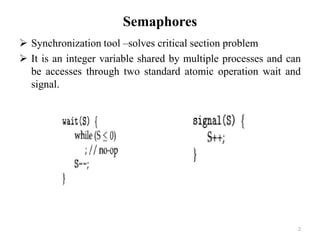
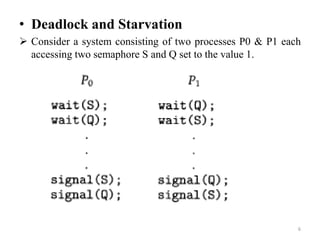
Semaphores are a synchronization tool that can solve critical section problems. They are integer variables that can be accessed atomically by multiple processes using wait and signal operations. Semaphores allow mutual exclusion without busy waiting, which wastes CPU cycles. Each process has an integer value and queue. When a process waits on a semaphore, it is added to the queue. A signal removes a process from the queue and resumes its execution. Semaphores can be implemented using binary semaphores with values of 0 or 1 to represent an empty or occupied critical section respectively. Processes are blocked or added to the queue depending on the semaphore value.