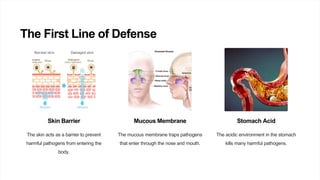
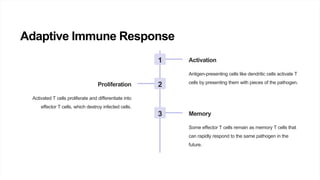
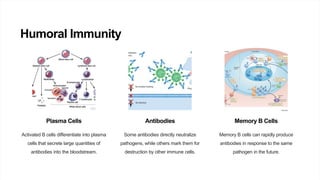
The immune system protects the body from pathogens through a variety of cells and processes. It has both innate defenses like skin, mucus, and stomach acid, as well as adaptive responses mediated by B cells, T cells, macrophages, and natural killer cells. The adaptive immune response involves activation of T cells by antigen-presenting cells, proliferation of effector T cells, and the creation of memory T cells. Immunizations boost immunity by training the immune system to recognize pathogens without causing disease.