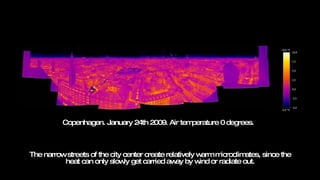
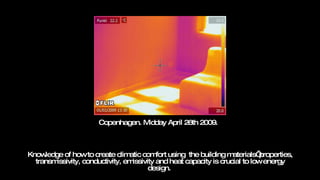
Urban areas experience higher temperatures than surrounding areas due to the urban heat island effect, primarily caused by solar heat absorption in dense city centers and waste heat from human activities. This phenomenon exacerbates energy consumption for cooling, contributes to increased smog due to higher temperatures, and can lead to extreme weather impacts. Effective urban planning that considers building materials, spatial design, and vegetation is essential for mitigating these effects and enhancing climatic comfort.