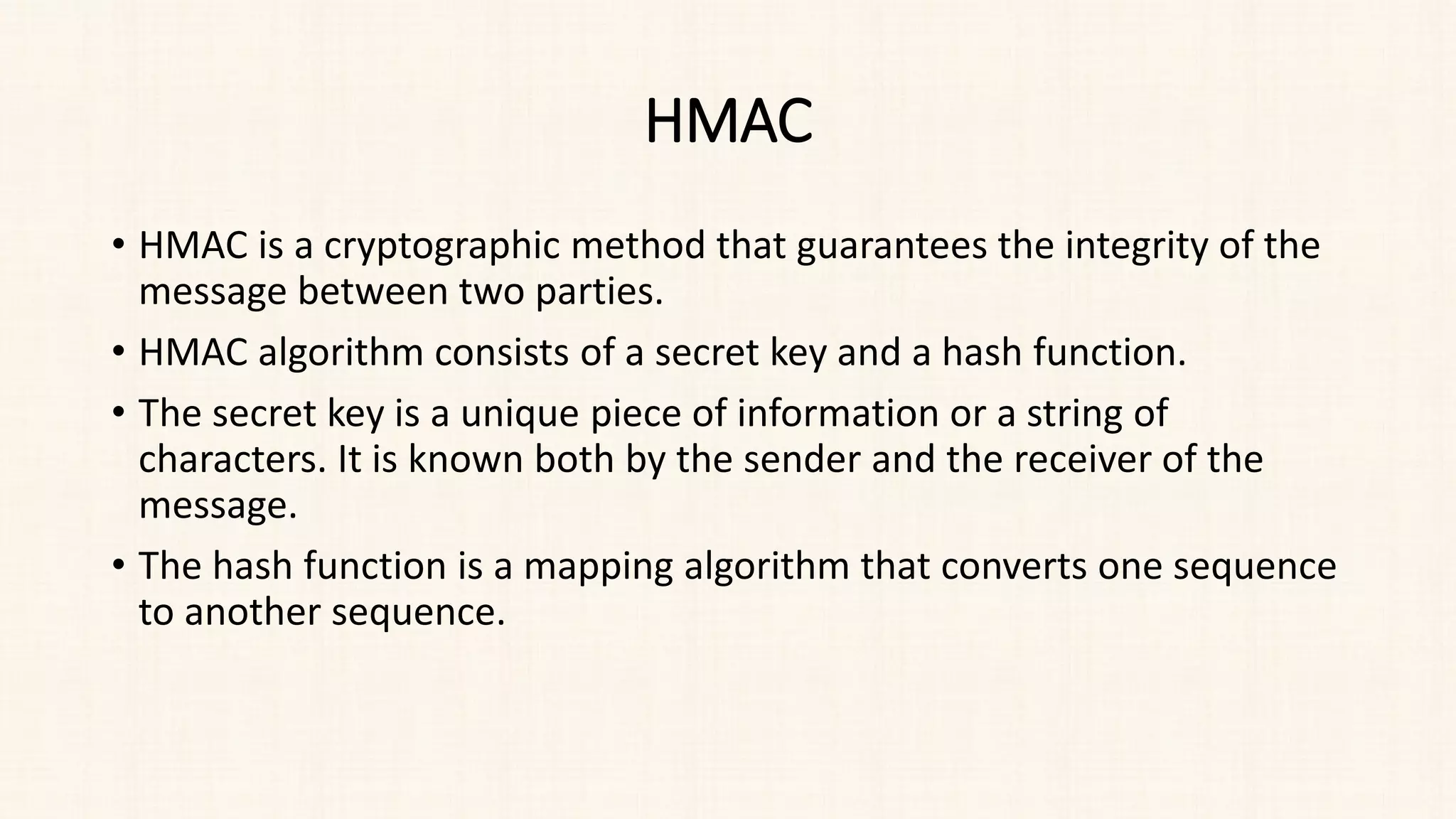
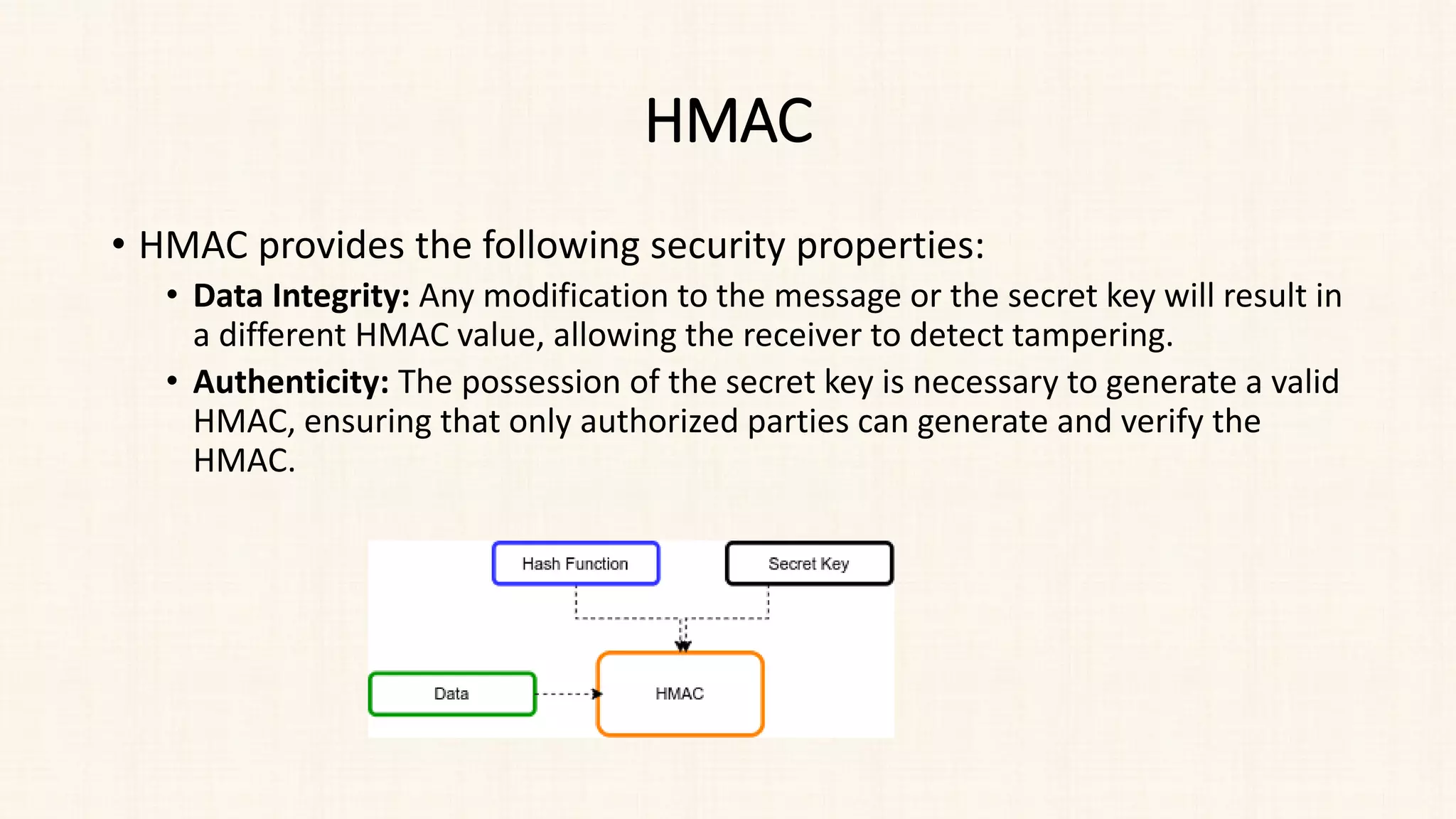
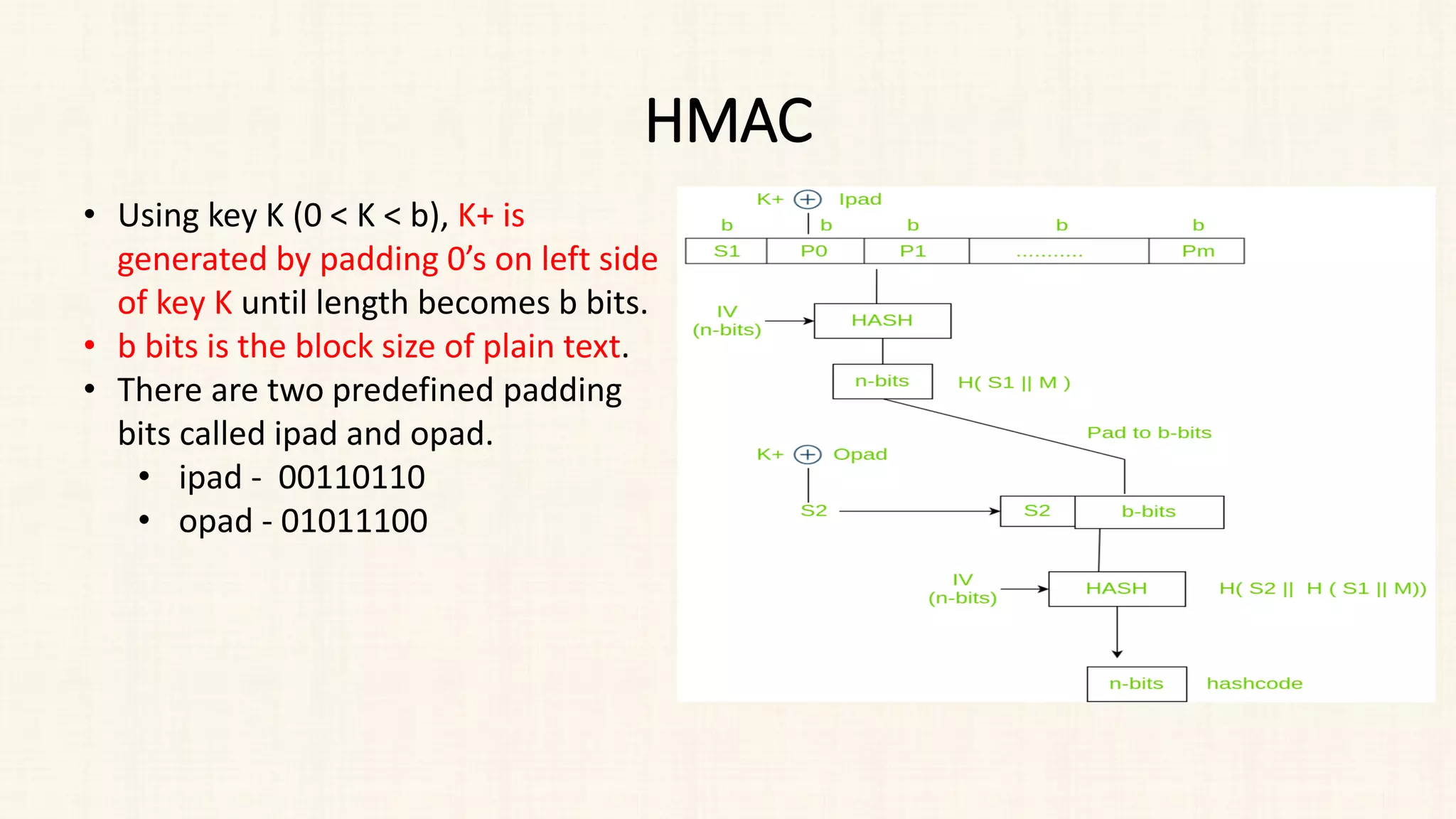
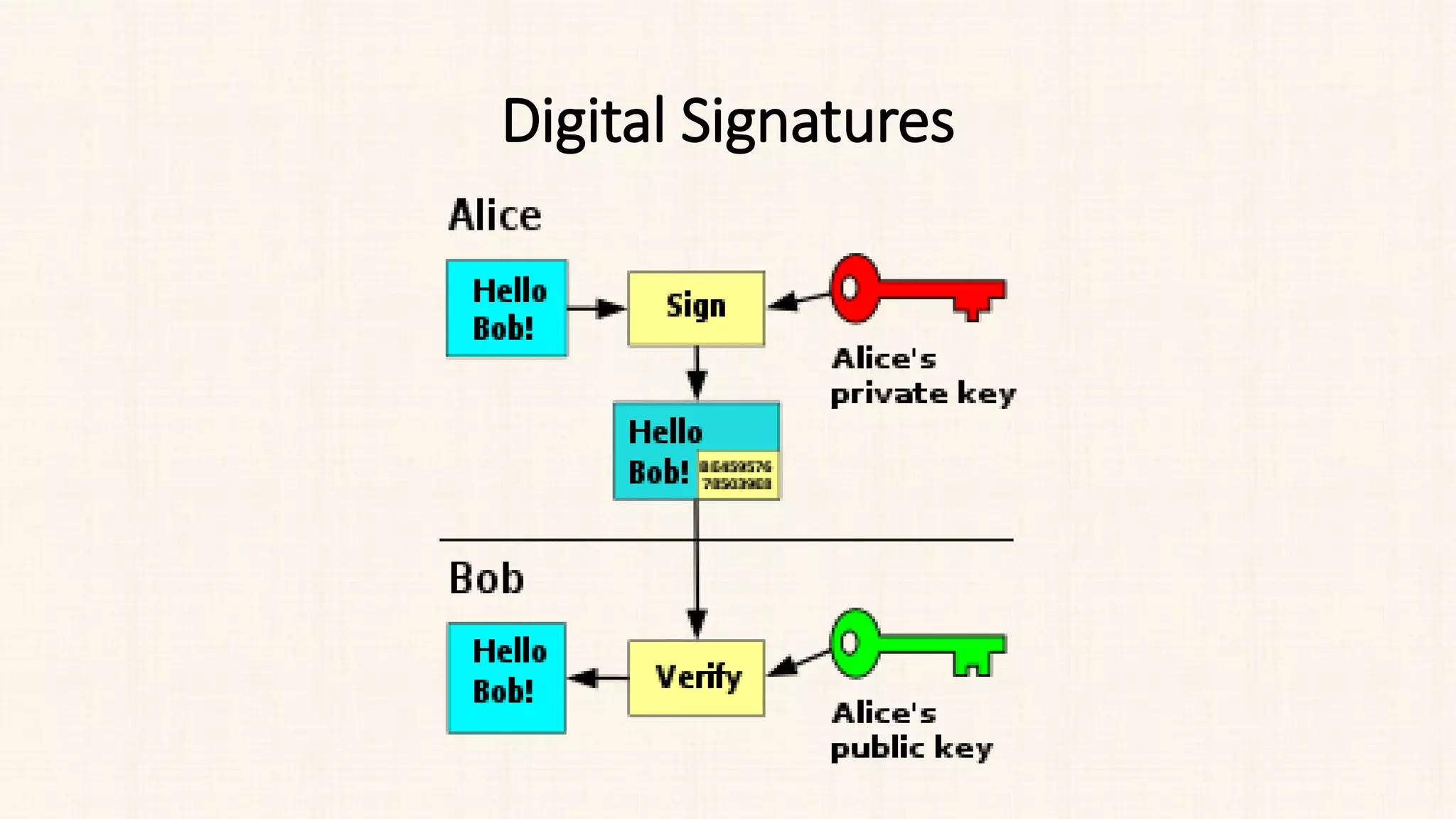
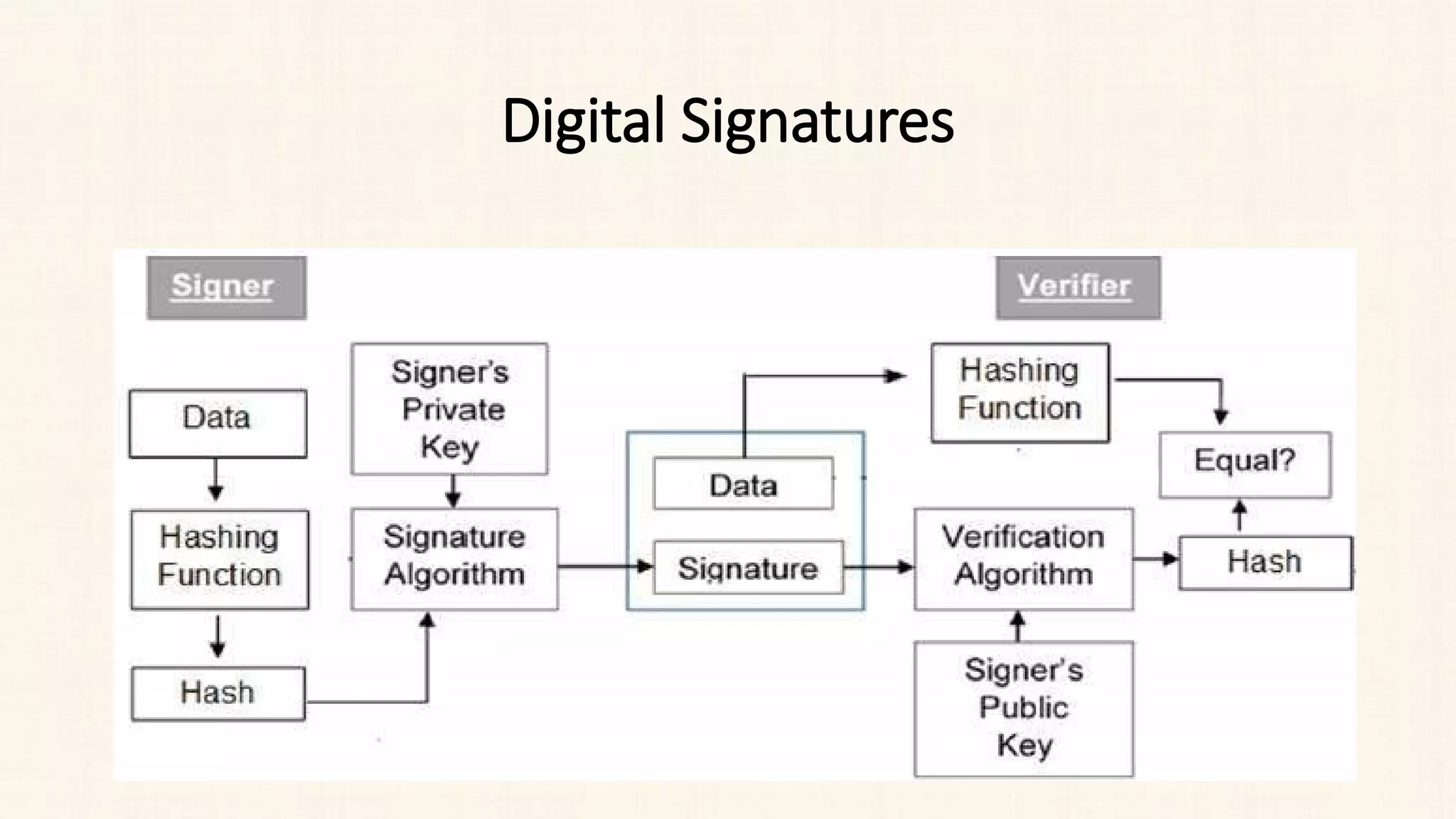
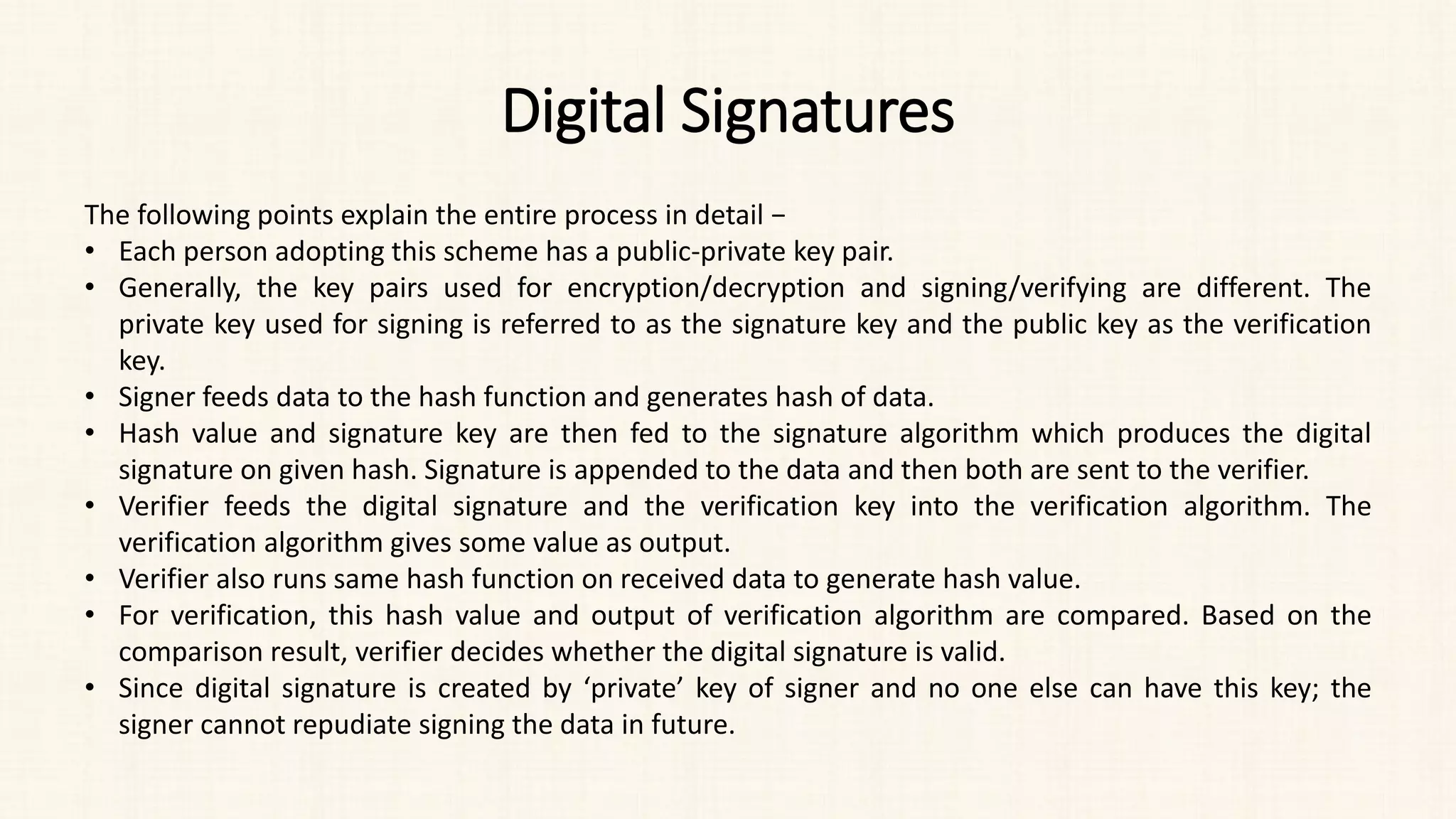
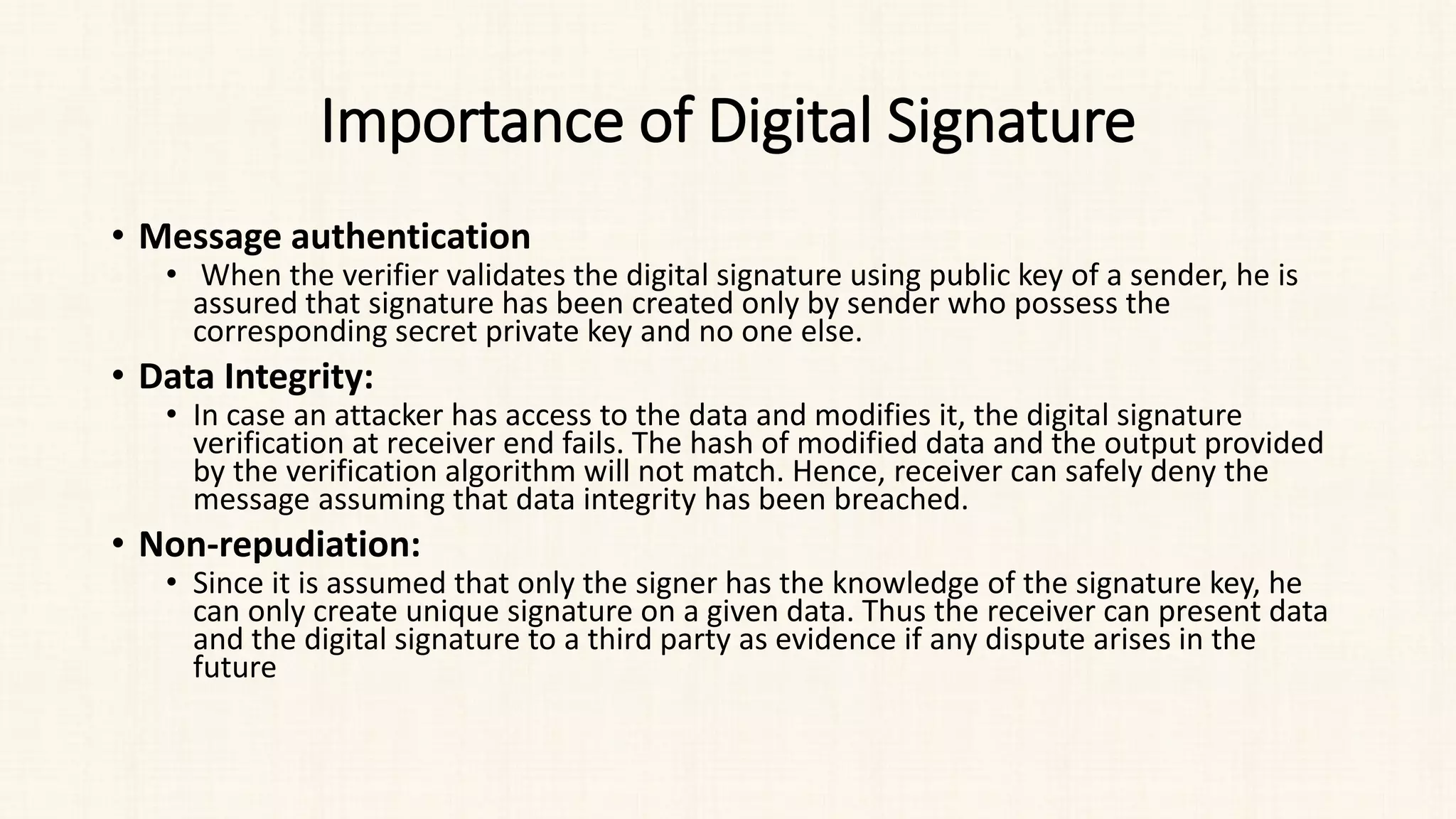
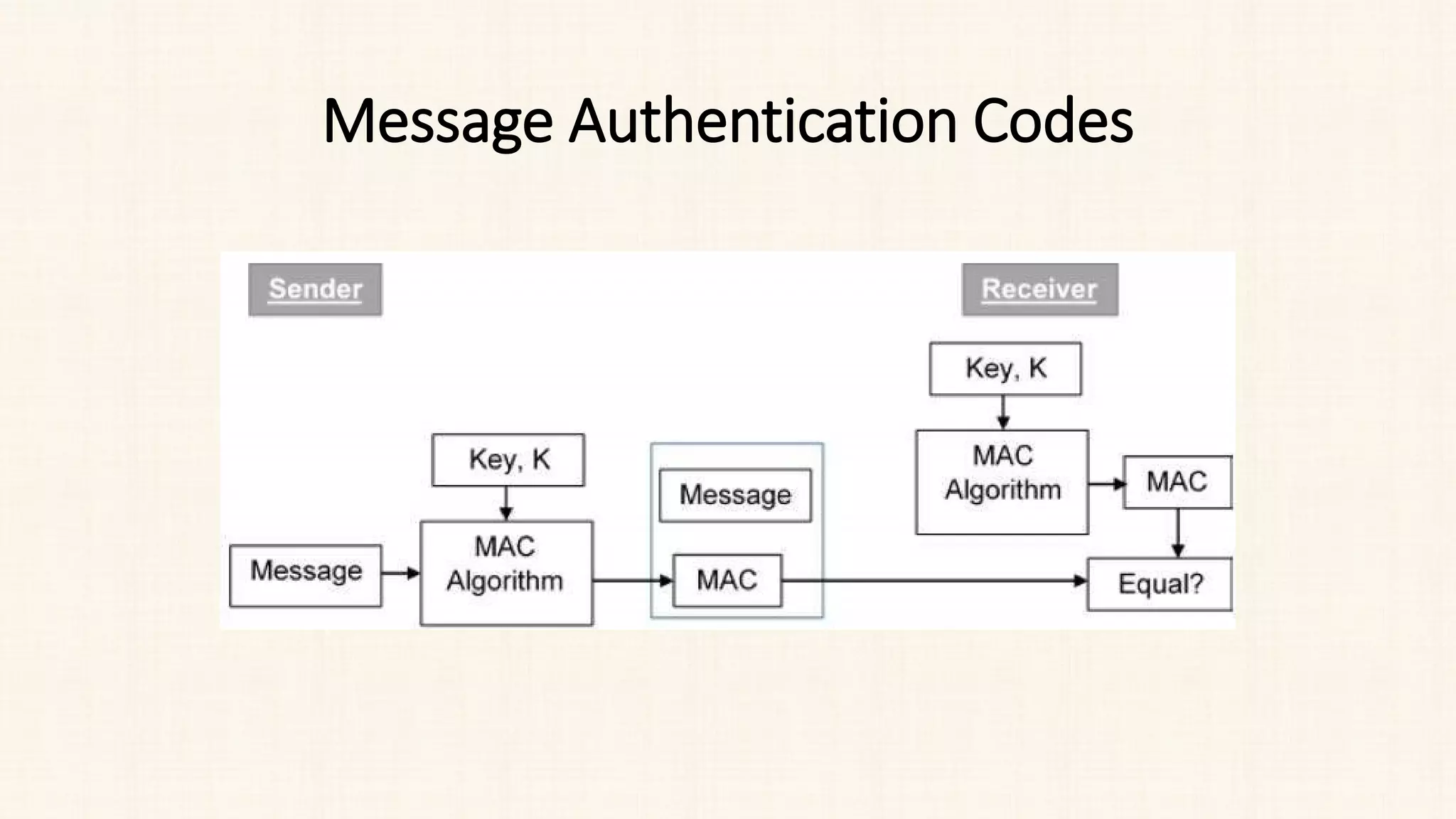
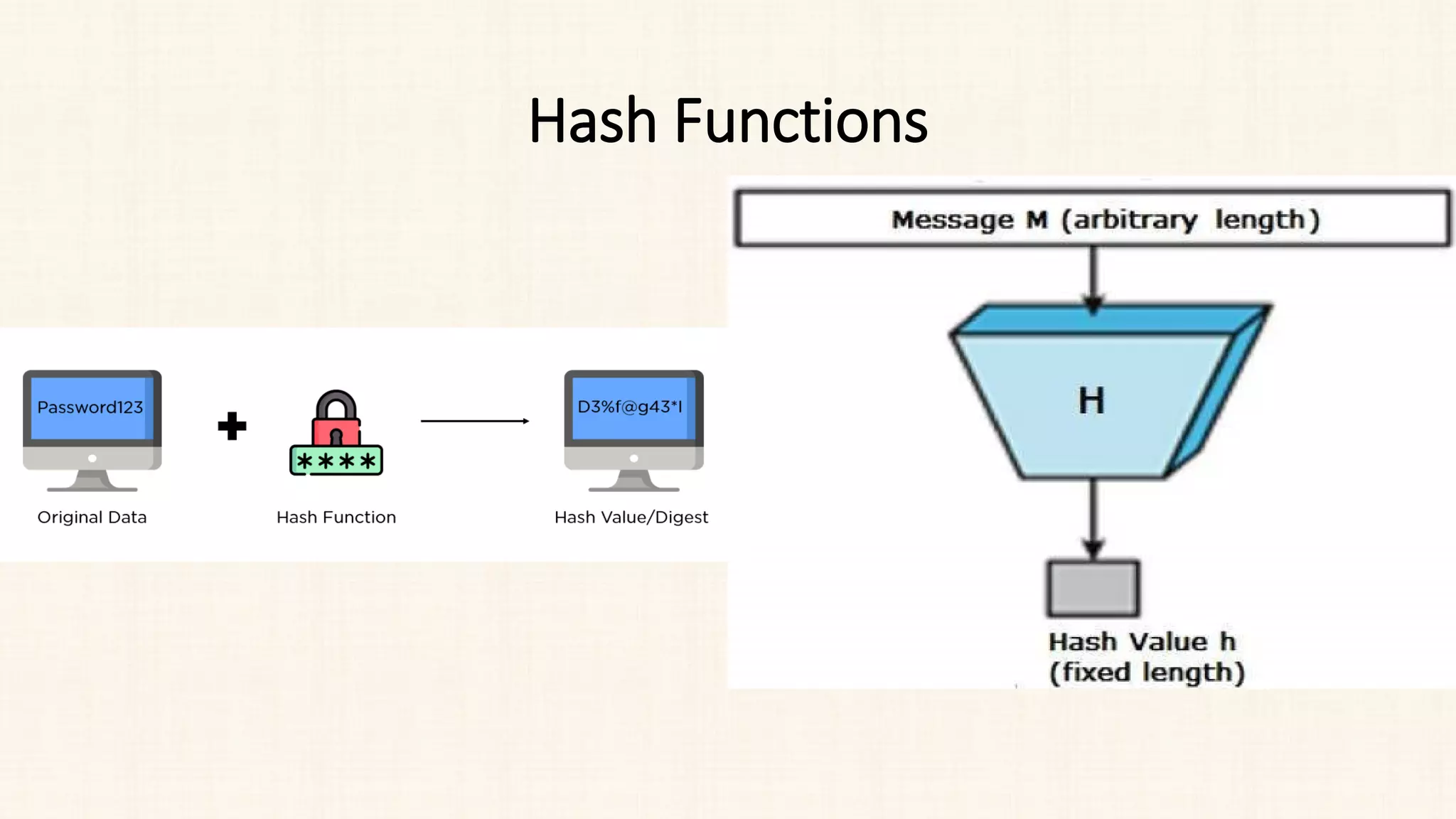
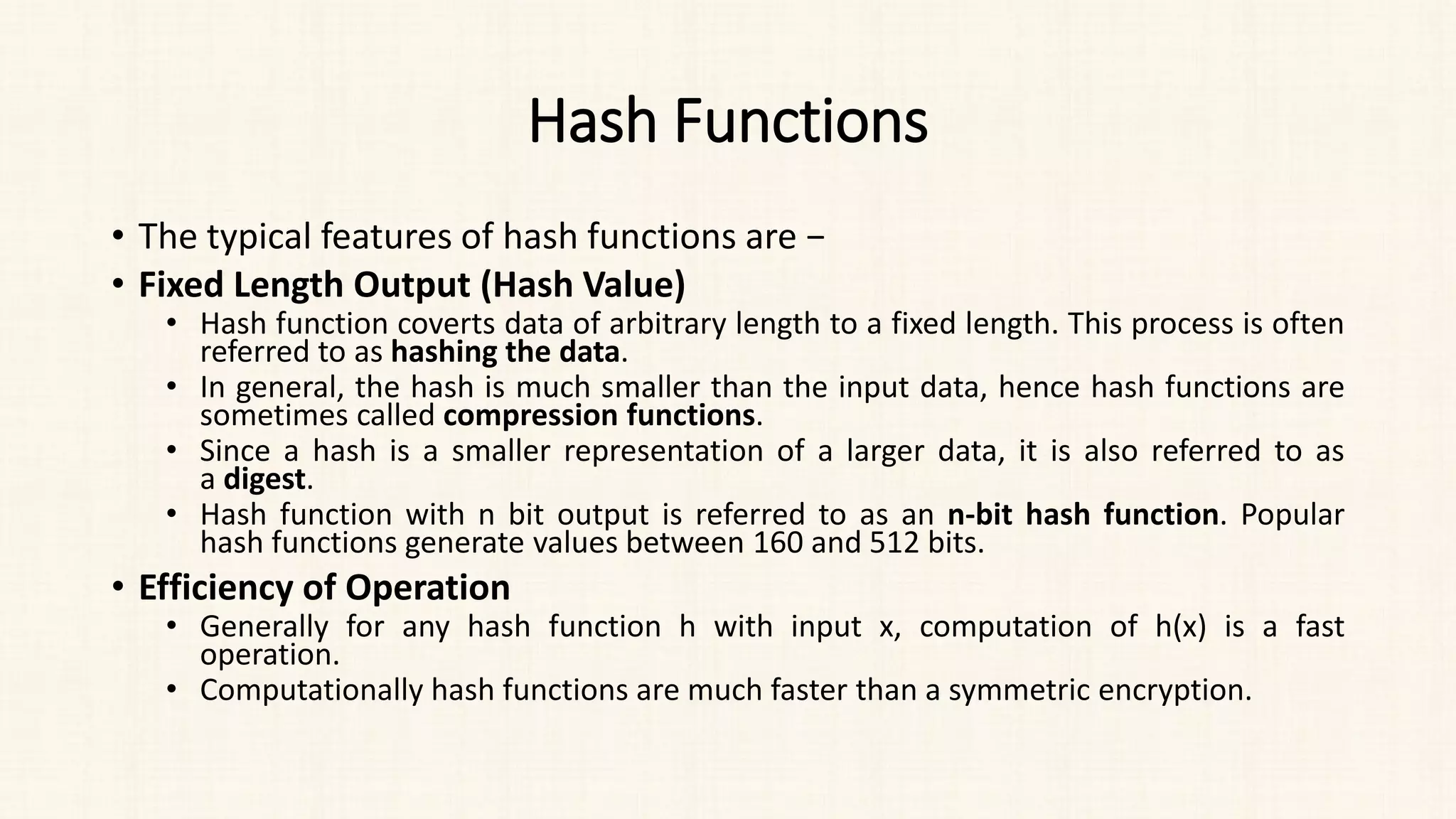
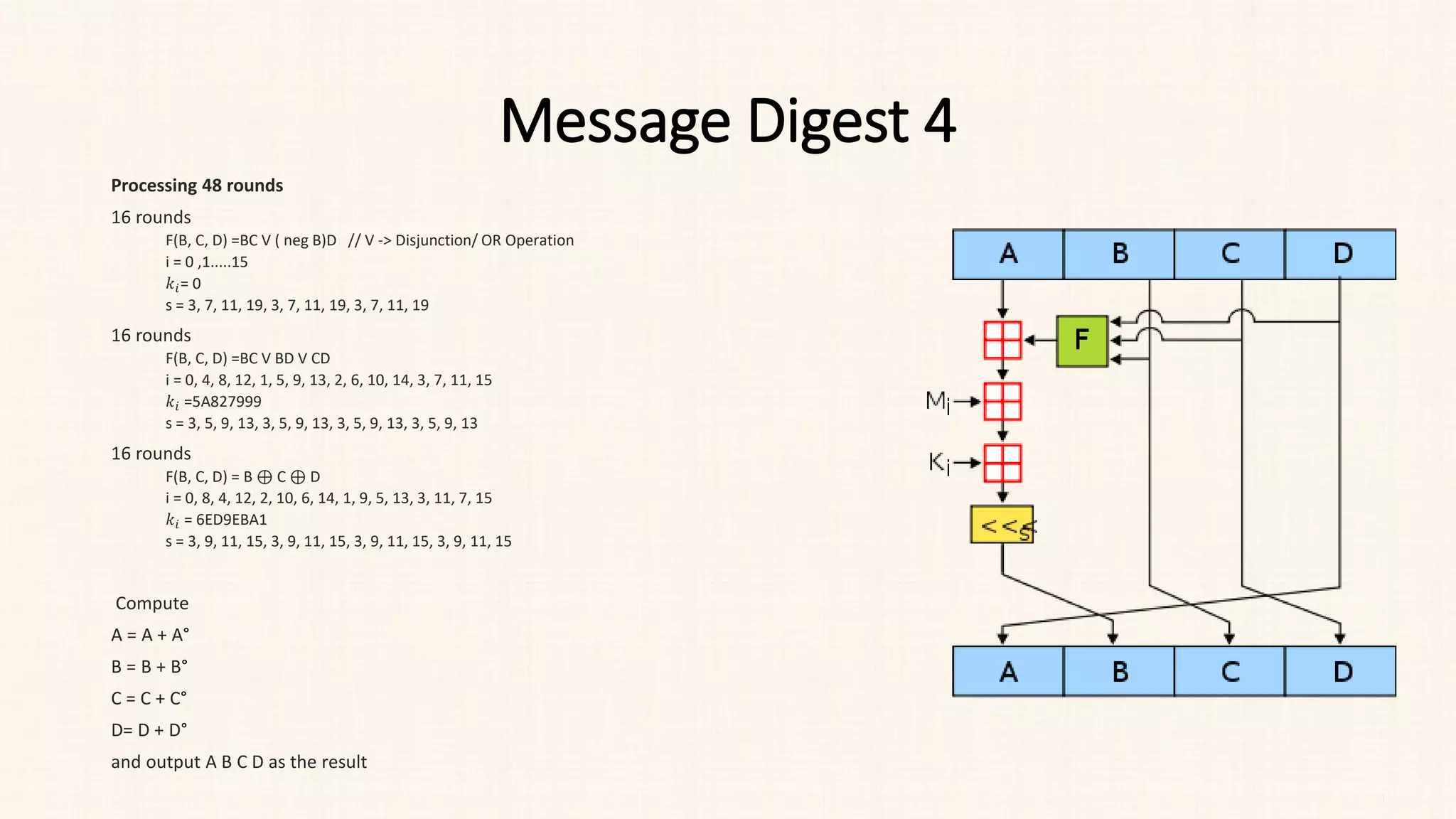
The document discusses message authentication and hash functions. It defines message authentication as a way to ensure data integrity and describes how message authentication codes (MACs) work using symmetric keys. It also explains how hash functions take an input of any length and produce a fixed-length output digest. Specific hash functions discussed include MD4, MD5, SHA-1, and how they work by padding the input, initializing buffers, processing the input in blocks, and outputting the digest.








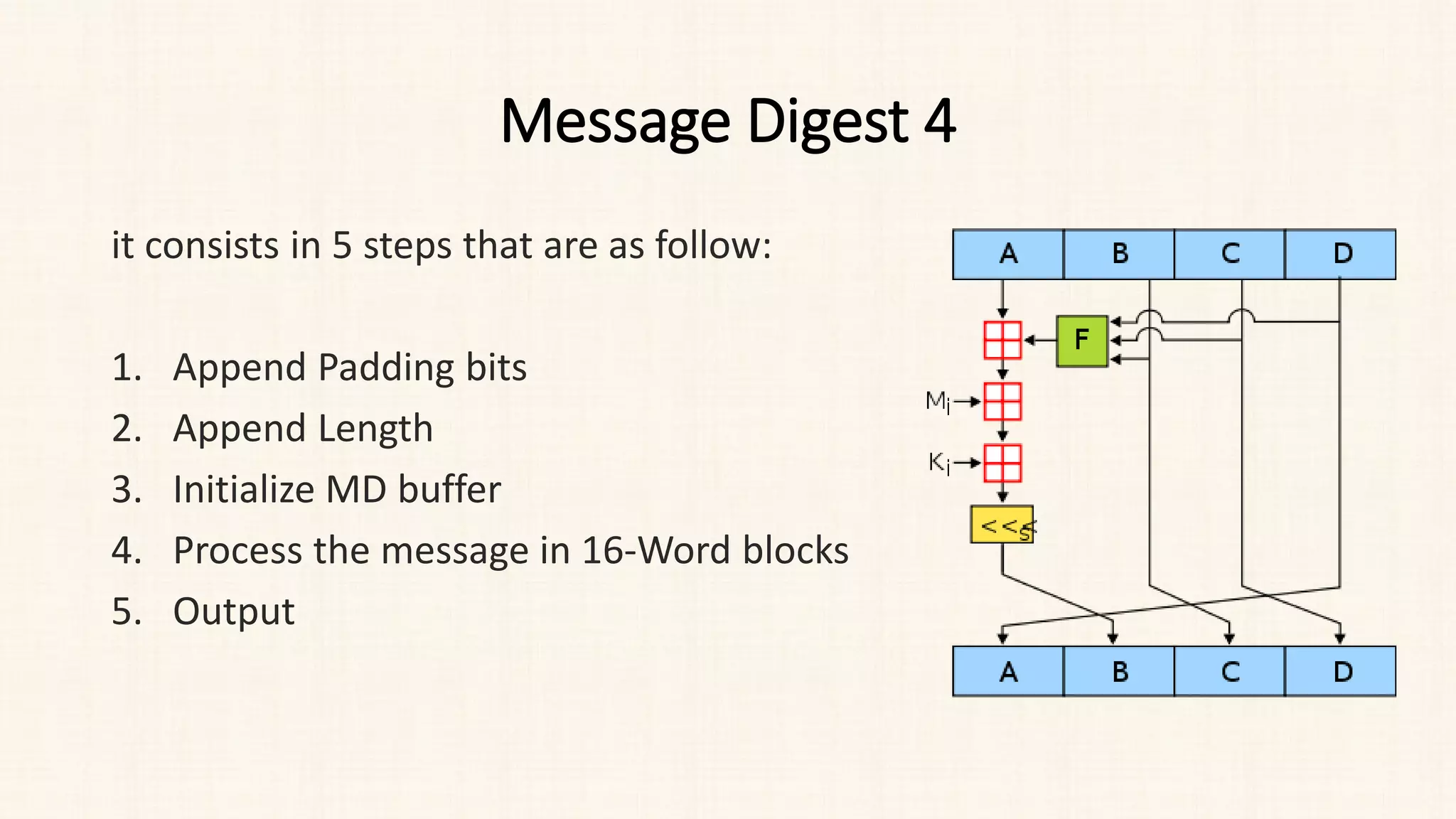









![Message Digest 5
Steps in MD5 Algorithm
• Process Each Block:
• Each 512-bit block gets broken down further into 16 sub-blocks of 32 bits
each. There are four rounds of operations, with each round utilizing all the
sub-blocks, the buffers, and a constant array value.
• It perform 64 rounds.
• This constant array can be denoted as T[1] -> T[64].
• Each of the sub-blocks are denoted as M[0] -> M[15].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-3-230810025102-df839292/75/Unit-3-pdf-23-2048.jpg)
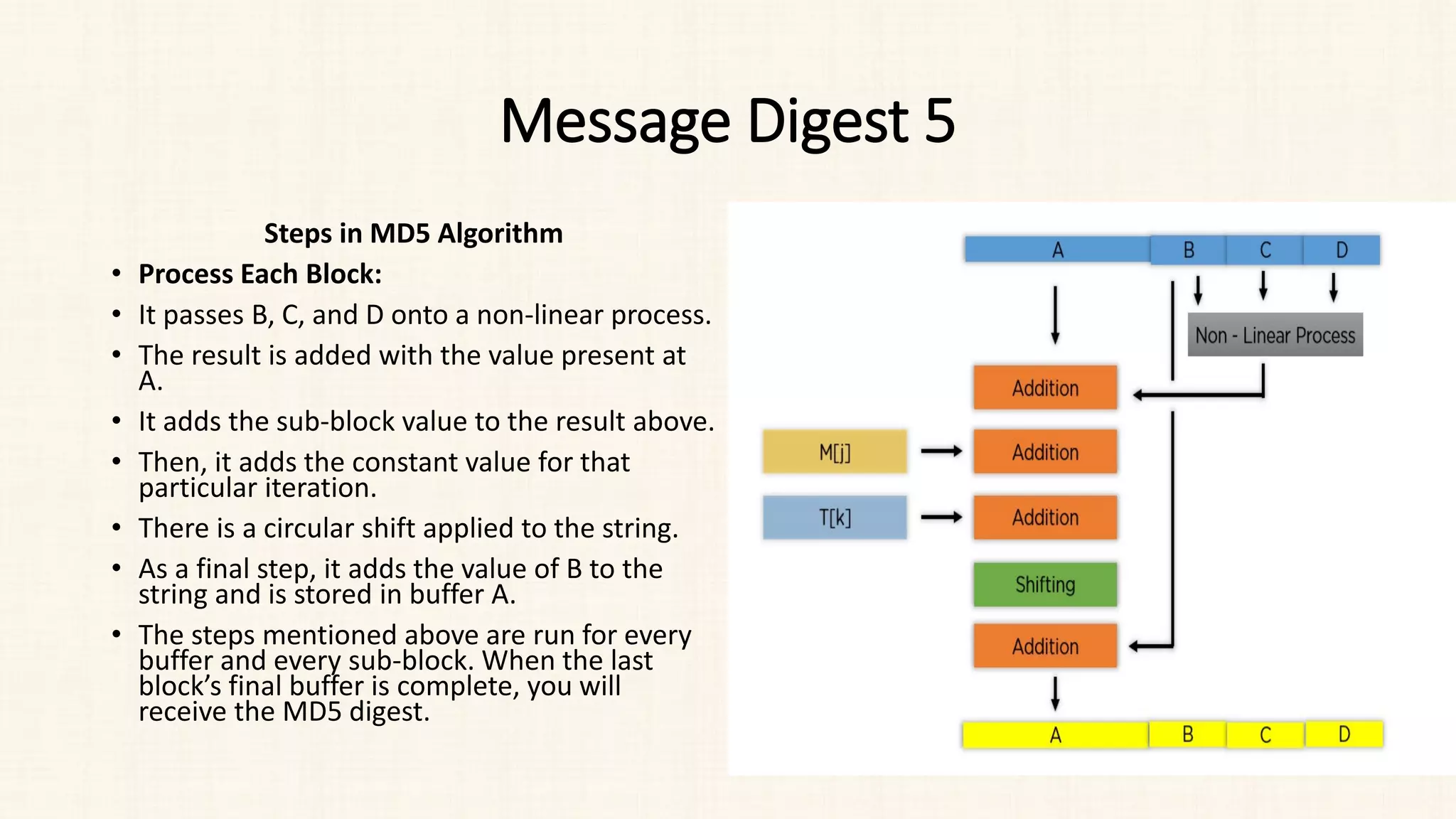
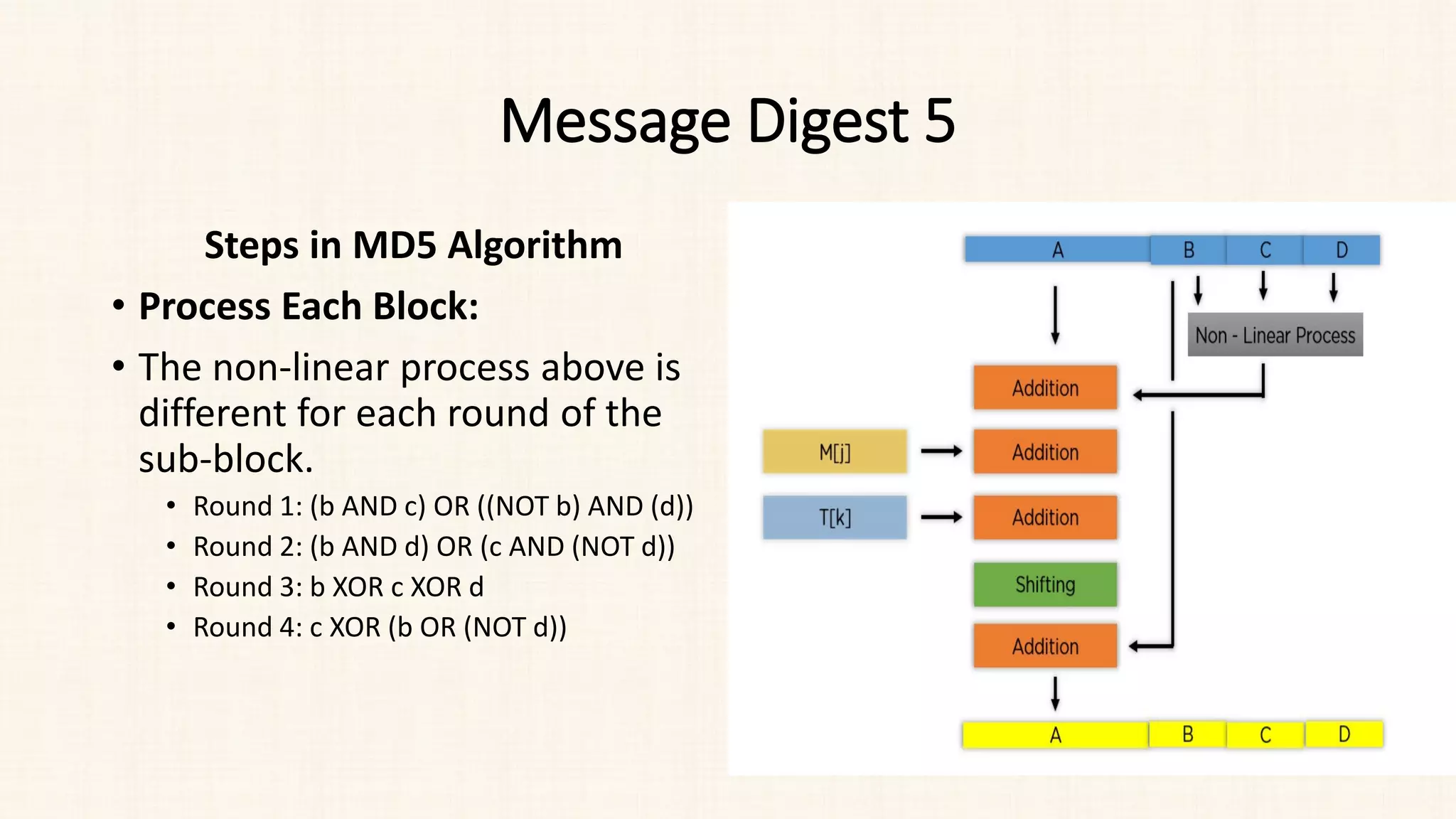
![Message Digest 5
Steps in MD5 Algorithm
• Process Each Block:
• Each round has a repeating
sequence of 4 shift amounts (s in
[abcd k s i]) :
• 7, 12, 17 and 22 for the round 1
• 5, 9, 14 and 20 for the round 2
• 4, 11, 16 and 23 for the round 3
• 6, 10, 15 and 21 for the round 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-3-230810025102-df839292/75/Unit-3-pdf-26-2048.jpg)


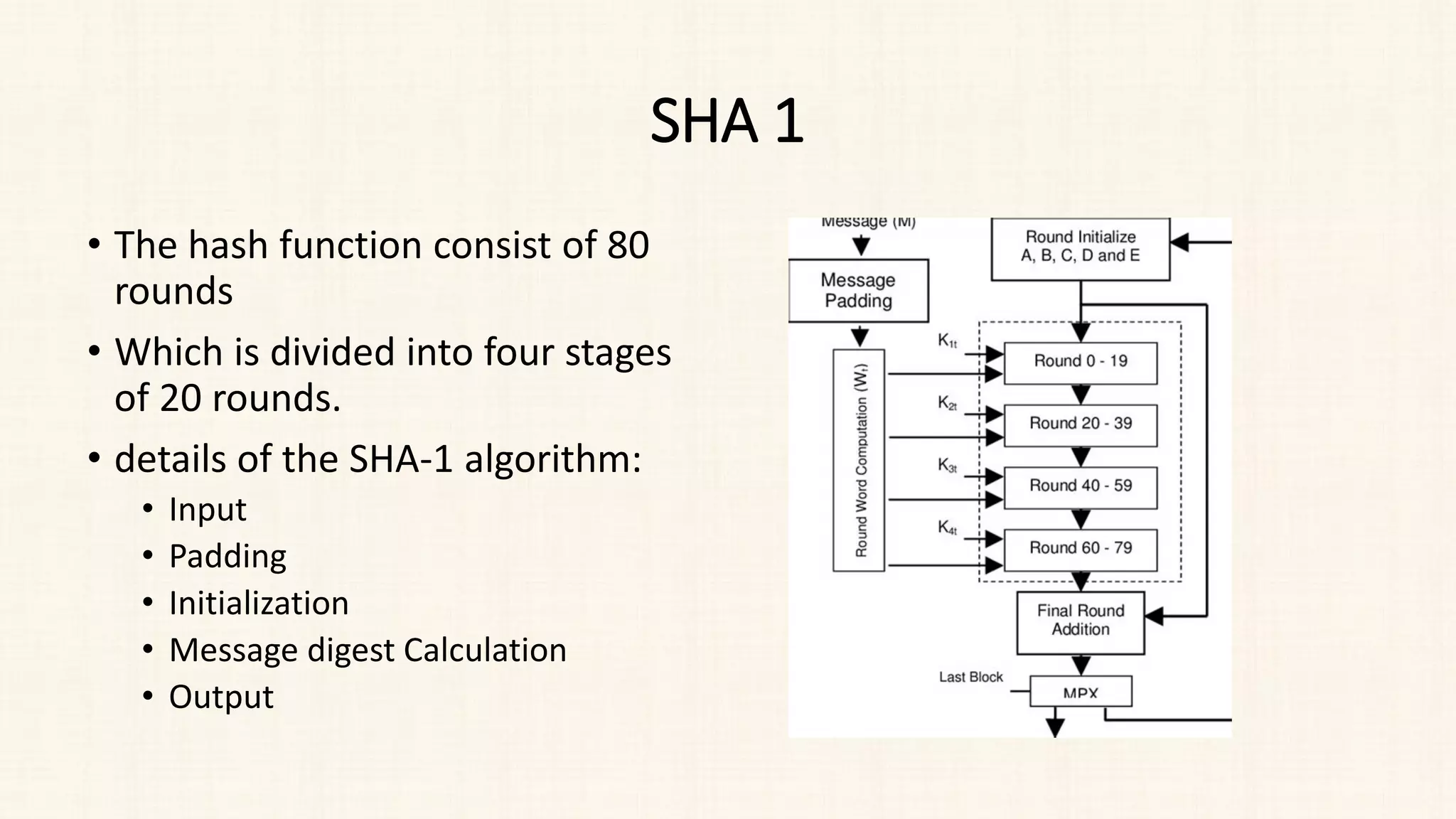


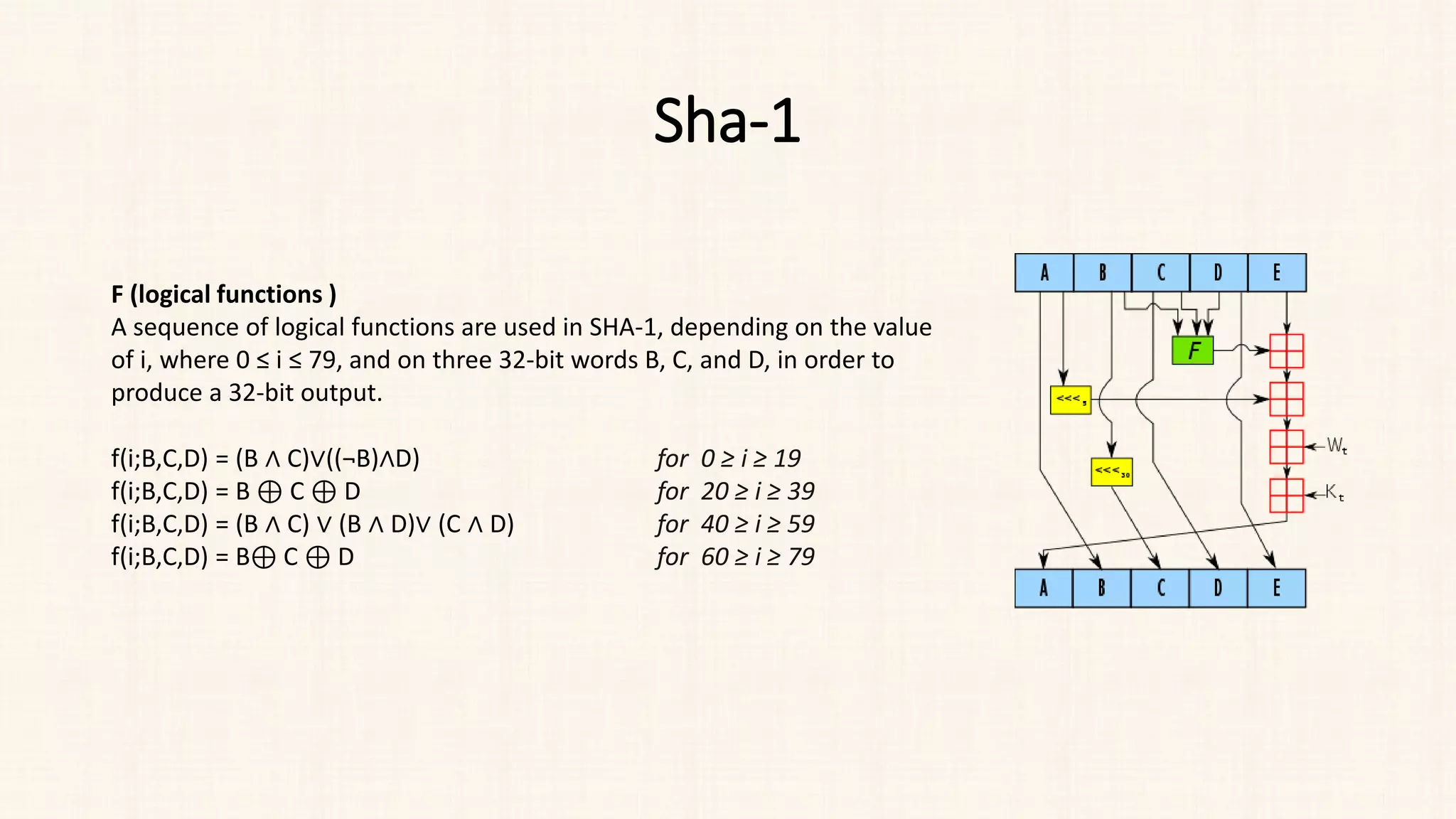
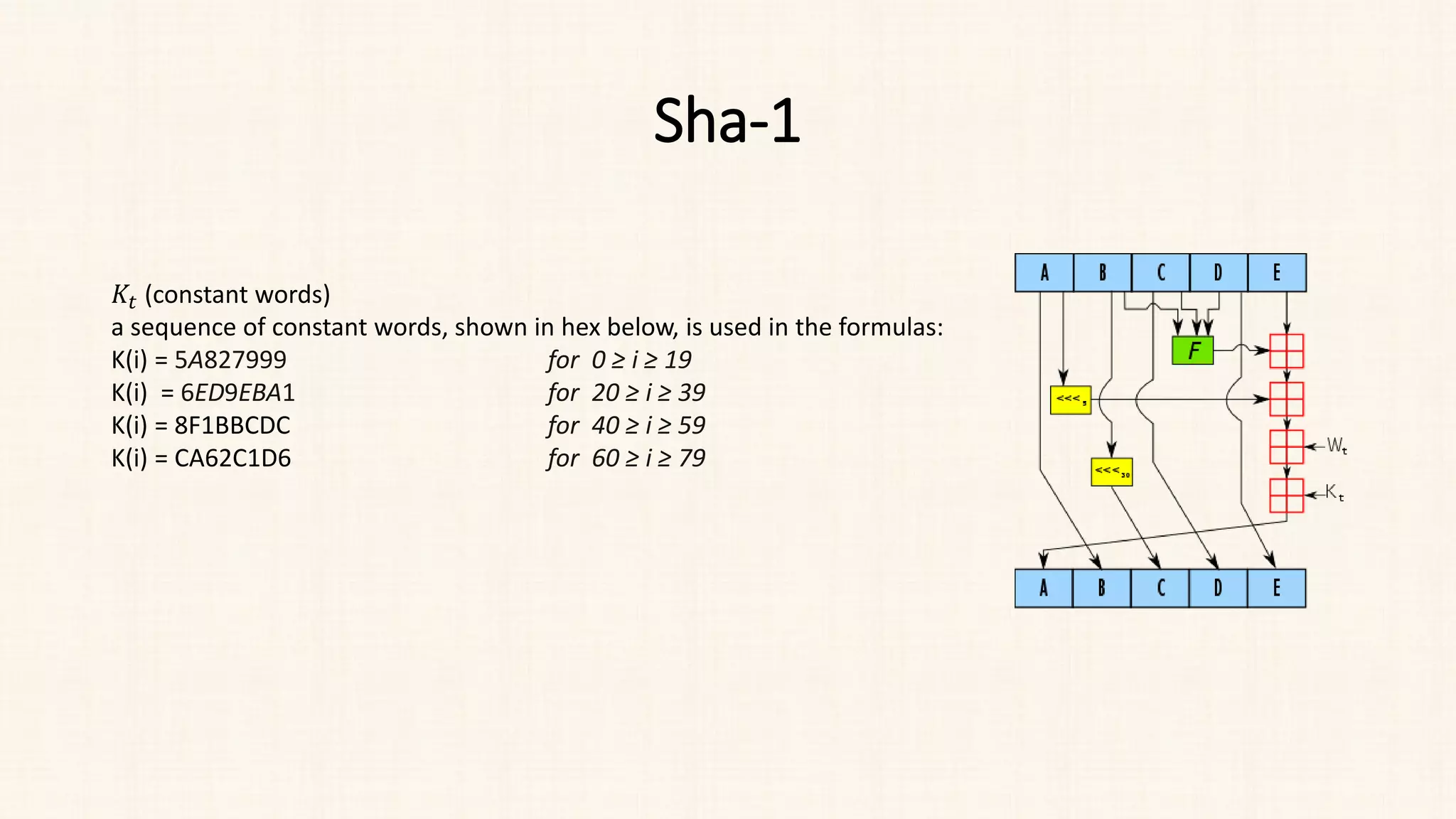
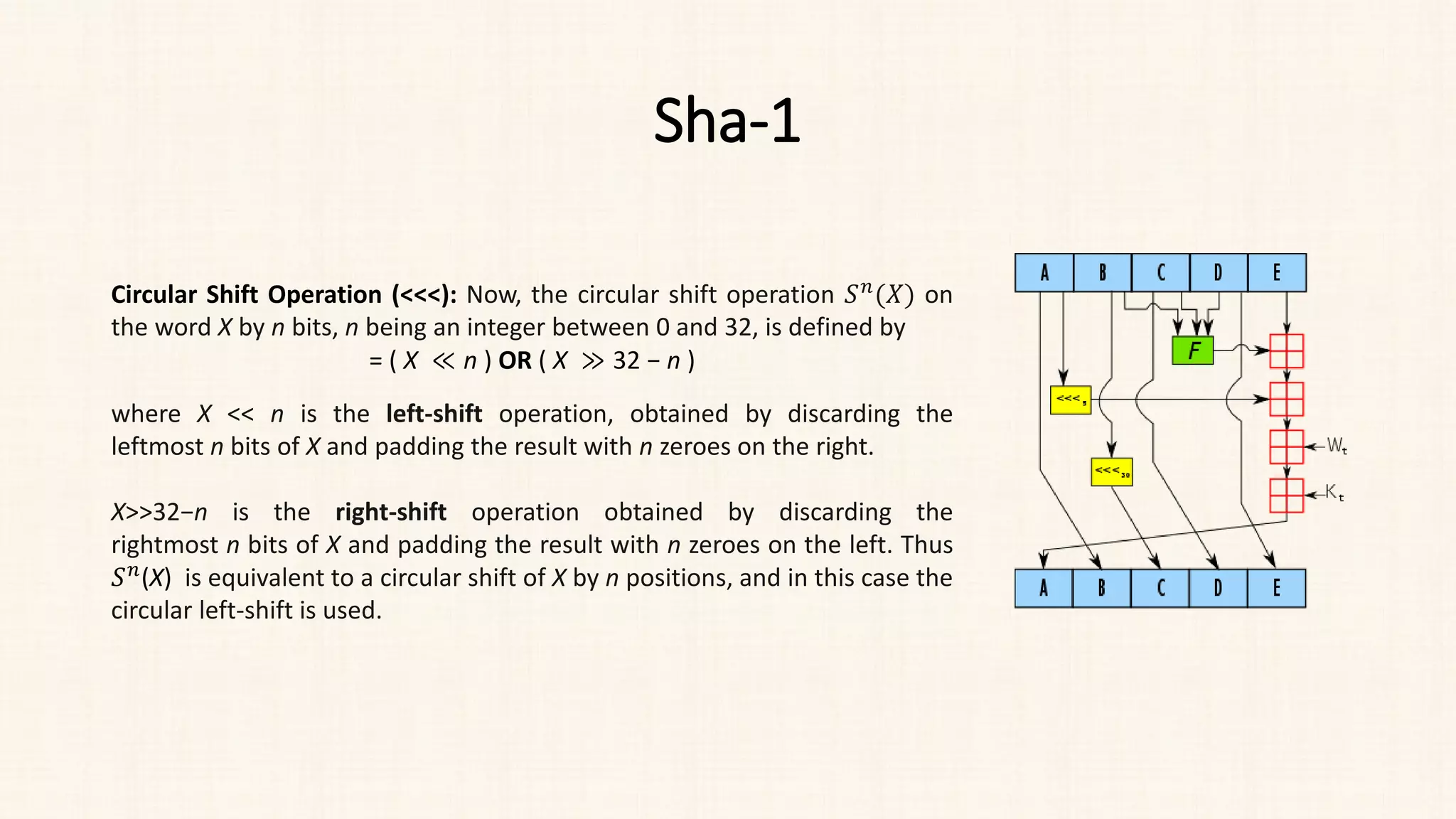
![Sha-1
Output:
• Perform 80 rounds of operations on the words W[0] to W[79].
• In each round, the temporary variables are updated based on a
combination of logical functions (bitwise operations) and bitwise
rotations.
• After 80 rounds, the final values of A, B, C, D, and E represent the
message digest.
• The message digest generated by SHA-1 is a 160-bit (20-byte) hash
value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-3-230810025102-df839292/75/Unit-3-pdf-35-2048.jpg)