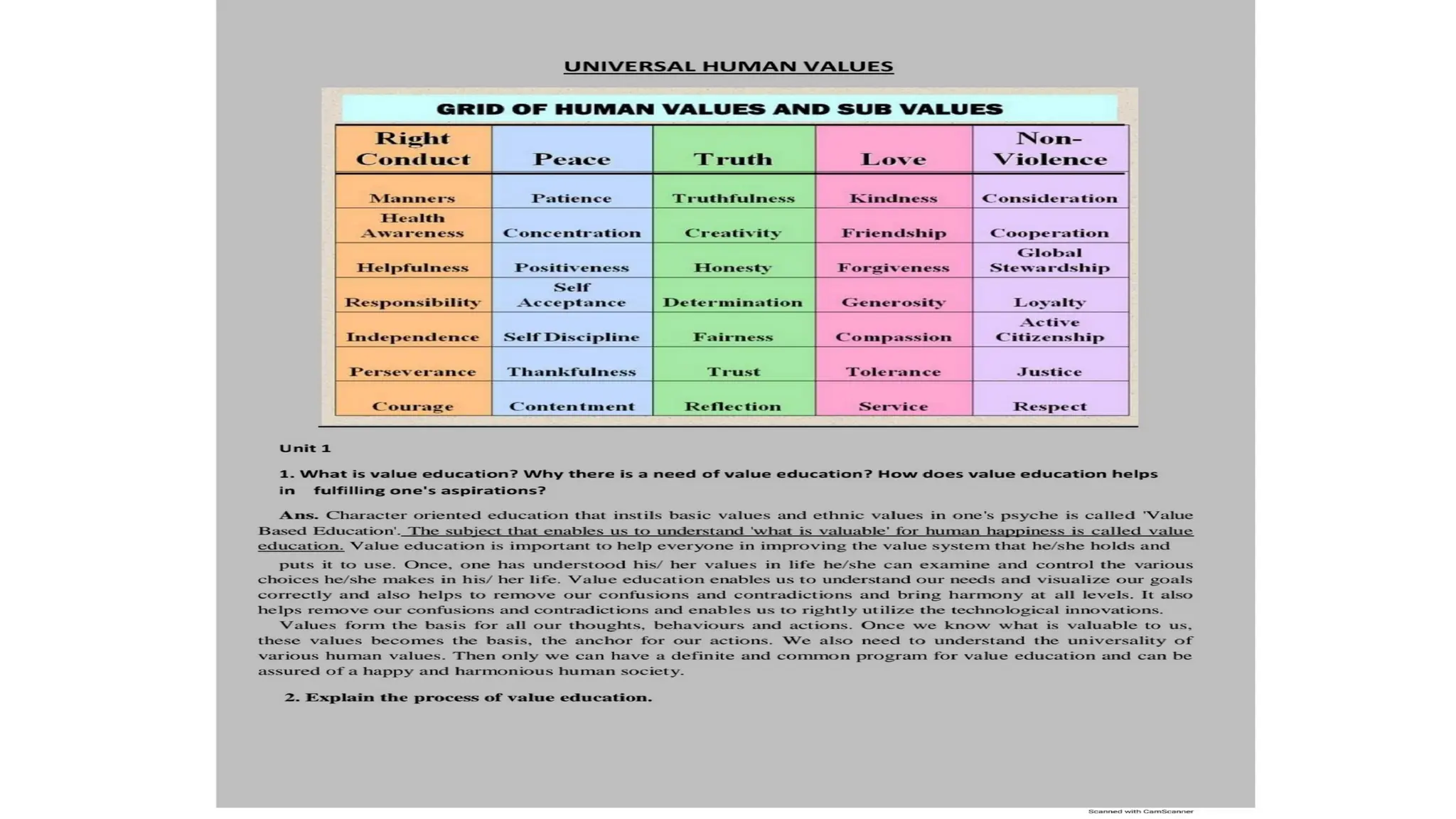
Universal human values are fundamental principles promoting harmony and respect across cultures, including concepts like respect, integrity, and compassion. These values are crucial for fostering peace, equality, and justice in society, while addressing global challenges collaboratively. Challenges such as globalization and cultural differences must be navigated through ongoing dialogue and education to uphold these essential values.