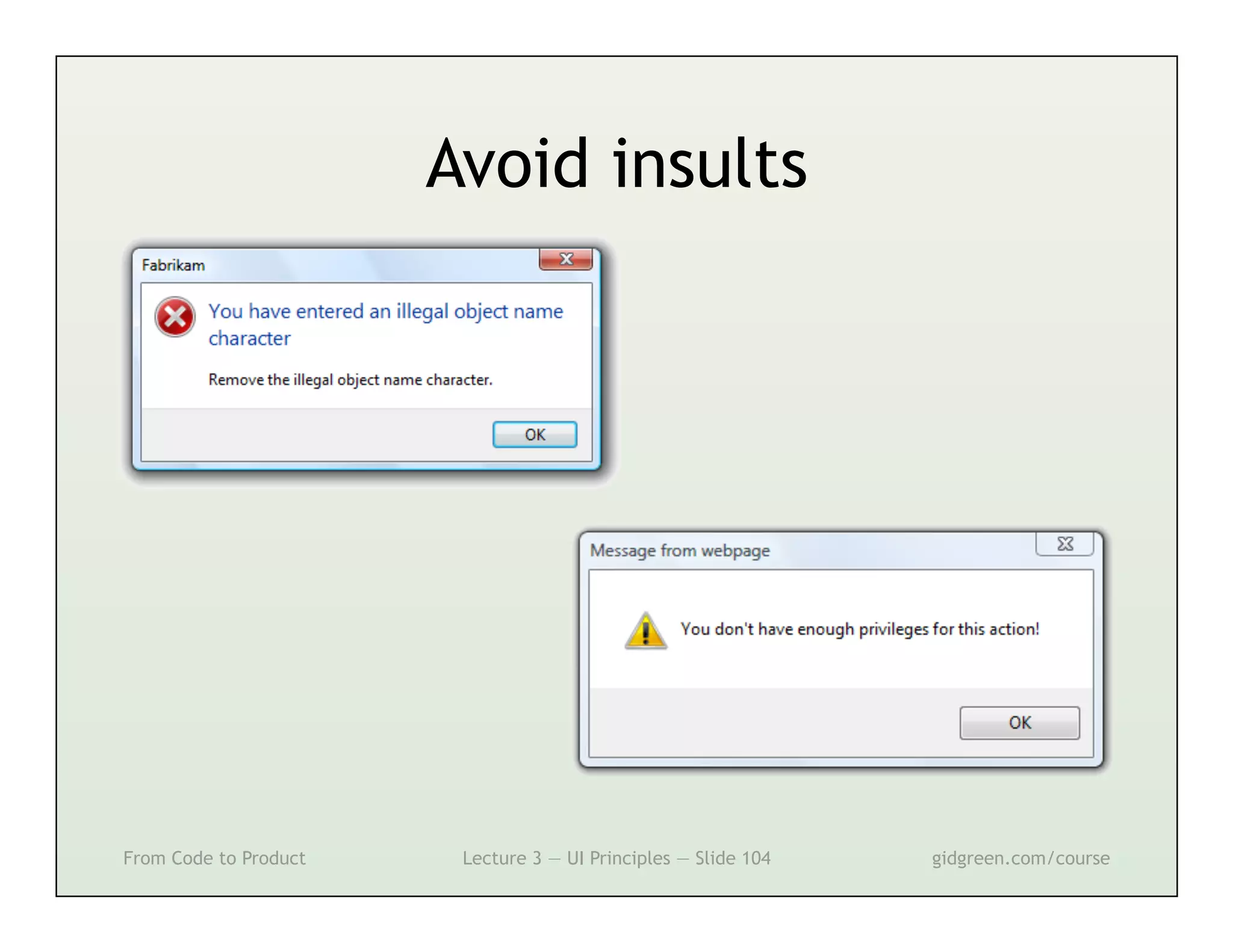
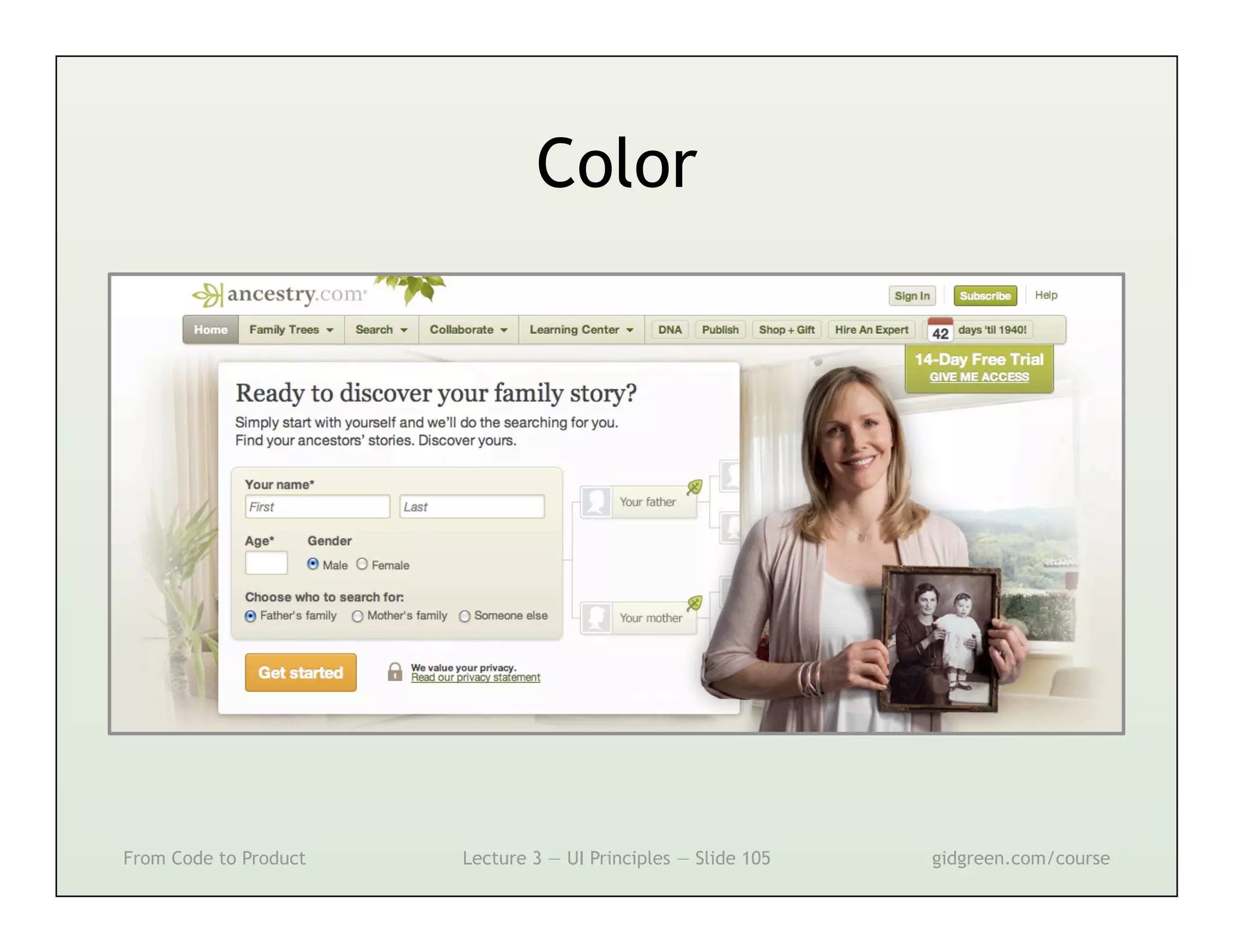
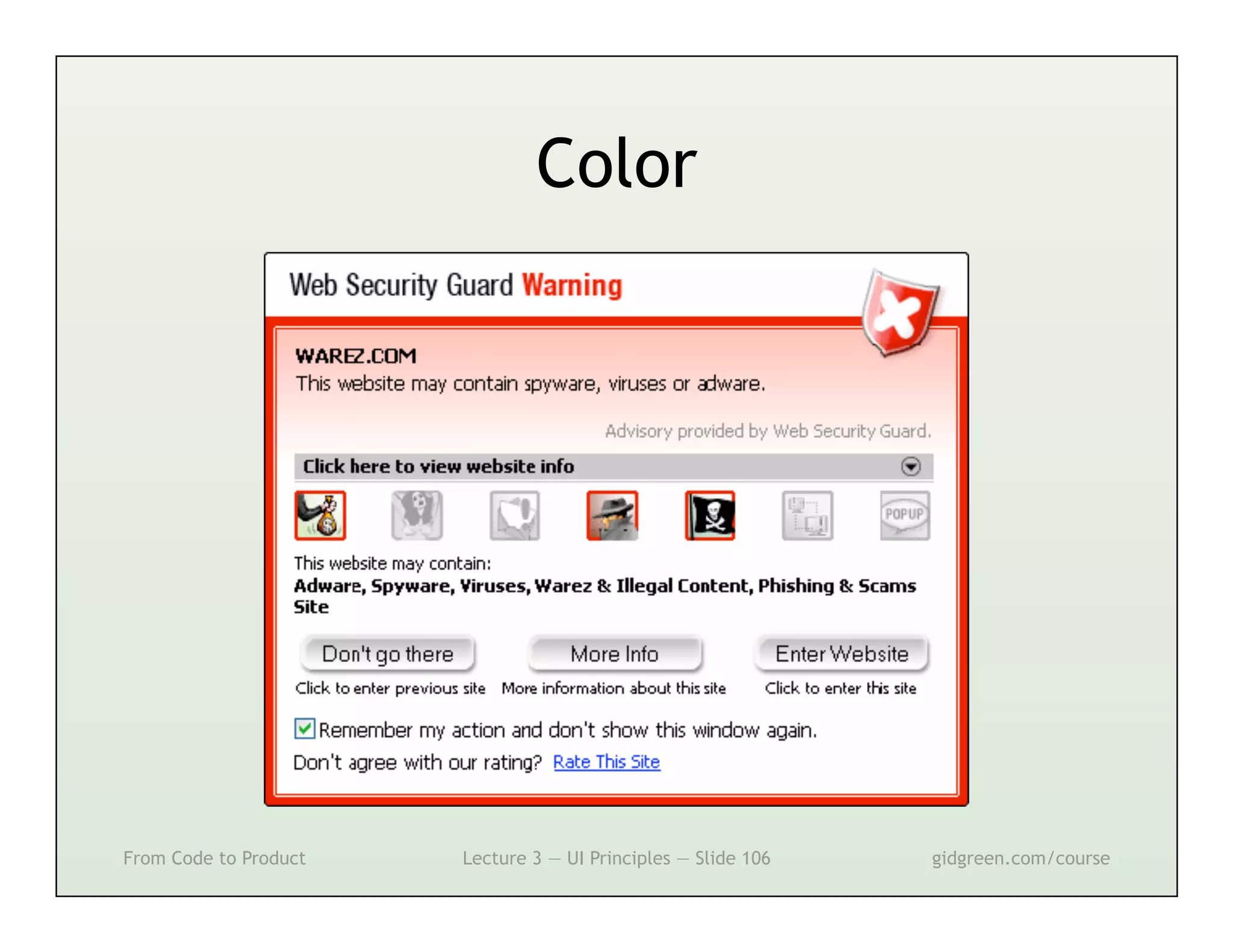
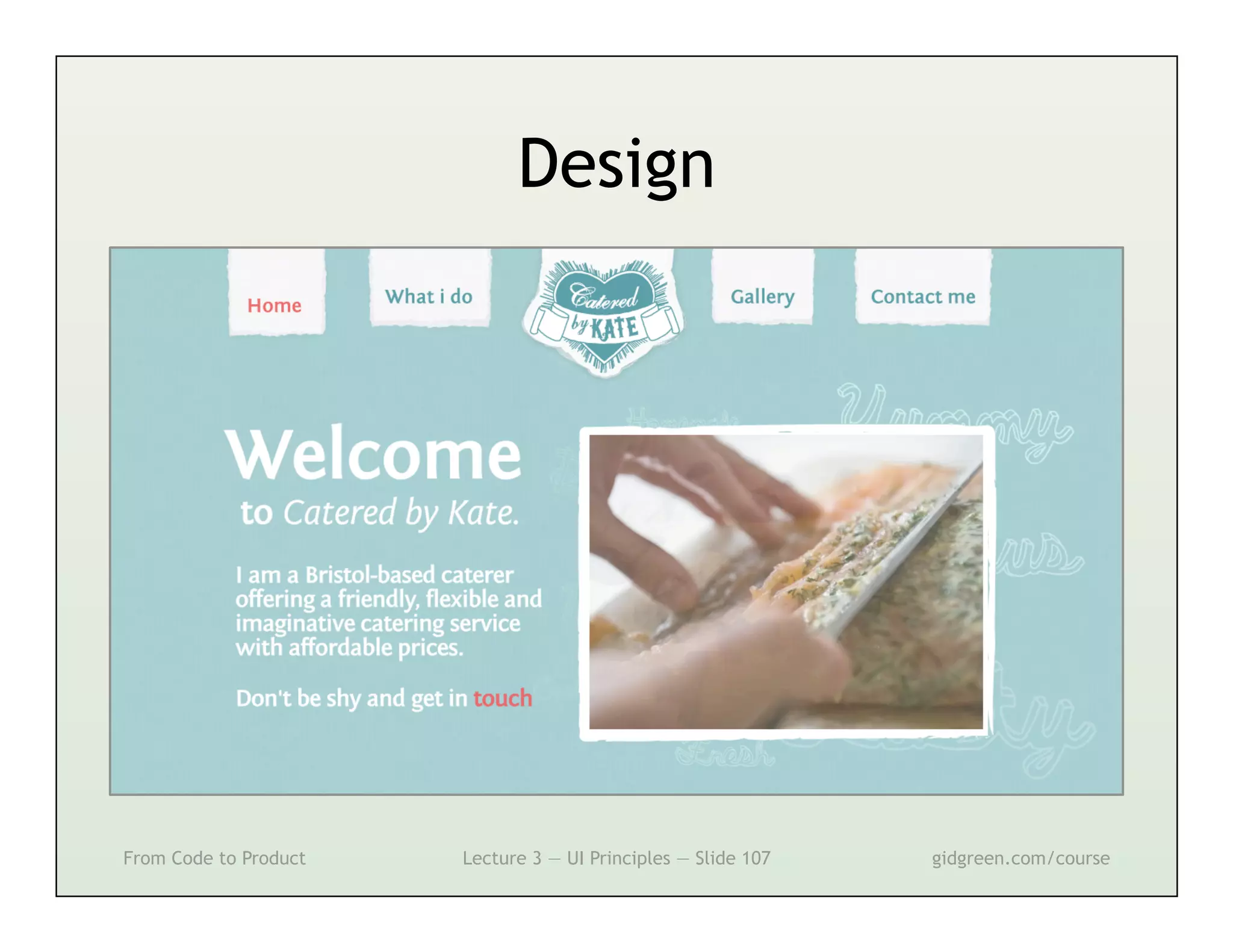
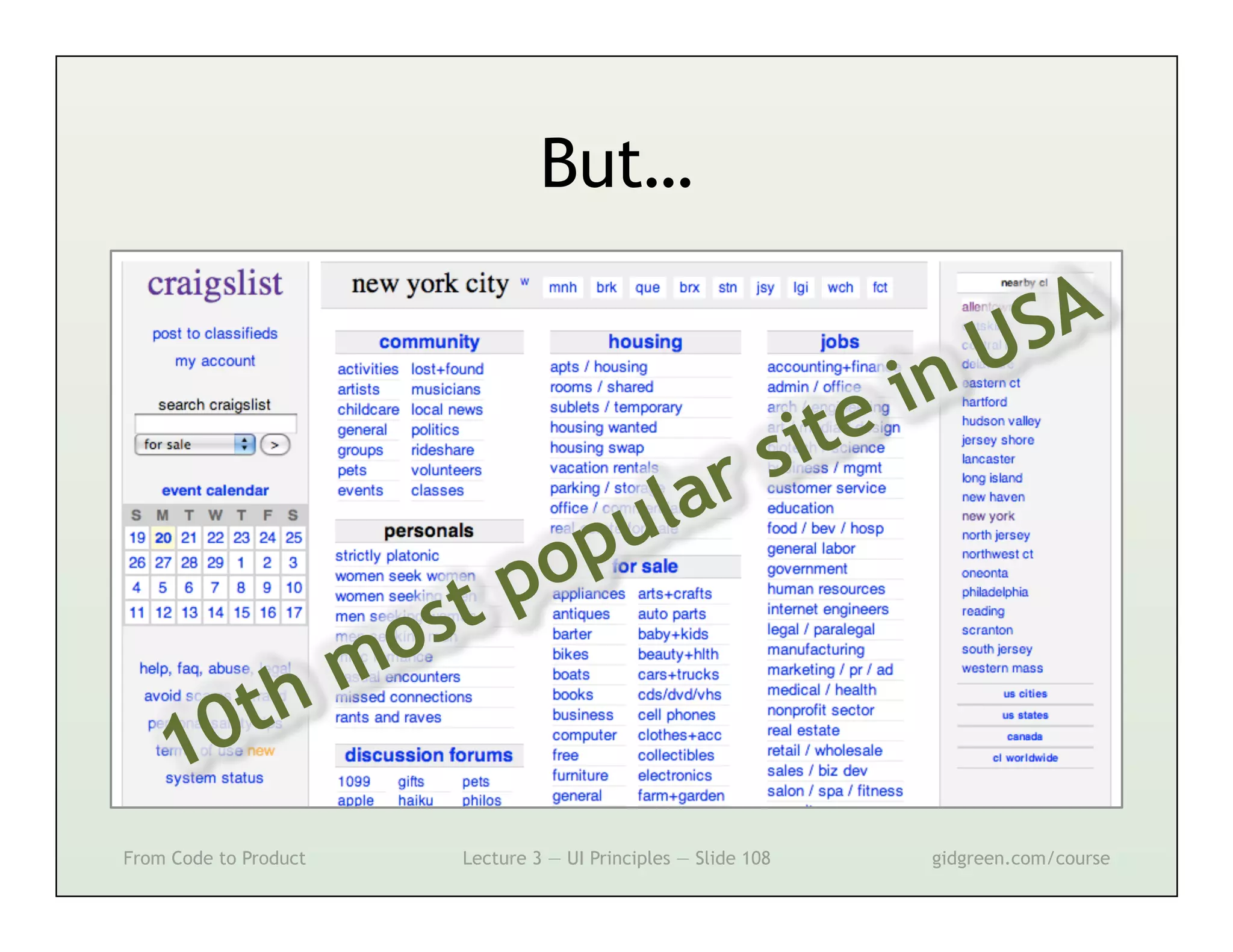
This document summarizes a lecture on user interface principles. It covers topics like vision, cognition, memory, action, and emotion as they relate to designing interfaces. Specific principles discussed include proximity, similarity, continuity, symmetry, structure, prominence, sequence, clutter, minimalism, affordances, mental models, metaphors, and direct manipulation. The goal is to design intuitive interfaces that are easy for users to understand and interact with.